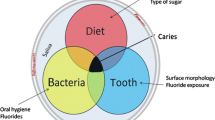
Abstract
Aim: To provide a review of the existing literature on early childhood caries (ECC) with particular reference on the nomenclature, case definition, epidemiology, aetiology and risk assessment. Methods: An electronic search was used to identify and critically review papers that have been published and are pertinent to the above issues, and then evaluate and compile the reported evidence. Results: The term ECC has been adopted to more accurately describe dental caries that affects primary dentitions, replacing previously used terminology that associated the disease with the nursing habit. Suggested ECC case definition uses caries patterns as defining criteria, however, further refinement to include different clinical expressions of a varying severity is necessary. Significant percentages of preschool child populations are affected by ECC today, with the disease concentrating disproportionately in deprived families. Early colonization by mutans streptococci (MS) is associated with increased ECC development, with bacteria being transmitted in both vertically and horizontally. Dietary factors related to sugar consumption predispose to early MS colonization and establishment and increase the risk for ECC development, being part of the causal chain. Inappropriate bottle and breast-feeding behaviours also increase the risk, without showing a direct causal relationship. High risk children belong to ethnic minority groups and to low income families with poor parental behaviours and attitudes. Conclusions: Further high-quality studies are needed to explore the role bacteria other than MS may play in caries initiation and progression, elucidate the interaction of the saliva immune defense system with a potentially defective tooth, and investigate the effect distant behavioural factors have on the causal chain that leads to ECC development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AAPD: Policy on breast — feeding. Ped Dent 2003; 25:111.
Al Ghanim NA, Adenubi JO, Wyne AA, Klein NB. Caries prediction model in preschool children in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Int J Ped Dent 1998;8:115–122.
Al Malik MI, Holt RD, Bedi. Prevalence and patterns of caries, rampant caries and oral health in two-to five-year-old children in Saudi Arabia. J Dent Child 2003;70:235–242.
Alaluusua S, Malmivirta R. Early plaque accumulation-a sign for caries risk in young children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1994;22:273–276.
Alaluusua S, Renkonen OV. Streptococcus mutans establishment and dental caries experience in children from 2 to 4 years old. Scand J Dent Res 1983;91:453–457.
Alaluusua S. Longitudinal study of salivary IgA in children form 1 to 4 years old with reference to dental caries. Scand J Dent Res 1983;91:163–168.
Alanen P, Hurskainen K, Isokangas P. Clinician’s ability to identify caries risk subjects. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1994;22:86–90.
Albert RJ, Cantin RY, Cross HG, Castaldi CR. Nursing caries in the Inuit children of the Keewatin. J Can Dent Assoc 1988;54:751–758.
Alvarez JO, Caceda J, Woolley TW. A longitudinal study of dental caries in the primary teeth of children who suffer from infant malnutrition. J Dent Res 1993;72:1573–1576.
Anderson MH, Shi W. A probiotic approach to caries management. Ped Dent 2006;28:151–153.
Arkin EB. The Healthy Mothers, Healthy Babies Coalition: four years of progress. Public Health Rep 1986;101:147–156.
Armfield JM, Robents-Thomson KF, Spencer AJ. The child Dental Health Survey Australia 1999: Trends across the 1990s, (No AIHW Cat. No. DEN 95). Adelaide: The University of Adelaide (AIHW Dental Statistics and Research Series No.27), 2003.
Barnes GP, Parker WA, Lyon TC, Drum MA, Coleman GC. Ethnicity, location, age and fluoridation factors in baby bottle tooth decay and caries prevalence of Head Start children. Public Health Rep 1992;107:167–172.
Becker MR, Paster BJ, Leys EJ, et al. Molecular analysis of bacterial species associated with childhood caries. J Clin Microbiol 2002;40:1001–1009.
Berkowitz RJ, Turner J, Hugles C. Microbial characteristics of the human dental caries associated with prolonged bottle-feeding. Arch Oral Biol 1984;29:949–951.
Berkowitz RJ, Turner J, Green P. Maternal salivary levels of Streptococcus mutans and primary oral infection in infants. Arch Oral Biol 1981;26:147–149.
