Abstract
Rationale
Salvinorin A is the active component of the hallucinogenic plant Salvia divinorum. The potential mode of action of this hallucinogen was unknown until recently. A recent in vitro study detected high affinity and efficacy of salvinorin A at κ-opioid receptors. It was postulated that salvinorin A would produce discriminative stimulus effects similar to those of a high efficacy κ-agonist (U69,593) in rhesus monkeys.
Methods
Monkeys were previously trained to discriminate U69,593 (0.0056 or 0.013 mg/kg; SC) from vehicle in a food-reinforced FR20 (fixed ratio 20) operant conditioning procedure (n=3). The ability of salvinorin A to cause generalization (≥90% U69,593-appropriate responding) was examined in time course and cumulative dose-effect curve studies.
Results
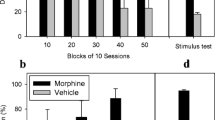
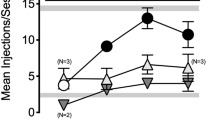
All subjects dose-dependently emitted full U69,593-appropriate responding after salvinorin A (0.001–0.032 mg/kg, SC). Salvinorin A-induced generalization started 5–15 min after injection, and dissipated by 120 min. The opioid antagonist quadazocine (0.32 mg/kg) fully blocked the effects of salvinorin A. The κ-selective antagonist GNTI (1 mg/kg; 24 h pretreatment) did not cause significant antagonism of the effects of salvinorin A (GNTI, under these conditions, was only effective as an antagonist in two of three monkeys). The NMDA antagonist ketamine (0.1–3.2 mg/kg) was not generalized by any subject, indicating that not all compounds that produce hallucinogenic or psychotomimetic effects in humans are generalized by subjects trained to discriminate U69,593.
Conclusions
The naturally occurring hallucinogen salvinorin A produces discriminative stimulus effects similar to those of a high efficacy κ-agonist in non-human primates.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowdle TA, Radant AD, Cowley DS, Kharasch ED, Strassman RJ, Roy-Byrne PP (1998) Psychedelic effects of ketamine in healthy volunteers: relationship to steady-state plasma levels. Anesthesiology 88:82–88
Butelman ER, Kreek MJ (2001) Kappa-opioid receptor agonist-induced prolactin release in primates is blocked by dopamine D(2)-like receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 423:243–249
Butelman ER, Harris TJ, Perez A, Kreek MJ (1999) Effects of systemically administered dynorphin A(1–17) in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290:678–686
Butelman ER, Ball JW, Kreek MJ (2002) Comparison of the discriminative and neuroendocrine effects of centrally-penetrating kappa-opioid agonists in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 164:115–120
Butelman ER, Ball JW, Kreek MJ (2003) Peripheral selectivity and apparent efficacy of dynorphins: comparison to non-peptidic kappa-opioid agonists in rhesus monkeys. Psychoneuroendocrinology (in press)
Drug Enforcement Administration (2002) List of drugs and chemicals of concern. Internet website: www deadiversion usdoj gov/drugs_concern/salvia_d/summary.htm
France CP, Snyder AM, Woods JH (1989) Analgesic effects of phencyclidine-like drugs in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 250:197–201
Giroud C, Felber F, Augsburger M, Horisberger B, Rivier L, Mangin P (2000) Salvia divinorum: an hallucinogenic mint which might become a new recreational drug in Switzerland. Forens Sci Int 112:143–150
Krystal JH, Karper LP, Seibyl JP, Freeman GK, Delaney R, Bremner JD, Heninger GR, Bowers MB Jr, Charney DS (1994) Subanesthetic effects of the noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, ketamine, in humans. Psychotomimetic, perceptual, cognitive, and neuroendocrine responses. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:199–214
Negus SS, Mello NK, Linsenmayer DC, Jones RC, Portoghese (2002) Kappa antagonist effects of the novel kappa antagonist 5’-guanidinonaltrindole (GNTI) in an assay of schedule controlled behavior. Psychopharmacology 163:412–419
Observateur francais des drogues et des toxicomanies (2002) Premier identification du principle actif de la salvia divinorum dans SINTES. Internet website: www.drogues.gouv fr/fr/professionels/info_rapides_trend/info19_07_2002.html
Ortega A, Blount JF, Marchand P (1982) Salvinorin, a new trans-neoclerodane diterpene from Salvia divinorum (Labiatae). J Chem Soc Perkins Transact 1:2505–2508
Pfeiffer A, Brantl V, Herz A, Emrich HM (1986) Psychotomimesis mediated by kappa opiate receptors. Science 233:774–776
Remmers AE, Clark MJ, Mansour A, Akil H, Woods JH, Medzihradsky F (1999) Opioid efficacy in a C6 glioma cell line stably expressing the human kappa opioid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:827–833
Roth BL, Baner K, Westkaemper R, Siebert D, Rice KC, Steinberg S, Ernsberger P, Rothman RB (2002) Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist . Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11934–11939
Sheffler DJ, Roth BL (2003) Salvinorin A: the “magic mint” hallucinogen finds a molecular target in the kappa opioid receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:107–109
Siebert DJ (1994) Salvia divinorum and salvinorin A: new pharmacologic findings. J Ethnopharmacol 43:53–56
Ur E, Wright DM, Bouloux PM, Grossman A (1997) The effects of spiradoline (U-62066E), a kappa-opioid receptor agonist, on neuroendocrine function in man. Br J Pharmacol 120:781–784
Valdes LJ (1994) Salvia divinorum and the unique diterpene hallucinogen, salvinorin (divinorin) A. J Psychoact Drugs 26:277–283
Valdes LJ, Diaz JL, Paul AG (1993) Ethnopharmacology of ska Maria Pastora (Salvia divinorum, Epling and Jativa-M.). J Ethnopharmacol 7:287–312
Walsh SL, Strain EC, Abreu ME, Bigelow GE (2001) Enadoline, a selective kappa opioid agonist: comparison with butorphanol and hydromorphone in humans. Psychopharmacology 157:151–162
Acknowledgement
The present studies were supported by National Institutes of Health/NIDA grants DA11113 (E.R.B.), DA05130 and DA00049 (M.J.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butelman, E.R., Harris, T.J. & Kreek, M.J. The plant-derived hallucinogen, salvinorin A, produces κ-opioid agonist-like discriminative effects in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 172, 220–224 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1638-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1638-0