Summary
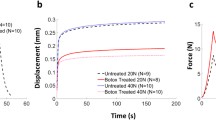
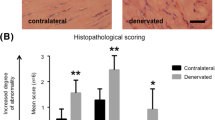
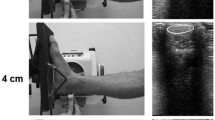
We examined the influence exerted, through disuse of the hindlimb, on the collagen fibres of the achilles tendon in rats. With disuse the body mass decreased by 28%, and the mass of soleus muscle decreased by 20%. A decrease in the surface area and diameter was observed in the experimental group when compared to the control group. A histogram of the collagen fibres showed a decrease of the thick fibres in the experimental group. The maximum surface area of collagen fibres in the experimental group was seen to be only 43% of that of the control group. These results showed a decrease in the thickness of the collagen fibres of the achilles tendon through disuse. This seemed to suggest that resistance to tension is decreased by disuse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akeson WH (1961) An experimental study of joint stiffness. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 43:1022–1034
Desplanches D, Mayet MH, Sempore B, Flandrois R (1987) Structural and functional responses to prolonged hindlimb suspension in rat muscles. J Appl Physiol 63:558–563
Flynn DE, Max SR (1985) Effect of suspension hypokinesia/hypodynamia on rat skeletal muscle. Aviat Space Environ Med 56:1065–1069
Globus RK, Bikle DD, Morey-Holton E (1984) Effects of simulated weightlessness on bone mineral metabolism. Endocrinology 114:2264–2270
Hauschka ED, Roy RR, Edgerton VR (1987) Size and metabolic properties of single muscle fibers in rat soleus after hindlimb suspension. J Appl Physiol 62:2338–2347
Laros GS, Tipton CM, Cooper RR (1971) Influence of physical activity on ligament insertions in the knee of dogs. J Bone Joint Surgy [Am] 53:275–286
Morey ER (1979) Spaceflight and bone turnover: correlation with a new rat model of weightlessness. BioScience 29:168–172
Musacchia XJ, Steffen JM, Deavers DR (1983) Rat hindlimb muscle responses to suspension hypokinesia/hypodynamia. Aviat Space Environ Med 54:1015–1020
Nakagawa Y, Sato T, Fukuda Y, Hirota K (1988) Effect of aerobic and anaerobic training on collagen fiber of tendon in rats. Jpn J Phys Fitness Sports Med 37:100–108
Noyes FR (1977) Functional properties of knee ligaments and alterations induced by immobilization. Clin Orthop 123:210–242
Noyes FR, Torvic PJ, Hyde WB, Delucas JL (1974) Biomechanics of ligament failure. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 56A:1406–1418
Rothman RH, Slogoff S (1967) The effect of immobilization on vascular bed of tendon. Surg Gynecol Obstet 124:1064–1066
Steffen JM, Deavers DR, Musacchia XJ (1980) Increased excretion of water, urea, Na+ and K− during head-down-tilt hypokinesia: a question of diet or antiorthostrasis. Physiologist 23:84
Thomason DB, Herrick RE, Baldwin KM (1987) Activity influences on soleus muscle myosin during rodent hindlimb suspension. J Appl Physiol 63:138–144
Tipton CM, Schild RJ, Tomanek RJ (1967) Influence of knee ligaments in rats. Am J Physiol 212:783–787
Tipton CM, James SL, Mergner W, Tcheng TK (1970) Influence of exercise on strength of medical collateral knee ligament of dogs. Am J Physiol 218:894–902
Tipton CM, Tcheng T, Mergner W (1971) Ligamentous strength measurements from hypophysectomized rats. Am J Physiol 221:1144–1150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakagawa, Y., Totsuka, M., Sato, T. et al. Effect of disuse on the ultrastructure of the achilles tendon in rats. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 59, 239–242 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386194
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02386194