Birkeland JM, Broch L, Jorkjend L. Caries experience as predictor for caries incidence. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1997;4:66–70.
Bolton RW, Hlava GL. Evaluation of salivary IgA antibodies to cariogenic microorganisms in children. Correlation with dental caries activity. J Dent Res 1982;61:1225–1228.
Bone D, Arman E, Turby G. A bacteriological study of rampant caries in children. J Dent Res 1987;:23–28.
Bowen WH, Pearson SK. Effect of milk on cariogenesis. Caries Res 1993;27:461–466.
Broderick E, Marby J, Robertson D, Thompson J. Baby bottle tooth decay in native American children in Head Start centers. Public Health Rep 1989;104:50–54.
Carlsson J, Grahnen H, Johnsson G. Lactobacilli and streptococci in the mouth of children. Caries Res 1975; 9:333–339.
Caufield PW, Cutter GR, Dasanayake AP. Initial acquisition of mutans streptococci by infants: evidence for a discrete window of infectivity. J Dent Res 1993;72:37–45.
Challocombe SJ. Serum and salivary antibodies to Streptococcus mutans in relation to the development and treatment of human dental caries. Arch Oral Biol 1980;25:495–502.
Davies GN. Early childhood caries-a synopsis. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1998;26 (suppl 1):106–116.
Declerck D, Leroy R, Martens L, Lesaffre E, Garcia-Zattera MJ. Factors associated with prevalence and severity of caries experience in preschool children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2007; 1–11.
Demers M, Brodeur JM, Mouton C. A multivariate model to predict caries increment in Montreal children age 5 years. Community Dent Health 1992;9:373–376.
Derkson GD, Ponti P. Nursing bottle syndrome, prevalence and etiology in a non-fluoridated city. J Can Dent Assoc 1982;48:389–393.
Disney JA, Graves RC, Stamm JW, Bohannan HM, Abernathy JR. The University of North Carolina caries — risk assessment study: further developments in caries risk prediction. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1992;20:64–75.
Douglass JM, Tinanoff N, Tang JMW, Altmen D.: Dental caries patterns and oral health behaviours in Arizona infants and toddlers. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2001;29:14–22.
Drury TF, Horowitz AM, Ismail AI, Maertens MP, Selwitz RH. Diagnosing and reporting early childhood caries for research purposes. J. Public Health Dent 1999;59:192–200.
Dye BA, Shenkin JD, Ogden CL, et al. The relationship between healthful eating practices and dental caries in children aged 2–5 years in the United States, 1988–1994. JADA 2004;135:55–66.
Edelstein B, Tinanoff N. Correlation of dental caries in young children with a non-laboratory method of salivary S.mutans sampling. Ped Dent 1989;11:129–132.
Edgar WM, Bibby BG, Mundorff S, Rowley J. Acid production in plaque after eating snacks: modifying factors in foods. J Amer Dent Assoc 1975;90:418–425.
Emanuelsson IR, Li Y, Bratthall D. Genotyping shows different strains of mutans streptococci between father and child and within parental pairs in Swedish families. Oral Microbiol Immunol 1998;13:271–277.
Emanuelsson IR, Thornqvist E. Genotypes of mutans streptococci tend to persist in their host for several years. Caries Res 2000;34:133–139.
Erickson PR, Mazhari E. Investigation of the role of human breast milk I caries development. Ped Dent 1999;21:86–90.
Erickson PR, McClintock KL, Green N, LaFleur J. Estimation of the caries-related risk associated with infant formulas. Ped Dent 1998;20:395–403.
Ersin NK, Eronat N, Cogely D, Uzel A, Aksit J. Association of maternal-child characteristics as a factor in early childhood caries and salivary bacterial counts. J Dent child 2006;73:105–111.
Fass E. Is bottle-feeding of milk a factor in dental caries? J Dent Child 1962;29:245–251.
Febres C, Echeverri EA Keene HJ. Parental awareness, habits and social factors and their relationship to baby bottle tooth decay. Ped Dent 1997;19:22–27.
