Abstract
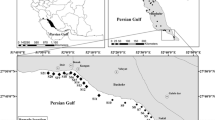
In risk assessment of aquatic sediments, much attention is paid to the difference between acid-volatile sulfide (AVS) and simultaneously extracted metals (SEMs) as indicators of metal availability. Ten representative sampling sites were selected along the estuary of the Guadalete River. Surficial sediments were sampled in winter and summer to better understand SEM and AVS spatial and seasonal distributions and to establish priority risk areas. Total SEM concentration (ΣSEM) ranged from 0.3 to 4.7 μmol g−1. It was not significantly different between seasons, however, it showed a significant difference between sampling stations. AVS concentrations were much more variable, showing significant spatial and temporal variations. The values ranged from 0.8 to 22.4 μmol g−1. The SEM/AVS ratio was found to be <1 at all except one station located near the mouth of the estuary. The results provided information on a potential pollution source near the mouth of the estuary, probably associated with vessel-related activities carried out in a local harbor area located near the station.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen HE, Fu G, Deng B (1993) Analysis of acid volatile sulfide (AVS) and simultaneously extracted metals (SEM) for the estimation of potential toxicity in aquatic sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1441–1453. doi:10.1897/1552-8618(1993)12[1441:AOASAA]2.0.CO;2
Ankley GT, Di Toro DM, Hansen DJ, Berry WJ (1996) Technical basis and proposal for deriving sediment quality criteria for metals. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:2056–2066. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1996)015<2056:TBAPFD>2.3.CO;2
Ankley GT, Thomas NA, DiToro DM, Hansen DJ, Mahony JD (1994) Assessing potential bioavailability of metals in sediments: a proposed approach. EPA/600/J-94/257
Boothman WS, Hansen DJ, Berry WJ, Robson DL, Helmstetter A, Corbin JM, Pratt SD (2001) Biological response to variation of acid-volatile sulfides and metals in field-exposed spiked sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(2):264–272. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<0264:BRTVOA>2.0.CO;2
Boothman WS, Helmstetter A (1992) Vertical and seasonal variability of acid volatile sulfides in marine sediments. Final Research Report. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Narragansett, RI
Burton GA, Nguyen LTH, Janssen C, Baudo R, McWilliam R, Boussuyt B, Beltrami M, Green A (2005) Field validation of sediment zinc toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:541–553. doi:10.1897/04-031R.1
Campbell PGC, Chapman PM, Hale BA (2006) Risk assessment of metals in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 22:102–131
Chapman PM, Cano M, Fritz AT, Gaudet C, Menzie CA, Sprenger M, Stubblefield WA (1997) Contaminated site cleanup decisions. Workgroup summary report on contaminated site cleanup decisions. In: Ingersoll CG, Dillon T, Biddinger GR (eds) Ecological risk assessment of contaminated sediments. SETAC Press, pp 83–114
Day KE, Clements WH, DeWitt T, Landis WG, Landrum P, Morrisey DJ, Reiley M, Rosenberg DM, Suter GW II (1997) Critical issues in ecological relevance: workgroup summary report on critical issues of ecological relevance in sediment risk assessment. In: Ingersoll CG, Dillon T, Biddinger GR (eds) Ecological risk assessment of contaminated sediments. SETAC Press, pp 167–198
Dean WE (1974) Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: comparison with other method. J Sed Res 44:242–248
Di Toro DM, Mahony JD, Hansen DJ, Scott KJ, Hicks MB, Mayr SM, Redmond MS (1990) Toxicity of cadmium in sediments: the role of acid volatile sulfide. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1487–1502. doi:10.1897/1552-8618(1990)9[1487:TOCIST]2.0.CO;2
Di Toro DM, Mahony JD, Hansen DJ, Berry WJ (1996) A model of the oxidation of iron and cadmium sulfide in sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:2168–2186. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1996)015<2168:AMOTOO>2.3.CO;2
Gonzalez AM (1996) A laboratory-formulated sediment incorporating synthetic acid-volatile sulfide. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:2209–2220. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1996)015<2209:ALFSIS>2.3.CO;2
Grabowski LA, Houpis JLJ, Woods WI, Johnson KA (2001) Seasonal bioavailability of sediment-associated heavy metals along the Mississippi river floodplain. Chemosphere 45:643–651. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00037-6
