Abstract
Rationale
Previous research indicates a complex link between methamphetamine (METH) and driving performance. Acute dosing with amphetamines has improved driving-related performance in some laboratory studies, while epidemiological studies suggest an association between METH use, impaired driving, and accident culpability.
Methods
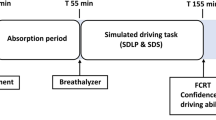
Current METH users were compared to a control group of nonusers on driving simulator performance. Groups were matched for age, gender, and driving experience. Subjects were assessed for current drug use, drug dependence, and drug levels in saliva/blood as well as personality variables, sleepiness, and driving performance.
Results
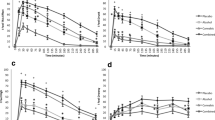
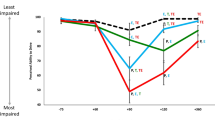
METH users, most of whom met the criteria for METH dependence, were significantly more likely to speed and to weave from side to side when driving. They also left less distance between their vehicle and oncoming vehicles when making a right-hand turn. This risky driving was not associated with current blood levels of METH or its principal metabolite, amphetamine, which varied widely within the METH group. Other drugs were detected (principally low levels of THC or MDMA) in some METH users, but at levels that were unlikely to impair driving performance. There were higher levels of impulsivity and antisocial personality disorder in the METH-using cohort.
Conclusions
These findings confirm indications from epidemiological studies of an association between METH use and impaired driving ability and provide a platform for future research to further explore the factors contributing to increased accident risk in this population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åkerstedt T, Gillberg M (1990) Subjective and objective sleepiness in the Active Individual. Int J Neurosci 52:29–37
Augsburger M, Donze N, Menetrey A, Brossard C, Sporkert F, Giroud C, Mangin P (2005) Concentration of drugs in blood of suspected impaired drivers. Forensic Sci Int 153:11–15
Barkley RA, Murphy KR, O'Connell T, Anderson D, Connor DF (2006) Effects of two doses of alcohol on simulator driving performance in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychology 20(1):77–87
Baskin-Sommers A, Sommers I (2006) The co-occurrence of substance use and high-risk behaviours. J Adolesc Health 38:609–611
Boorman SM, Papafotiou K (2007) The Victorian legislative framework for testing drivers for impairment caused by drugs other than alcohol: an evaluation of the characteristics of drivers tested from 2000 to 2005. Traffic Inj Prev 8:217–223
Cornish JL, Clemens, KJ, Thompson MR, Callaghan PD, Dawson B, McGregor IS (2008) High ambient temperature increases intravenous methamphetamine self-administration on fixed and progressive ratio schedules in rats. J Psychopharmacol (Oxf) 22:100–110
Couper FJ, Logan BK (2004) Drugs and human performance facts sheet. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), US Department of Transportation Report Number: DOT HS 809 725
Cox DJ, Merkel RL, Kovatchev B, Seward R (2000) Effect of stimulant medication on driving performance of young adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: a preliminary double-blind placebo controlled trial. J Nerv Ment Dis 188(4):230–234
Cruikshank CC, Dyer KR (2009) A review of the clinical pharmacology of methamphetamine. Addiction 104:1085–1099
Degenhardt L, Topp L (2003) “Crystal meth” use among polydrug users in Sydney’s dance party subculture: characteristics, use patterns and associated harm. Int J Drug Policy 14:17–24
Degenhardt L, Dillon P, Duff C, Ross J (2006) Driving, drug use behaviour and risk perceptions of nightclub attendees in Victoria, Australia. Int J Drug Policy 17:41–46
Drummer OH, Gerostamoulos J, Batziris H, Chu M, Caplehorn JRM, Robertson MD, Swann P (2003) The incidence of drugs in drivers killed in Australian road traffic crashes. Forensic Sci Int 134:154–162
Emonson DL, Vanderbeek RD (1995) The use of amphetamines in US Air-force tactical operations during desert shield and storm. Aviat Space Environ Med 66:260–263
Fals-Stewart W, O'Farrell TJ, Freitas TT (2000) The timeline followback reports of psychoactive substance use by drug-abusing patients: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol 68:133–144
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of the patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Gorlyn M, Keilp JG, Tryon WW, Mann JJ (2005) Performance test correlates of component factors of impulsiveness. Pers Individ Dif 38:1549–1559