Gregory RL, Filler SJ, Michalek SM, McGhee JR. Salivary immunoglobulin A and serum antibodies to streptococcus mutans ribosomal preparations in dental caries-free and caries-susceptible human subjects. Infect Immun 1986;51:348–351.
Grindefjord M, Dahloff G, Ekstrom G, Hojer B, Modeer. Caries prevalence in 2.5 year old children. Caries Res 1993;27:505–510.
Grindefjord M, Dahloff G, Nilsson B, Modeer T. Stepwise prediction of dental caries in children up to 3.5 years of age. Caries Res 1996; 30:256–266.
Gronroos L, Saarela M, Matoos J, et al. Mutacin production by Streptococcus mutans may promote of bacteria from mother to child. Infect Immun 1998;66:2595–2600.
Hallet KB, O’Rourke PK. Social and behavioural determinants of early childhood caries. Aust Dent J 2003;48:27–33.
Hallett KB, O’Rourke PK. Early childhood caries and infant feeding practice. Community Dent Health 2002;19:237–242.
Hallonsten AL, Wendt LK, Mejare I, et al. Dental caries and prolonged breast-feeding in 18-month0old Swedish children. Int J Ped Dent 1995;5:149–155.
Haugejiorden O, Birkeland JM. Evidence for reversal of the caries decline among Norwegian Children. Int J Paediatr Dent 2002;12:306–315.
Hausen H. Caries prediction — state of the art. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1997;25:87–96.
Horowitz HS. Research issues in early childhood caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1998;26 (suppl 1):67–81.
Ismail A, Sohn W. A systematic review of clinical diagnostic criteria of early childhood caries. J Public Health Dent 1999;59:171–191.
Johnsen DC. Characteristics and backgrounds of children with nursing caries. Ped Dent 1982;4:218–224.
Karjalainen S, Soderling E, Sewon L, Lapinleimn H, Simell O. A prospective study on sucrose consumption, visible plaque and caries in children 3 to 6 years of age. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2001;29:136–142.
Karn T, O’Sullivan D, Tinanoff N. Colonization of mutans streptococci in 8-to 15-month-old children. J Public Health Dent 1998;58:248–249.
Kaste LM, Gift HC. Inappropriate infant bottle feeding status of the healthy people 2000 objective. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1995;149:786–791.
Kaste LM, Selwitz RH, Oldakowski RJ, et al. Coronal caries in the primary and permanent dentition of children and adolescents 1–17 years of age: United States, 1988–1991. J Dent Res 1996;75 (Spec Iss):631–641.
Kelly M, Bruerd B. The prevalence of baby bottle tooth decay among two Native American populations. J Public Health Dent 1987;47:94–97.
Klein MI, Florio FM, Pereira AC, Hofling JF, Gonzalves PB. Longitudinal study of transmission, diversity and stability of Streptococcus mutans and streptococcus sobrinus genotypes in Brazilian nursery children. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:4620–4626.
Kohler B, Andreen I, Johnsson B. The earlier the colonization by mutans streptococci, the higher the caries prevalence at 4 years of age. Oral Microbiol Immunol 1988;3:14–17.
Kohler B, Lundberg AB, Birkhed D, Papapanon PN. Longitudinal study of intra-familiar mutans streptococci ribotypes. Eur J Oral Sci 2003;111:383–389.
Lai PY, Seow WK, Rogers YI, Tudehope DI. Enamel hypoplasia and dental caries in very low birthweight children: a longitudinal, case controlled study. Ped Dent 1997;19:42–49.
Leroy R, Hoppenbrouwers K, Jara A, Declerck D. Parental smoking behaviour and caries experience in preschool children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2007;1–9.
Li Y, Caufield PW. The fidelity of initial acquisition of mutans streptococci by infants from their mothers. J Dent Res 1995;74:681–685.
Li Y, Navia JM, Bian JY. Caries experience in deciduous dentition of rural Chinese children 3 to 5 years old in relation to the presence or absence of enamel hypoplasia. Caries Res 1996;30:8–15.
