Abstract
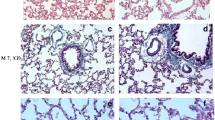
Despite extensive studies, there is no effective treatment currently available other than pirfenidone for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. A protective effect of pantothenic acid and its derivatives on cell damage produced by oxygen radicals has been reported, but it has not been tested in bleomycin (BLM)--induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the preventive effect of dexpanthenol (Dxp) on pulmonary fibrosis. Thirty-two rats were assigned to four groups as follows: (1) control group, (2) dexpanthenol (Dxp) group; 500 mg/kg Dxp continued intraperitoneally for 14 days, (3) bleomycin (BLM) group; a single intratracheal injection of BLM (2.5 mg/kg body weight in 0.25-ml phosphate buffered saline), and (4) BLM + Dxp-treated group; 500 mg/kg Dxp was administered 1 h before the intratracheal BLM injection and continued for 14 days i.p. The histopathological grades of lung inflammation and collagen deposition, tissue levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and myeloperoxidase (MPO) were measured. BLM provoked inflammation and collagen deposition (p < 0.0001), with a marked increase in myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity resembling increased inflammatory activity (p < 0.0001), which was prevented by Dxp (p < 0.0001, p = 0.02). BLM reduced tissue activities of SOD, GPx, and CAT compared to controls (p = 0.01, 0.03, 0.009). MDA was increased with BLM (p = 0.003). SOD (p = 0.001) and MDA (p = 0.016) levels were improved in group 4. The CAT levels in the BLM + Dxp group were close to those in the control group (p > 0.05). We showed that Dxp significantly prevents BLM-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Further studies are required to evaluate the role of Dxp in the treatment of lung fibrosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic, New York, pp 673–677
Akgedik R, Akgedik S, Karamanli H, Uysal S, Bozkurt B, Ozol D, Armutcu F, Yildirim Z (2012) Effect of resveratrol on treatment of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Inflammation 35(5):1732–1741
Altintas R, Parlakpinar H, Beytur A, Vardi N, Polat A, Sagir M, Odabas GP (2012) Protective effect of dexpanthenol on ischemia-reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats. Kidney Blood Press Res 36:220–230
Aytemur ZA, Hacievliyagil SS, Iraz M, Samdanci E, Ozerol E, Kuku I, Nurkabulov Z, Yildiz K (2012) Effects of iloprost on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats compared with methyl-prednisolone. Rev Port Pneumol 18(6):272–277
Caspary WJ, Lanzo DA, Niziak C (1982) Effect of deoxyribonucleic acid on the production of reduced oxygen by bleomycin and iron. Biochemistry 21:334–338
Ceylan H, Yapici S, Tutar E, Ceylan NO, Tarakcioglu M, Demiryurek AT (2011) Protective effects of dexpanthenol and y-27632 on stricture formation in a rat model of caustic esophageal injury. J Surg Res 171:517–523
Chaudhary NI, Schnapp A, Park JE (2006) Pharmacologic differentiation of inflammation and fibrosis in the rat bleomycin model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173:769–776
Colak C, Parlakpinar H (2012) Hayvan Deneyleri: In Vivo Denemelerin Bildirimi: ARRIVE Kılavuzu-Derleme. J Turgut Ozal Med Cent 19:128–131
Cottin V (2013) The role of pirfenidone in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res 14(1):5. doi:10.1186/1465-9921-14-S1-S5
Coward WR, Saini G, Jenkins G (2010) The pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ther Adv Respir Dis 4:367–388
Demerdash EE (2011) Anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects of methyl palmitate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 254:238–244
Ebner F, Heller A, Rippke F, Tausch I (2002) Topical use of dexpanthenol in skin disorders. Am J Clin Dermatol 3:427–433
El-Khouly D, El-Bakly W, Awad AS, El-Mesallamy HO, El-Demerdash E (2012) Thymoquinone blocks lung injury and fibrosis by attenuating bleomycin-induced oxidative stress and activation of nuclear factor Kappa-B in rats. Toxicology 302:106–113
Etensel B, Ozkisacik S, Ozkara E, Karul A, Oztan O, Yazici M, Gursoy H (2007) Dexpanthenol attenuates lipid peroxidation and testicular damage at experimental ischemia and reperfusion injury. Pediatr Surg Int 23:177–181