Grotenhermen F, Leson G, Berghaus G, Drummer OH, Krüger HP, Longo M (2007) Developing limits for driving under cannabis. Addiction 102(12):1910–1917
Homer BD, Solomon TM, Moeller RW, Mascia A, DeRaleau L, Halkitis PN (2008) Methamphetamine abuse and impairment in social functioning: a review of the underlying neurophysiological causes and behavioral implications. Psychol Bull 134:565–567
Johnson BA, Ait-Daoud N, Wells LT (2000) Effects of isradipine, a dihydropyridine-class calcium channel antagonist, on d-methamphetamine-induced cognitive and physiological changes in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 22(5):504–512
Jones AW, Holmgren A (2005) Abnormally high concentrations of amphetamine in blood of impaired drivers. J Forensic Sci 50:1–6
Kaye S, Darke S, Duflou J, McKetin R (2008) Methamphetamine-related fatalities in Australia: demographics, circumstances, toxicology and major organ pathology. Addiction 103:1353–1360
Kelly TH, Foltin RW, Fischman MW (1991) The effects of repeated amphetamine exposure on multiple measures of human behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38:417–426
Kloeden CN, McLean AJ, Moore VM, Ponte J (1997) Travelling speed and the risk of crash involvement. Volume 1—findings. CR 172. Federal Office of Road Safety, Canberra
Kolbrich EA, Goodwin RS, Gorelick DA, Hayes RJ, Stein EA, Huestis MA (2008) Plasma pharmacokinetics of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine after controlled oral administration to young adults. Ther Drug Monit 30:320–332
Krasnova IN, Cadet JL, Krasnova IN, Cadet JL (2009) Methamphetamine toxicity and messengers of death. Brain Res Rev 60:379–407
Lapworth K, Dawe S, Davis P, Kavanagh D, Young R, Saunders J (2009) Impulsivity and positive psychotic symptoms influence hostility in methamphetamine users. Addict Behav 34:380–385
Lecrubier Y, Sheehan DV, Weiller E (1997) The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI). A short diagnostic structured interview: reliability and validity according to the CIDI. Eur Psychiatry 12:224–231
Liguori A (2009) Simulator studies of drug induced driving impairment. In: Verster JC, Pandi-Perumal SR, Ramaekers JG, De Gier JJ (eds) Drugs, driving and traffic safety. Birkhauser, Switzerland
Logan BK, Schwilke EW (1996) Drug and alcohol use in fatally injured drivers in Washington State. J Forensic Sci 41(3):505–510
Logan BK, Fligner CL, Haddix T (1998) Cause and manner of death in fatalities involving methamphetamine. J Forensic Sci 43(1):28–34
Louwerens JW, Gloerich ABM, de Vries G, Brookhuis K, O'Hanlon JF (1987) The relationship between driver's blood alcohol concentration (BAC) and actual driving performance during high speed travel. In: Noordzij PC, Roszbach R (eds) Alcohol, drugs and traffic safety: proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Alcohol, Drugs and Traffic Safety. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 183–192
Mancino MJ, Gentry BW, Feldman Z, Mendelson J, Oliveto A (2011) Characterizing methamphetamine withdrawal in recently abstinent methamphetamine users: a pilot field study. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 37:131–136
Mas M, Farre M, de la Torre R, Roset PN, Ortuno J, Segura J, Cami J (1999) Cardiovascular and neuroendocrine effects and pharmacokinetics of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290:136–145
Maxwell JC (2005) Emerging research on methamphetamine. Curr Opin Psychiatr 18:235–242
McGregor C, Srisurapanont M, Jittiwutikarn J, Laobhripatr S, Wongtan T, White JM (2005) The nature, time course and severity of methamphetamine withdrawal. Addiction 100(9):1320–1329
Meredith CW, Jaffe C, Ang-Lee K, Saxon AJ (2005) Implications of chronic methamphetamine use: a literature review. Harv Rev Psychiatry 13(3):141–154
Mitler MM, Hajdukovic R, Erman MK (1993) Treatment of narcolepsy with methamphetamine. Sleep 16(4):306–317
O'Hanlon JF (1984) Driving performance under the influence of drugs: rationale for, and application of a new test. Br J Clin Pharmacol 18:S121–S132
Paaver M, Eensoo D, Pulver A, Harro J (2006) Adaptive and maladaptive impulsivity, platelet monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity and risk-admitting in different types of risky drivers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 186:32–40
Patton JH, Stanford MS, Barratt ES (1995) Factor structure of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale. J Clin Psychol 51:568–774