Li Y, Navia JM, Caufield PW. Colonization by humans’ streptococci in the months of 3- and 4- year-old Chinese children with or without enamel hypoplasia. Arch Oral Biol 1994;39:1057–1062.
Lingstrom P, van Ruyren FO, van Houte J, Kent R. The pH of dental plaque in relation to early enamel caries and dental plaque flora in humans. J Dent Res 2000;79:770–777.
Litt MD, Reisine S, Tinanoff N. Multidimensional causal model of dental caries development in low-income preschool children. Public Health Rep 1995;110:607–617.
Louie R, Brunell JA, Maggiore ED, Beck RW. Caries prevalence in Head Start children, 1986–87. J Public Health Dent 1990;50:299–305.
Marino RV, Bomze K, Scholl TO, Anhalt N. Nursing bottles caries: Characteristics of children at risk. Clin Pediatr 1989;28:129–131.
Marques APF, Messer LB. Nutrient intake and dental caries in the primary dentition. Ped Dent 1992;14:314–321.
Marthaler TM. Caries status in Europe and predictions of future trends. Caries Res 1990;24:381–396.
Marthaler TM, O’Mullane DM, Vrbic V. The prevalence of dental caries in Europe. Caries Res 1996;30:237–255.
Masuda N, Tsutsumi N, Sobue S, Hamada S. Longitudinal survey of the distribution of various serotypes of streptococcus mutans of infants. J Clin Microbiol 1979;10:497–502.
Matee MIN, Mikx F, Maselle S, Van Palenstein, Helderman W. Mutans streptococci and lactobacilli in breast-fed children with rampant caries. Caries Res 1992;26:183–187.
Matee MIN, Van’Hof MA, Maselle SY, Mikx FHM, van Palenstein Helderman WH. Nursing caries, linear hypoplasia and nursing as weaning habits in Tanzanian infants. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1994;22:289–293.
Mattila ML, Rautava P, Aromaa M, et al. Behavioural and demographic factors during early childhood and poor dental health at 10 years of age. Caries Res 2005;39:85–91.
Mattos-Graner RO, Li Y, Caufield PW, Duncan M, Smith DJ. Genotypic diversity of mutans streptococci in Brazilian nursery children suggests horizontal transmission. J Clin Microbiol 2001;39:2313–2316.
McMahon J, Parnell WR, Spears GFS. Diet and dental caries in preschool children. Eur J Clin Nutr 1993;47:794–802.
Mikkelsen L. Effect of sucrose intake on numbers of bacteria in plaque expressing extracellular carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes. Caries Res 1996;30:65–70.
Milgrom P, Riedy CA, Weinstein P, et al. Dental caries and its relationship to bacterial infection, hypoplasia, diet, and oral hygiene in 6-to 36-month old children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 2000;28:295–306.
Milnes AR. Description and epidemiology of nursing caries. J Public Health Dent 1996;56:38–50.
Mundorff SA, Billings RJ, Leverett DH. Saliva and dental caries risk assessment. Ann NY Acad Sci 1993;694:302–304.
National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference statement. Diagnosis and management of dental caries throughout life. JADA 2001;132:1153–1161.
Neeser JR, Golliard M, Woltz A, et al. In vitro modulation of oral bacterial adhesion to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite beads by milk casein derivatives. Oral Microbiol Immunol 1994;9:193–201.
O’Sullivan DM, Douglass JM, Chamany R, Eberling S. Caries experience in 2003 Native American preschool children. J Public Health Dent 1994;54:139–144.
O’Sullivan DM, Tinanoff N. Maxillary anterior caries associated with increased caries risk in other primary teeth. J Dent Res 1993;72:1577–1580.
O’Sullivan DM, Tinanoff N. The association of early dental caries patterns in preschool children with caries incidence. J Public Health Dent 1996;56:81–83.
Oulis C, Athanassouli T, Papagiannoulis L, et al. Oral health status of the Greek population — Oral health program of the Hellenic Dental Association, Athens 2005.