Fukumoto J, Harada C, Kawaguchi T, Suetsugu S et al (2010) Amphiregulin attenuates bleomycin-induced pneumopathy in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 298(2):L131–L138
Gross TJ, Hunninghake GW (2001) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 345:517–525
Harari S, Caminati A (2010) IPF: new insight on pathogenesis and treatment. Allergy 65:537–553
Inghilleri S, Morbini P, Oggionni T, Barni S, Fenoglio C (2006) In situ assessment of oxidant and nitrogenic stress in bleomycin pulmonary fibrosis. Histochem Cell Biol 125:661–669
Iraz M, Erdogan H, Kotuk M, Yagmurca M, Kilic T, Ermis H, Fadillioglu E, Yildirim Z (2006) Ginkgo biloba inhibits bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Pharmacol Res 53:310–316
Mata M, Ruíz A, Cerdá M, Martinez-Losa M, Cortijo J, Santangelo F, Serrano-Mollar A, Llombart-Bosch A, Morcillo EJ (2003) Oral N-acetylcysteine reduces bleomycin-induced lung damage and mucin Muc5ac expression in rats. Eur Respir J 22(6):900–905
Mengli C, Cheung FWK, Ming Hung C, Pak Kwan H, Siu-Po I, Yick Hin L, Chun-Tao C, Wing Keung L (2012) Protective roles of Cordyceps on lung fibrosis in cellular and rat models. J ethnopharmacol 143(2):448–54
Mouratis MA, Aidinis V (2011) Modeling pulmonary fibrosis with bleomycin. Curr Opin Pulm Med 17:355–361
Mungunsukh O, Griffin AJ, Lee YH, Day RM (2010) Bleomycin induces the extrinsic apoptotic pathway in pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 298:696–703
Ozyurt H, Sogut S, Yildirim Z et al (2004) Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (cape) on bleomycine-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Clin Chim Acta 339:65–75
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–170
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA et al (2011) An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183:788–824
Slyshenkov VS, Rakowska M, Moiseenok AG, Wojtczak L (1995) Pantothenic acid and its derivatives protect Ehrlich ascites tumor cells against lipid peroxidation. Free Radic Biol Med 19:767–772
Slyshenkov VS, Rakowska M, Wojtczak L (1996) Protective effect of pantothenic acid and related compounds against permeabilization of Ehrlich ascites tumour cells by digitonin. Acta Biochim Pol 43:407–410
Slyshenkov VS, Omelyanchik SN, Moiseenok AG, Trebukhina RV, Wojtczak L (1998) Pantothenol protects rats against some deleterious effects of gamma radiation. Free Radic Biol Med 24(6):894–899
Slyshenkov VS, Omelyanchik SN, Moiseenok AG, Petushok NE, Wojtczak L (1999) Protection by pantothenol and beta-carotene against liver damage produced by low-dose gamma radiation. Acta Biochim Pol 46:239–248
Slyshenkov VS, Piwocka K, Sikora E, Wojtczak L (2001) Pantothenic acid protects jurkat cells against ultraviolet light-induced apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 30:1303–1310
Slyshenkov VS, Dymkowska D, Wojtczak L (2004) Pantothenic acid and pantothenol increase biosynthesis of glutathione by boosting cell energetics. FEBS Lett 569:169–172
Sogut S, Ozyurt H, Armutcu F et al (2004) Erdosteine prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 494:213–220
Sun Y, Oberley L, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by tiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 34:271–278
Wei H, Frenkel K (1993) Relationship of oxidative events and DNA oxidation in Sencar mice to in vivo promoting activity of phorbol ester-type tumor promoters. Carcinogenesis 14:1195–1201
Wojtczak L, Slyshenkov VS (2003) Protection by pantothenic acid againts apoptosis and cell damage by oxygen free radicals-the role of glutathion. Biofactors 17:61–73
Yildirim Z, Turkoz Y, Kotuk M et al (2004) Effects of aminoguanidine and antioxidant erdosteine on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Nitric Oxide 11:156–165
Yildirim Z, Kotuk M, Erdogan H, Iraz M, Yagmurca M, Kuku I, Fadillioglu E (2006) Preventive effect of melatonin on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats. J Pineal Res 40:27–33
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare. This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ermis, H., Parlakpinar, H., Gulbas, G. et al. Protective effect of dexpanthenol on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 386, 1103–1110 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0908-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0908-6