Howard DE, Evans RD (1993) Acid-volatile sulfide (AVS) in a seasonally anoxic mesotrophic lake: seasonal and spatial changes in sediment AVS. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1051–1057. doi:10.1897/1552-8618(1993)12[1051:ASAIAS]2.0.CO;2
Langston WJ, Spence SK (1994) Metal analysis. In: Calow P (ed) Handbook of ecotoxicology, 2nd edn. Blackwell Scientific, Cambridge, pp 45–78
Leonard EN, Mattson VR, Benoit DA, Hoke RA, Ankley GT (1993) Seasonal variations of acid-volatile sulfide concentration in sediment cores from three north eastern Minnesota lakes. Hydrobiologia 271:87–95
Leonard EN, Cotter AM, Ankley GT (1996) Modified diffusion method for analysis of acid volatile sulfides and simultaneously extracted metals in freshwater sediment. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1479–1481. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1996)015<1479:MDMFAO>2.3.CO;2
Mackey AP, Mackay S (1996) Spatial distribution of acid-volatile sulfide concentration and metal bioavailability in mangrove sediments from the Brisbane River, Australia. Environ Pollut 93(2):205–209. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(96)00031-0
Morse JW, Rickard D (2004) Chemical dynamics of sedimentary acid volatile sulfide. Environ Sci Technol 38:131A
Morse JW, Millero FJ, Cornwell JC, Rickard D (1987) The chemistry of the hydrogen sulphide and iron sulphide systems in natural waters. Earth Sci Rev 24:1–42. doi:10.1016/0012-8252(87)90046-8
Peterson GS, Ankley GT, Leonard EN (1996) Effect of bioturbation on metal-sulfide oxidation in surficial freshwater sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:2147–2155. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1996)015<2147:EOBOMS>2.3.CO;2
Schiff K, Diehl D, Valkirs A (2004) Copper emission from antifouling paint on recreational vessels. Marine Pollut Bull 48:371–377. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.08.016
Simpson SL (2001) A rapid screening method for acid-volatile sulfide in sediments. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:2657–2661. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<2657:ARSMFA>2.0.CO;2
Solomon KR, Ankley GT, Baudo R, Burton GA, Ingersoll CG, Lick W, Luoma SN, MacDonald DD, Reynoldson TB, Swartz RC, Warren-Hicks WJ (1997) Critical issue in methodological uncertainty: workgroup summary report on methodological uncertainty. In: Ingersoll CG, Dillon T, Biddinger GR (eds) Ecological risk assessment of contaminated sediments. SETAC Press, pp 271–296
Stein A, Staritsky IG (1995) Spatial variability of soil contamination and the consequences for environmental risk assessment. The Netherlands Integrated Soil Research Programme Reports, vol 4, Wageningen, The Netherlands
van den Berg GA, Loch JPG, van der Heijdt LM, Zwolsman JJG (1998) Vertical distribution of acid-volatile sulfide and simultaneously extracted metals in a recent sedimentation area of the river Meuse in the Netherlands. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:758–763. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1998)017<0758:VDOAVS>2.3.CO;2
van den Hoop MAGT, den Hollander HA, Kerdijk HN (1997) Spatial and seasonal variations of acid volatile sulphide (AVS) and simultaneously extracted metals (SEM) in dutch marine and freshwater sediment. Chemosphere 35(10):2307–2316. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00309-3
Van Griethuysen C, Meijboom EW, Koelmans AA (2003) Spatial variation of metals and acid volatile sulfide in floodplain lake sediment. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:457–465. doi:10.1897/1551–5028(2003)022<0457:SVOMAA>2.0.CO;2
USEPA (1994) Briefing report to the EPA Science Board: equilibrium partitioning approach to predicting metal availability in sediments and the derivation of sediment quality criteria for metals. Office of Water and Office of Research and Development. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Zhuang Y, Allen HE, Fu G (1994) Effect of aeration of sediment on cadmium binding. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:717–724. doi:10.1897/1552-8618(1994)13[717:EOAOSO]2.0.CO;2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campana, O., Rodríguez, A. & Blasco, J. Identification of a Potential Toxic Hot Spot Associated with AVS Spatial and Seasonal Variation. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 56, 416–425 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9206-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9206-6