Oulis CJ, Berdouses ED, Vadiakas G. Feeding practices of Greek children with and without nursing caries. Ped Dent 1999;21:409–416.
Pannio P, Rautova P, Helenins H, Alanen P, Sillanpaa M. The Finnish family competence study: the relationship between caries, dental health habits and general health in 3-year-old Finnish children. Caries Res 1993;27:154–160.
Petersson GH, Bratthall D The caries decline: a review of reviews. Eur J Oral Sciences 1996;104:436–443.
Pitts NB, Boyles J, Nugent ZJ, Thomas N: The dental caries experience of 5 year-old children in England and Wales (2003/4) and in Scotland (2002/3). Surveys co-ordinated by the British Association for the Study of Community Dentistry. Community Dent Health 2005;22:46–56.
Poulsen S, Malling Pedersen M. Dental caries in Danish children: 1988–2001. Eur J Paediatr Dent 2002;3:195–198.
Psoter WJ, Pendrys DG, Morse DE, Zhang H, Mayne ST. Associations of ethnicity/race and socioeconomic status with early childhood caries patterns. J Public Health Dent 2006;66:23–29.
Reisine S, Douglass JM. Psychosocial and behavioural issues in early childhood caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1998;26 (suppl 1):32–44.
Reisine S, Litt M, Tinanoff N. A biopsychosocial model to predict caries in preschool children. Ped Dent 1994;16:413–418.
Reynolds EC, Cain CS, Webber FL, et al. Anticariogenicity of calcium phosphate complexes of tryptic casein phosphopeptides in the rat. J Dent Res 1995;74:1272–1279.
Ripa L. Nursing caries: a comprehensive review. Ped Dent 1988;10:268–282.
Roberts I, Roberts GJ. Relation between medicines sweetened with sucrose and dental disease. Br Med J 1979;2:14–16.
Rodrigues CS, Sheiham A. The relationship between dietary guidelines, sugar intake and caries in primary teeth in low income Brazilian 3-year-olds: a longitudinal study. Int J Ped Dent 2000;10:47–55.
Roeters J, Burgesdijk R, Truin GJ, van’t Hof M. Dental caries and its determinants in 2 -to 5 -year old children. ASDC J Dent Child 1995;62:401–408.
Rugg-Gunn AJ, Al-Mohammadi SM, Butler TJ. Malnutrition and developmental defects of enamel in 2 to 6 year old Saudi boys. Caries Res 1998;32:181–192.
Scheneyer L, Pigman W, Hanahan L, Gilmove R. Rate of human parotid, sublingual and submaxillary secretions during sleep. J Dent Res 1956;35:109–114.
Schwarz SS, Rosivack RC, Michelotti P. A child’s sleeping habit as a cause of nursing caries. J Dent Child 1993;60:22–25.
Seow WK, Humphrys C, Tudehope DJ. Increased prevalence of developmental defects in low-birth-weight children: A controlled study. Ped Dent 1987;9:221–225.
Seow WK. Biological mechanisms of early childhood caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1998;26 (Suppl):8–27.
Serwint JR, Mungo R, Negrete VF, Duggan AK, Korsch BM. Child rearing practices and nursing caries. Pediatrics 1993;92:233–237.
Sheikh C, Erickson PR. Evaluation of plaque pH changes following oral rinse with eight infant formulas. Ped Dent 1996;18:200–204.
Shiboski CH, Gansky SA, Ramos-Gomaz R et al. The association of early childhood caries and race/ethnicity among preschool children. J public Health Dent 2003;63:38–46.
Silver DH. A comparison of 3 year — old caries experience in 1973, 1981 and 1989, in a Hertfordshire town, related to family behaviour and social class. Br Dent J 1992;172:191–197.
Stecksen-Blicks C, Holm AK. Between — meal eating, tooth brushing frequency and dental caries in 4-year-old children in the north of Sweden. Int J Ped Dent 1995;5:67–72.
Steiner M, Helfenstein U, Marthaler TM. Dental predictors of high caries increment in children. J Dent Res 1992;71:1926–1933.
