Abstract
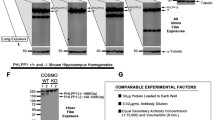
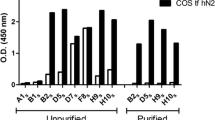
Phosducin-like protein is a protein with widespread expression that has been shown to be capable of inhibiting G-protein function in vitro. However, it is not clear whether it is expressed in sufficient amounts to actually exert such functions in vivo. Here we quantify the expression of the short and the long splice variants of phosducin-like protein, PhlPs and PhlPl. Western blots of various rat tissues showed that PhlPl was by far the dominant splice variant; its levels were 1.5–2 pmol/mg cytosolic protein in brain, liver and kidney, and about 0.5 pmol/mg cytosolic protein in lung, heart and skeletal muscle. These values correspond to concentrations of 150–200 nM and 50 nM, respectively. The levels of PhlPs were about 20-fold lower. Recombinant phosducin, PhlPl and PhlPs inhibited the interaction between G-protein α- und βγ-subunits with IC50-values of 6 nM, 6 nM and 90 nM, respectively, as determined by Gβγ-dependent ADP-ribosylation of Gαi1 by pertussis-toxin. Thus, tissue concentrations of PhlPl are clearly sufficient to affect G-protein function in vivo, while the expression levels and the Gβγ-affinity of PhlPs are most likely too low to have significant inhibitory effects on Gβγ (G-protein βγ-subunits).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schröder, S., Lohse, M. Quantification of the tissue levels and function of the G-protein regulator phosducin-like protein (PhlP). Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 362, 435–439 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100000298
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002100000298