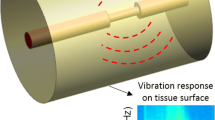
Abstract
Acute myocardial infarction and cerebral infarction are generally known to be caused primarily by the rupture of atherosclerotic plaques. It is thus necessary for clinical treatment to predict the rupture of these plaques. Blood-flow velocity around atherosclerotic plaques increases as the arteriostenosis lesion progresses, resulting in turbulence downstream of the lesion. The resulting change in blood pressure produces shear stress, and change in this stress affects the rupture of the atherosclerotic plaques. Cerebral ischemic paroxysm and cerebral infarction have been reported to occur in a high percentage of cases in which inner vessel diameter has decreased to less than 70% of its original diameter as a result of stenosis. This explains the use of standard ultrasonic diagnostic equipment to measure blood flow in the screening of the carotid arteries. On the other hand, the noise signal radiated from an aneurysm as a result of blood flow has been measured using the bruit sensor used to diagnose cerebrovascular diseases. Many unsolved problems with regard to the relationship between noise and turbulence in blood flow remain, however. Here, small vibrations on the arterial wall were measured transcutaneously and analyzed both upstream and downstream of the atherosclerotic plaque of a human carotid artery. Characteristics of the resultant vibrations upstream of the stenosis clearly differed from those downstream of it. These results should prove useful in predicting the rupture of atherosclerotic plaques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nonogi H: The Pathorogenesis and treatment of acute coronary syndrome. Recent advances in cardiovascular disease 1998; 14: 100–113. [in Japanese]
Hasegawa H, Kanai H, Chubachi N, et al: Evaluation of elastic modulus of the arterial wall by accurate noninvasive measurement of change in thickness of arterial wall. JPN J Med Ultrasonics 1997; 24 (6): 851–860. [in Japanese]
Kobayashi T, Ryu H, Yamaguchi T: A computational mechanical analysys of rupture of atheromatous plaque and acute coronary syndrome (ACS). JJME 1998; 36 (Suppl): 441. [in Japanese]
Sugawara M: Introduction to Blood Flow: Foundation for Ultrasonic Doppler Measurements,Tokyo, MS Press, 1998; pp. 1–32. [in Japanese]
Asaoka N, Matsuoka H: Jpn. J. Clin. Radiol (Supplement) 1998; 43 (11): 1396–1402. [in Japanese]
Yasaka M, Tutiya T, Yamaguchi T, et al: Ageing and diseases 1990; 3 (6): 893–900. [in Japanese]
Kikuchi K, Mekata K, Hasegawa K, et al: On the relationship between blood flow sounds from the cervical carotid artery and cerebrovascular lesions. IEICJ Technical Report 1998; EA97–103 (3): 1–8. [in Japanese]
Fukunaka N, Inoue Y, Hasegawa J: Detection system of intracranial blood flow noise for diagnosis of vessel malformation. IEICJ Technical Report 1993; EA93–79 (12): 17–22. [in Japanese]
Kanai H, Sato M, Koiwa Y, et al: Transcutaneous measurement and spectrum analysis of heart wall vibrations.IEEE Trans. on UFFC 1996; 43: 791–810.
Hasegawa H, Kanai H, Hoshimiya N, et al: Measurement of Spatial Distribution of Elasticity of Arterial Wall Using Ultrasound. Reports of the 1999 spring meeting the Acoustical Society of Japan 1999: 1125–1126. [in Japanese]
Antal G. Hudetz: Incremental elastic modules for orthotropic incompressible arteries.J Biomech 1979; 12: 651–655.
Sano M, Kubota Y, Sumita Y: Medical Technology 1997; 25 (5): 405–427. [in Japanese]
Kanai H: Spectrum Analysis of Sound and Vibration. Tokyo, Corona Publishing Co., Ltd., 1999: pp. 269–271. [in Japanese]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Sunagawa, K., Kanai, H., Koiwa, Y. et al. Simultaneous measurement of vibrations on arterial wall upstream and downstream of arteriostenosis lesion and their analysis. J Med Ultrasonics 28, 157–173 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481353
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481353