Stephan RM. Effects of different types of human foods on dental health in experimental animals. L Dent Res 1966;45:1551–1561.
Tang JM, Altman DS, Robertson DC, et al. Dental caries prevalence and treatment levels in Arizona preschool children. Public Health Rep 1997;112:319–329.
Tanner ACR, Milgrom PM, Kent R, et al. The microbiota of young children from tooth and tongue samples. J Dent Res 2002;81:53–57.
Tenovuo J, Lumikeri M. Organic factors in human saliva in relation to dental caries. In: Johnson NW, editor. Risk markers for oral diseases. Vol 1. Dental caries. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ Pr; p. 382–398, 1991
Thibodeau EA, O’Sullivan DM. Salivary mutans streptococci and dental caries patterns in pre-school children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1996;24:164–168.
Thibodeau EA, O’Sullivan DM, Tinanoff N. Mutans streptococci and caries prevalence in preschool children. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 1993;21:288–291.
Tinanoff N, Palmer CA. Dietary determinants of dental caries and dietary recommendations for preschool children. J Public Health Dent 2000;60:197–206.
Tinanoff N, Kanellis MJ, Vargas CM. Current understanding of the epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention of dental caries in preschool children. Ped Dent 2002;24:543–550.
Twetman, S. Prevention of Early Childhood caries (ECC) — review of the literature published 1998–2007. Eurrop J Paediatr Dent 2008;9(1);12–19.
van Houte J, Gibbs G, Butera C. Oral flora of children with “nursing — bottle caries”. J Dent Res 1982;61:382–385.
van Houte J, Lopman J, Kent R. The final pH of bacteria comprising the predominant flora on sound and carious root and enamel surfaces. J Dent Res 1996;75:1008–1014.
van Loveren, Buijs JF, ten Kate JM. Similarity of bacteriocin activity profiles of mutans streptococci within the family when the children acquire the strains after the age of 5. Caries Res 2000;34:481–485.
van Palenstein Helderman WH, van’t Hof MA, van Loveren C. Prognosis of caries increment with past caries experience variables. Caries Res 2001;35:186–192.
van Ruyren FO, Lingstrom P, van Houte J, Kent R. Relationship among mutans streptococci, “low-pH” bacteria and lodophilic polysaccharide-producing bacteria in dental plaque and early enamel caries in humans. J Dent Res 2000;79:778–784.
Vanobbergen J. The development and application of a risk prediction model for dental caries in primary schoolchildren in Flanders. Thesis, University of Gent, 2001.
Vanobbergen J, Martens L, Lesaffre E, Bogaerts K, Declerck D. The value of baseline multiple caries risk assessment model in the primary dentition for the prediction of caries incidence in the permanent dentition. Caries Res 2001;35:442–450.
Vargas CM, Croll JS Schneider DA. Sociodemographic distribution of pediatric dental caries: NHANES III, 1988–1994 JADA 1998;129:1229–1238.
Wan AK, Seow WK, Purdie DM, et al. Oral colonization of Streptococcus mutans in six-month old predentate infants. J Dent Res 2001;80:2060–2065.
Wan AK, Seow WK, Purdie DM, et al. A longitudinal study of Streptococcus mutans colonization in infants after tooth eruption. J Dent Res 2003;82:504–508.
Weinstein P, Domoto P, Wohlers K, Koday M. Mexican-American parents with children at risk for baby bottle tooth decay: pilot study at a migrant farm workers clinic. J Dent Child 1992;59:376–383.
Wendt LK, Hallonsten AL, Koch G, Birkhed, D. Analysis of caries related factors in infants and toddlers living in Sweden. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica 1996;54:131–137.
WHO Technical Report Series 916, 2003. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases: report of a joint WHO/FAO expert consultation. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Ye W, Feng XP, Liu YL. Epidemiological study of the risk factors of rampant caries in Shanghai children. Chinese Journal of Dental Research 1999;2:58–62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vadiakas, G. Case definition, Aetiology and Risk assessment of Early Childhood Caries (ECC): A revisited review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 9, 114–125 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03262622
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03262622