Summary
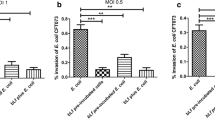
To assess the role of local immune response against bacterial invasion of the urinary tract we studied 168 patients with bacteriuria. Urinary secretory immunoglobulins A (sIgA) were measured using radial immunodiffusion or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In particular, ELISA is a very suitable assay for measuring the low levels of sIgA in urine. Furthermore, we used a quantitative in vitro adherence assay to investigate the attachment of Escherichia coli to human uroepithelial cells after incubation in urine from patients with urinary tract infection. Urine from patients with ileocystoplasty was significantly more potent in inhibiting bacterial adherence than was urine from other groups of patients with urinary tract infection. The presence of high urinary sIgA may help explain the increased antiadherence activity of urine in patients with ileocystoplasty. Mean urinary sIgA in patients with upper urinary tract infection was higher than in patients with uncomplicated infection in the lower urinary tract. Alterations in mucosal immune functions may account for the propensity toward bacterial colonization in women prone to uncomplicated urinary tract infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fliedner M, Mehls O, Rauterberg EW, Ritz E (1986) Urinary sIgA in children with urinary tract infection. J Pediatr 109:416
Hjelm EM (1984) Local cellular immune response in ascending urinary tract infection: occurrence of T-cells, immunoglobulin-producing cells and Ia-expressing cells in rat urinary tract tissue. Infect Immun 44:627
Hopkins WJ, Uchling DT, Balish E (1987) Local and systemic antibody responses accompany spontaneous resolution of experimental cystitis in Cynomolgus monkeys. Infect Immun 55:1951
Jensen J, Uehling DT, Kim K, Seagren-Rasmunssen K, Balish E (1984) Enhanced immune response in the urinary tract of the rat following vaginal immunization. J Urol 132:164
Kallenius G, Winberg J (1978) Bacterial adherence to periurethral epithelial cells in girls prone to urinary-tract infections. Lancet II:540
Kaufmann DN, Katz R, McIntosh RN (1970) Secretory IgA in urinary tract infection. Br Med J 4:463
Mansson W, Colleen S, Low K, Mardh PA, Lundblad A (1985) Immunoglobulins in urine from patients with ileal and colonic conduits and reservoirs. J Urol 133:713
McDermott MR, Bienenstock J (1979) Evidence for a common mucosal immunological system: I. Migration of B immunoblasts into intestinal, respiratory and genital tissues. J Immunol 122:1892
Riedasch G, Heck P, Rauterberg E, Ritz E (1983) Dose low urinary sIgA predispose to urinary tract infection? Kidney Int 23:759
Savoia D, Martinetto P, Achino A, Pugliese A (1983) Adhesion of Proteus species to various cell types. Eur J Clin Microbiol 2:571
Schaeffer AJ, Jones JM, Dunn JK (1981) Association of in vitro Escherichia coli adherence to vaginal and buccal epithelial cells with susceptibility of women to recurrent urinary-tract infections. N Engl J Med 304:1062
Silverblatt FJ, Cohen LS (1979) Antipili antibody affords protection against experimental ascending pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest 64:333
Svanborg Edén C, Hanson LA, Jodal U, Lindberg U, Sohl Akerlund A (1976) Variable adherence to normal human urinary tract epithelial cells of E. coli strains associated with various forms of urinary tract infections. Lancet II:490
Svanborg Edén C, Eriksson B, Hanson LA (1977) Adhesion of Escherichia coli to human uroepithelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun 18:767
Szabo RJ, Dairiki Shortliffe LM, Stamey TA (1987) Adherence of Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis to human transitional cells. J Urol 137:793
Tomasi TB (1972) Secretory immunoglobulins. N Engl J Med 287:500
Trinick TR, Laker MF (1984) Measurement of urinary immunoglobulins G, A and M by an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Chim Acta 139:113
Uehling DT, (1973) Immunoglobulin excretion in women with recurrent urinary tract infections. J Urol 109:302
Uehling DT, Steihm ER (1971) Elevated urinary secretory IgA in children with urinary tract infection. Pediatrics 47:40
Uehling DT, Hopkins WJ, Jensen J, Balish E (1987) Vaginal immunization against induced cystitis in monkeys. J Urol 137:327
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trinchieri, A., Braceschi, L., Tiranti, D. et al. Secretory immunoglobulin A and inhibitory activity of bacterial adherence to epithelial cells in urine from patients with urinary tract infections. Urol. Res. 18, 305–308 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300776
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300776