Abstract
Human potassium channels are widely inhibited by peptide toxins from venomous animals. However, no human endogenous peptide inhibitor has been discovered so far. In this study, we demonstrate for the first time using electrophysiological techniques, that endogenous human β–defensin 2 (hBD2) is able to selectively and dose-dependently inhibit the human voltage-gated Kv1.3 channel at picomolar peptide concentration. The co-immunoprecipitation assays further supported the selective binding of hBD2 to Kv1.3 channel. Using mutagenesis experiments, we found that the outer pore domain of Kv1.3 channel was the binding site of hBD2, which is similar to the interacting site of Kv1.3 channel recognized by animal toxin inhibitors. The hBD2 was able to suppress IL-2 production through inhibition of Kv1.3 channel currents in human Jurkat cells, which was further confirmed by the lack of hBD2 activity on IL-2 production after Kv1.3 knockdown in these cells. More interestingly, hBD2 was also found to efficiently inhibit Kv1.3 channel currents and suppress IL-2 production in both human primary CD3+ T cells and peripheral mononuclear cells from either healthy donors or psoriasis patients. Our findings not only evidenced hBD2 as the first characterized endogenous peptide inhibitor of human potassium channels, but also paved a promising avenue to investigate newly discovered function of hBD2 as Kv1.3 channel inhibitor in the immune system and other fields.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashcroft FM (2006) From molecule to malady. Nature 440(7083):440–447
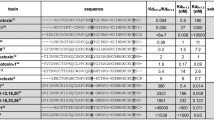
Mouhat S, Andreotti N, Jouirou B, Sabatier JM (2008) Animal toxins acting on voltage-gated potassium channels. Curr Pharm Des 14(24):2503–2518
Ohno-Shosaku T, Kim I, Sawada S, Yamamoto C (1996) Presence of the voltage-gated potassium channels sensitive to charybdotoxin in inhibitory presynaptic terminals of cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett 207(3):195–198
Han S, Yi H, Yin SJ, Chen ZY, Liu H, Cao ZJ, Wu YL, Li WX (2008) Structural basis of a potent peptide inhibitor designed for Kv1.3 channel, a therapeutic target of autoimmune disease. J Biol Chem 283(27):19058–19065
Mouhat S, Teodorescu G, Homerick D, Visan V, Wulff H, Wu Y, Grissmer S, Darbon H, De Waard M, Sabatier JM (2006) Pharmacological profiling of Orthochirus scrobiculosus toxin 1 analogs with a trimmed N-terminal domain. Mol Pharmacol 69(1):354–362
Lanigan MD, Pennington MW, Lefievre Y, Rauer H, Norton RS (2001) Designed peptide analogues of the potassium channel blocker ShK toxin. Biochemistry 40(51):15528–15537
Chen ZY, Hu YT, Yang WS, He YW, Feng J, Wang B, Zhao RM, Ding JP, Cao ZJ, Li WX, Wu YL (2012) Hg1, novel peptide inhibitor specific for Kv1.3 channels from first scorpion Kunitz-type potassium channel toxin family. J Biol Chem 287(17):13813–13821
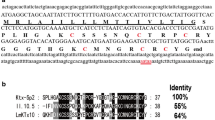
Pazgier M, Hoover DM, Yang D, Lu W, Lubkowski J (2006) Human beta-defensins. Cell Mol Life Sci 63(11):1294–1313
Yang D, Chertov O, Bykovskaia SN, Chen Q, Buffo MJ, Shogan J, Anderson M, Schroder JM, Wang JM, Howard OM, Oppenheim JJ (1999) Beta-defensins: linking innate and adaptive immunity through dendritic and T cell CCR6. Science 286(5439):525–528
Yount NY, Kupferwasser D, Spisni A, Dutz SM, Ramjan ZH, Sharma S, Waring AJ, Yeaman MR (2009) Selective reciprocity in antimicrobial activity versus cytotoxicity of hBD-2 and crotamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(35):14972–14977
Liu R, Zhang Z, Liu H, Hou P, Lang J, Wang S, Yan H, Li P, Huang Z, Wu H, Rong M, Huang J, Wang H, Lv L, Qiu M, Ding J, Lai R (2013) Human beta-defensin 2 is a novel opener of Ca2+-activated potassium channels and induces vasodilation and hypotension in monkeys. Hypertension 62(2):415–425
Mouhat S, Jouirou B, Mosbah A, De Waard M, Sabatier JM (2004) Diversity of folds in animal toxins acting on ion channels. Biochem J 378(Pt 3):717–726
Banerjee A, Lee A, Campbell E, Mackinnon R (2013) Structure of a pore-blocking toxin in complex with a eukaryotic voltage-dependent K+ channel. Elife 2:e00594
