Abstract
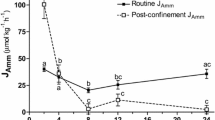
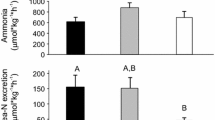
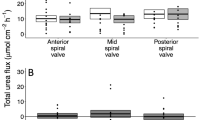
The endemic, anadromous cyprinidChalcalburnus tarichi is the only fish species known to occur in alkaline Lake Van (Eastern Anatolia, Turkey). EightC. tarichi were maintained individually in Lake Van water (17 – 19°C; pH 9.8; 153 mEq·I−1 total alkalinity; 22‰ total salinity) and tank water samples analyzed for 24 h in 2 to 4 h intervals. At zero time, < 1µM ammonia was present and urea was undetectable in the tank water; at 24 h, total ammonia and urea made up 114±32 and 35±25µM, respectively. Over the experimental period, ammonia-N and urea-N excretion averaged 1041±494 and 607±169μmoles·kg−1 fish·h−1, respectively. The extent of urea excretion was highly variable between specimens. Uric acid excretion was not detectable.
Urea was present at high concentrations in all tissues and plasma (25 – 35μmoles·g−1·ml−1) of freshly caughtC. tarichi; total ammonia content of the tissues was by a factor of 1.9 (liver) to 3.0 (brain) lower. High arginase activity (2.4±0.2 U·min−1·g−1) was detected in the liver ofC. tarichi but ornithine carbamoylphosphate transferase, a key enzyme of the ornithine-urea-cycle, was absent. Ureagenesis is likely through degradation of arginine and/or uricolysis. High glutamine synthetase activity (11±0.6 U·min−1·g−1) and low ammonia content in brain suggest that, like other teleosts,C. tarichi has an efficient ammonia detoxification in the brain, but in no other tissue.
Nitrogenous waste excretion at alkaline pH is discussed. The ability ofC. tarichi to excrete high levels of ammonia at extremely alkaline pH is unique among teleosts studied so far. The mechanism of ammonia excretion under Lake Van conditions remains to be elucidated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Arillo, A., Margiocco, C., Melodia, F., Mensi, P. and Schenone, G. 1981. Ammonia toxicity mechanism in fish: studies on rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri Rich.). Ecotoxicol. Environm. Safety 5: 316–328.
Berg, L.S. 1964. Freshwater Fishes of the USSR and Adjacent Countries. Vol. II. 4th ed. Academy of Sciences of the USSR. Zoological Institute. (translated into English)
Bradford, M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Brown, G.W. and Cohen, P.P. 1959. Comparative biochemistry of urea synthesis. I. Methods for the quantitative assay of urea cycle enzymes in liver. J. Biol. Chem. 234: 1769–1774.
Cvancara, V.A. 1969. Comparative study of liver uricase activity in fresh-water teleosts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 28: 725–732.
Danalut, E. and Selcuk, B. 1992. Life history and environmental conditions of the anadromousChalcalburnus tarichi (Cyprinidae) in the highly alkaline Lake Van. Eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Archiv für Hydrobiol. (In press).
Degens, E.T., Wong, H.K., Kempe, S. and Kurtman, F. 1984. A geological study of Lake Van, Eastern Turkey. Geologische Rundschau 73: 701–734.
Deyrolle, T. 1872. Notice sur une espèce remarquable de poisson qui vit dans les eaux du Lac de Van. Rev. Mag. Zool. (Paris). 2nde Sér. 23: 401–405.
Emerson, K., Russo, R.C., Lund, R.E. and Thurston, R.V. 1975. Aqueous ammonia equilibrium calculations: Effect of pH and temperature. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 32: 2379–2383.
Forster, R.P. and Goldstein, L. 1969. Formation of excretory products.In Fish Physiology, Vol. 1. pp. 313–350. Edited by W.S. Hoar and D.J. Randall. Academic Press, New York.
Gessner, F. 1957. Van Gölü. Zur Limnologie des großen Soda-Sees in Ostanatolien (Türkei). Arch. f. Hydrobiol. 53: 1–22.
Goldstein, L. and Forster, R.P. 1965. The role of uricolysis in the production of urea by fishes and other aquatic vertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 14: 567–576.
Gregory, R.B. 1977. Synthesis and total excretion of waste nitrogen by fish of the Periophthalmus (mudskipper) and Scartelaos families. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 57A: 33–36.
Grubinko, V.V., Yakovenko, B.V. and Yavonenko, A.F. 1987. Effects of starvation on arginase activity and urea contents in the carp,Cyprinus carpio. J. Ichthyol. 27: 107–110.
Guerin-Ancey, O. 1976. Etude expérimentale de l'excrétion azotée du bar (Dicentrarchus labrax) en cours de croissance. III. Effects du volume et de la concentration initiale en ammoniac sur l'excrétion d'ammoniac et d'urée. Aquaculture 9: 253–258.
