Abstract.
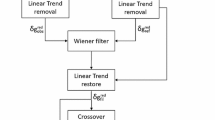
Recent advances in the performance of scalar airborne gravimetry, routinely yielding gravity data with an accuracy as high as 1 mGal with a minimum spatial resolution (full wavelength) of 10 km, allow for the use of airborne gravity in precise geoid computations. Theoretical issues related to geoid determination from discrete samples of band-limited airborne gravity and practical geoid computations based on high-frequency synthetic data and actual observations are discussed. The mathematical model for geoid determination from band-limited airborne gravity which is introduced is based on Helmert's reduction of gravity/co-geoid and the application of the discretized integral formula developed specifically for airborne gravity data. Computational formulae are derived for the following specifications of airborne gravity data: almost-white observation noise, a band-limited frequency content of processed observations, and a smooth regular surface on which gravity observations are collected.
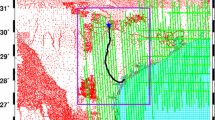
Two major applications of airborne gravity data for geoid determination are discussed. Airborne gravimetry can be used over areas with a sparse or no ground gravity coverage to provide the medium- to high-frequency components of the Earth's gravity field. These data can be used in combination with global gravity models for the computation of the gravimetric geoid. Airborne gravimetry can also be used to fill in gaps in existing ground gravity coverage (mainly in inaccessible areas). Both approaches are tested with actual airborne data observed using an inertially referenced airborne gravimeter at the Alexandria test range near Ottawa, Canada. Observed airborne gravity disturbances, combined with either ground or global gravity data, are used for the determination of the gravimetric geoid in the two applications outlined above. The combined solutions are compared to the latest official Canadian gravimetric geoid and to available GPS/levelling data in the area. Numerical results show that airborne data can be used for geoid determination with centimetre-level accuracy (medium- and high-frequency information) over areas with negligible topographical effects on gravity and the geoid.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 August 2001 / Accepted: 12 April 2002
Correspondence to: P. Novák Research Institute of Geodesy, Topography and Cartography, Zdiby 98, 250 66 Czech Republic Tel: +420 323 649 235, Fax: +420 323 649 236 e-mail: pnovak@pecny.asu.cas.cz
Acknowledgements. Financial support for this research through the Canadian GEOIDE Network of Centres of Excellence within the project `Airborne Gravity for Exploration and Mapping', and to Prof. B. Heck by the German Research Foundation (DFG), is gratefully acknowledged. The authors wish to thank Mr. Marc Véronneau of Natural Resources Canada for providing all the necessary ground gravity and elevation data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Novák, P., Kern, M., Schwarz, KP. et al. On geoid determination from airborne gravity. Journal of Geodesy 76, 510–522 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-002-0284-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-002-0284-3