Rauer H, Pennington M, Cahalan M, Chandy KG (1999) Structural conservation of the pores of calcium-activated and voltage-gated potassium channels determined by a sea anemone toxin. J Biol Chem 274(31):21885–21892
Lee HC, Wang JM, Swartz KJ (2003) Interaction between extracellular Hanatoxin and the resting conformation of the voltage-sensor paddle in Kv channels. Neuron 40(3):527–536
Swartz KJ, MacKinnon R (1997) Mapping the receptor site for hanatoxin, a gating modifier of voltage-dependent K+ channels. Neuron 18(4):675–682
Kanda N, Kamata M, Tada Y, Ishikawa T, Sato S, Watanabe S (2011) Human beta-defensin 2 enhances IFN-gamma and IL-10 production and suppresses IL-17 production in T cells. J Leukoc Biol 89(6):935–944
Jansen PA, Rodijk-Olthuis D, Hollox EJ, Kamsteeg M, Tjabringa GS, de Jongh GJ, van Vlijmen-Willems IM, Bergboer JG, van Rossum MM, de Jong EM, den Heijer M, Evers AW, Bergers M, Armour JA, Zeeuwen PL, Schalkwijk J (2009) Beta-defensin 2 protein is a serum biomarker for disease activity in psoriasis and reaches biologically relevant concentrations in lesional skin. PLoS One 4(3):e4725
Beeton C, Wulff H, Standifer NE, Azam P, Mullen KM, Pennington MW, Kolski-Andreaco A, Wei E, Grino A, Counts, Wang PH, LeeHealey CJ, SA B, Sankaranarayanan A, Homerick D, Roeck WW, Tehranzadeh J, Stanhope KL, Zimin P, Havel PJ, Griffey S, Knaus HG, Nepom GT, Gutman GA, Calabresi PA, Chandy KG (2006) Kv1.3 channels are a therapeutic target for T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(46):17414–17419
Hu L, Pennington M, Jiang Q, Whartenby KA, Calabresi PA (2007) Characterization of the functional properties of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 in human CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol 179(7):4563–4570
Takacs Z, Toups M, Kollewe A, Johnson E, Cuello LG, Driessens G, Biancalana M, Koide A, Ponte CG, Perozo E, Gajewski TF, Suarez-Kurtz G, Koide S, Goldstein SA (2009) A designer ligand specific for Kv1.3 channels from a scorpion neurotoxin-based library. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(52):22211–22216
Cahalan MD, Chandy KG, DeCoursey TE, Gupta S (1985) A voltage-gated potassium channel in human T lymphocytes. J Physiol 358:197–237
Partiseti M, Choquet D, Diu A, Korn H (1992) Differential regulation of voltage- and calcium-activated potassium channels in human B lymphocytes. J Immunol 148(11):3361–3368
Zsiros E, Kis-Toth K, Hajdu P, Gaspar R, Bielanska J, Felipe A, Rajnavolgyi E, Panyi G (2009) Developmental switch of the expression of ion channels in human dendritic cells. J Immunol 183(7):4483–4492
Cheong A, Li J, Sukumar P, Kumar B, Zeng F, Riches K, Munsch C, Wood IC, Porter KE, Beech DJ (2011) Potent suppression of vascular smooth muscle cell migration and human neointimal hyperplasia by Kv1.3 channel blockers. Cardiovasc Res 89(2):282–289
McCloskey C, Jones S, Amisten S, Snowden RT, Kaczmarek LK, Erlinge D, Goodall AH, Forsythe ID, Mahaut-Smith MP (2010) Kv1.3 is the exclusive voltage-gated K+ channel of platelets and megakaryocytes: roles in membrane potential, Ca2+ signalling and platelet count. J Physiol 588(Pt 9):1399–1406
Yin SJ, Jiang L, Yi H, Han S, Yang DW, Liu ML, Liu H, Cao ZJ, Wu YL, Li WX (2008) Different residues in channel turret determining the selectivity of ADWX-1 inhibitor peptide between Kv1.1 and Kv1.3 channels. J Proteome Res 7(11):4890–4897
Chen ZY, Zeng DY, Hu YT, He YW, Pan N, Ding JP, Cao ZJ, Liu ML, Li WX, Yi H, Jiang L, Wu YL (2012) Structural and functional diversity of acidic scorpion potassium channel toxins. PLoS One 7(4):e35154
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2010CB529800), the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (Nos. 31170789 and 31200557), and Wuhan City Science and Technology Foundation of China (No. 2013070204020046).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Weishan Yang and Jing Feng are contributed equally to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Feng, J., Xiang, F. et al. Endogenous animal toxin-like human β-defensin 2 inhibits own K+ channels through interaction with channel extracellular pore region. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 845–853 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1715-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1715-z