Hauer, J. 1957. Rotatorien aus dem Plankton des Van-Sees. Arch. f. Hydrobiol. 53: 23–29.
Haywood, G.P. 1983. Ammonia toxicity in teleost fishes. A review. Can. Tech. Rep. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1177: 1–35.
Henriksson, J., Chi, M.M.-Y., Hintz, C.S., Young, D.A., Kaiser, K.K., Salmons, S. and Lowry, O.H. 1986. Chronic stimulation of mammalian muscle: changes in enzymes of six metabolic pathways. Am. J. Physiol. 251: C614-C632.
Huggins, A.K., Skutsch, G. and Baldwin, E. 1969. Ornithine urea cycle enzyme in teleostean fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 28: 587–602.
Ivancic, I. and Degobbis, D. 1984. An optimal manual procedure for ammonia analysis in natural waters by the indophenol blue method. Water Res. 18: 1143–1147.
Kempe, S., Kazmierczak, J., Landmann, G., Konuk, T., Reimer, A. and Lipp, A. 1991. Largest known microbialities discovered in Lake Van, Turkey. Nature, Lond. 349: 605–608.
Ladiges, W. 1960. Süßwasserfische der Türkei. i. Teil: Cyprinidae. Mitt. Hamburg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 58: 105–150.
Love, R.M. 1980. The Chemical Biology of Fishes. Vol. II. Academic Press, London.
Mommsen, T.P. and Walsh, P.J. 1989. Evolution of urea synthesis: the piscine connection. Science 243: 72–75.
Olson, K.R. and Fromm, P.O. 1971. Excretion of urea by two teleosts exposed to different concentrations of ambient ammonia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 40A: 999–1007.
Randall, D.J. and Wright, P.A. 1987. Ammonia distribution and excretion in fish. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 3: 107–120.
Randall, D.J., Wood, C.M., Perry, S.F., Bergman, H., Maloiy, G.M.O., Mommsen, T.P. and Wright, P.A. 1989. Urea excretion as a strategy for survival in a fish living in a very alkaline environment. Nature, Lond. 337: 165–166.
Sachs, L. 1974. Angewandte Statistik. Springer Verlag, Berlin.
Saha, N. and Ratha, B.K. 1989. Comparative study of ureogenesis in freshwater, air-breathing teleosts. J. Exp. Zool. 252: 1–8.
Schreckenbach, K., Spangenberg, R. and Krug, S. 1975. Die Ursache der Kiemennekrose. Z. Binnenfischerei DDR 22: 257–288.
Smith, H.W. 1929. The excretion of ammonia and urea by the gills of fish. J. Biol. Chem. 81: 727–742.
Vassef, A.A. 1978. Direct micromethod for colorimetry of serum ornithine carbamoyltransferase activity, with use of a linear standard curve. Clin. Chem. 24: 101–107.
Vellas, F. and Serfaty, A. 1974. L'ammoniaque et l'urée chez un téléostéen d'eau douce: la carpe (Cyprinus carpio L.). J. Physiol., Paris 68: 591–614.
Walsh, P.J., Danulat, E. and Mommsen, T.P. 1990. Variation in urea excretion in the gulf toadfishOpsanus beta. Mar. Biol. 106: 323–328.
Webb, J.T. and Brown, G.W. jr. 1980. Glutamine synthetase: Assimilatory role in liver as related to urea retention in marine chondrichthyes. Science 208: 293–295.
Wood, J. 1958. Nitrogen excretion in some marine teleosts. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 36: 1237–1242.
Wood, C.M., Perry, S.F., Wright, P.A., Bergman, H.L. and Randall, D.J. 1989. Ammonia and urea dynamics in the Lake Magadi tilapia, a ureotelic teleost fish adapted to an extremely alkaline environment. Resp. Physiol. 77: 1–20.
Wright, P.A. and Wood, C.M. 1985. An analysis of branchial ammonia excretion in the freshwater rainbow trout: effects of environmental pH change and sodium uptake blockade. J. Exp. Biol. 114: 329–353.
Wright, P.A., Randall, D.J. and Wood, C.M. 1988. The distribution of ammonia and H between tissue compartments in lemon sole (Parophrys vetulus) at rest, during hypercapnia and following exercise. J. Exp. Biol. 136: 149–175.
Wright, P.A., Randall, D.J. and Perry, S.F. II 1989. Fish gill boundary layer: a site of linkage between carbon dioxide and ammonia excretion. J. Comp. Physiol. 158B: 627–635.
Wynants, J., Petrov, B., Nighof, J. and Van Belle, H. 1987. Optimization of a high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of nucleosides and their catabolites. Application to cat and rabbit heart perfusate. J. Chromatogr. 386: 297–308.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danulat, E., Kempe, S. Nitrogenous waste excretion and accumulation of urea and ammonia inChalcalburnus tarichi (Cyprinidae), endemic to the extremely alkaline Lake Van (Eastern Turkey). Fish Physiol Biochem 9, 377–386 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02274218
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02274218