Abstract.
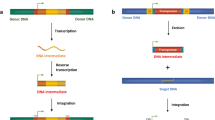
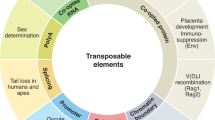
Transposable elements (TEs) are commonly viewed as molecular parasites producing mainly neutral or deleterious effects in host genomes through their ability to move. However, during the past two decades, major interest has been focusing on the positive contribution of these elements in the evolution of gene regulation and in the creation of diverse structural host genes. Indeed, DNA transposons carry an attractive and elaborate enzymatic machinery as well as DNA components that have been co-opted in several cases by the host genome via an evolutionary process referred to as molecular domestication. A large number of transposon-derived genes known to date have been recruited by the host to function as transcriptional regulators; however, the biological role of the majority of them remains undetermined. Our knowledge on the structure, distribution, evolution and mechanism of transposons will continue to provide important contributions to our understanding of host genome functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 2 July 2008; received after revision 1 October 2008; accepted 14 October 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinzelle, L., Izsvák, Z. & Ivics, Z. Molecular domestication of transposable elements: From detrimental parasites to useful host genes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 1073–1093 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-8376-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-8376-3