Pennay AE, Lee NK (2010) Putting the call out for more research: the poor evidence base for treating methamphetamine withdrawal. Drug Alcohol Rev 30:216–222
Ramaekers JG, Kuypers KPC, Samyn N (2006) Stimulant effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) 75 mg and methylphenidate 20 mg on actual driving during intoxication and withdrawal. Addiction 101(11):1614–1621
Ramaekers JG, Berghaus G, van Laar MW, Drummer OH (2009) Dose related risk of motor vehicle crashes after cannabis use: an update. In: Verster JC, Pandi-Perumal SR, Ramaekers JG, de Gier JJ (eds) Drugs, driving and traffic safety. Birkhauser, Switzerland
Rapoport JL, Banina MC (2007) Impact of psychotropic medications on simulated driving—a critical review. CNS Drugs 21:503–519
Richards JB, Sabool KE, de Wit H (1999) Effects of methamphetamine on the adjusting amount procedure, a model of impulsive behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 146:432–439
Ryb GE, Dischinger PC, Kufera JA, Read KM (2006) Risk perception and impulsivity: association with risky behaviors and substance abuse disorders. Accid Anal Prev 38:567–573
Sekine Y, Ouchi Y, Sugihara G, Takei N, Yoshikawa E, Nakamura K, Iwata Y, Tsuchiya KJ, Suda S, Suzuki K, Kawai M, Takebayashi K, Yamamoto S, Matsuzaki H, Ueki T, Mori N, Gold MS, Cadet JL (2008) Methamphetamine causes microglial activation in the brains of human abusers. J Neurosci 28:5756–5761
Shappell SA, Kearns GL, Valentine JL, Neri DF, DeJohn CA (1996) Chronopharmacokinetics and chronopharmacodynamics of dextromethamphetamine in man. J Clin Pharmacol 36:1051–1063
Shearer J, Darke S, Rodgers C, Slade T, van Beek I, Lewis J, Brady D, McKetin R, Mattick RP, Wodak A (2009) A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of modafinil (200 mg/day) for methamphetamine dependence. Addiction 104:224–233
Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Harnett-Sheehan K (1998) The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychol 59(Suppl 20):22–33
Silber BY, Croft RJ, Papafotiou K, Stough CK (2006) The acute effects of d-amphetamine and methamphetamine on attention and psychomotor performance. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 187:154–169
Silber BY, Croft RJ, Downey LA, Camfield DA, Papafotiou K, Swann P, Stough C (2012) The effect of d,l-methamphetamine on simulated driving performance. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 219:1081–1087
Stough C, Downey LA, King R, Papafotiou K, Swann PEO (2012) The acute effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine and methamphetamine on driving: a simulator study. Accid Anal Prev 45:493–497
Suzanne GD, Fatovich DM, McCoubrie DL, Daly FF (2007) Amphetamine-related presentations to an inner-city tertiary emergency department: a prospective evaluation. Med J Aust 186:336–339
Tombaugh TN, McIntyre NJ (1992) The Mini-Mental State Examination: a comprehensive review. J Am Geriatr Soc 40:922–935
Vassallo S, Smart D, Sanson A, Cockfield S, Harris A, McIntyre A, Harrison W (2008) Risky driving among young Australian drivers II: co-occurrence with other problem behaviours. Accid Anal Prev 40:376–386
Vermeeren A, Leufkens T, Verster JC (2009) Effects of anxiolytics on driving. In: Verster JC, Pandi-Perumal SR, Ramaekers JG, de Gier JJ (eds) Drugs, driving and traffic safety. Birkhauser, Switzerland
Verster JC, Roth T (2011) Standard operation procedures for conducting the on-the-road driving test, and measurement of the standard deviation of lateral position (SDLP). Int J Gen Med 4:359–371
Voon V, Pessiglione M, Brezing C, Gallea C, Fernandez HH, Dolan RJ, Hallett M (2010) Mechanisms underlying dopamine-mediated reward bias in compulsive behaviors. Neuron 65:135–142
Walburga M, Laar V, Volkerts ER, Van Paul WAP (1992) Therapeutic effects and effects on actual driving performance of chronically administered buspirone and diazepam in anxious outpatients. J Clin Psychopharmacol 12:86–95
Winek CL, Wahba WW, Winek CL Jr, Balzer TW (2001) Drug and chemical blood-level data 2001. Forensic Sci Int 122(2–3):107–123
Zorick T, Nestor L, Miotto K, Sugar C, Hellemann G, Scanlon G, Rawson R, London ED (2010) Withdrawal symptoms in abstinent methamphetamine-dependent subjects. Addiction 105:1809–1818
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosanquet, D., MacDougall, H.G., Rogers, S.J. et al. Driving on ice: impaired driving skills in current methamphetamine users. Psychopharmacology 225, 161–172 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2805-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2805-y