Summary
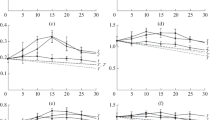
The enzymatic hydrolysis of cellobiose and cellulose by the cell-free culture filtrate of Trichoderma reesei QM 9414 was investigated. The concentrations of cellobiose and glucose were measured as a function of time for different initial concentrations of cellobiose. It was not possible to describe these concentration variations by a model which considers only the cellobiase hydrolysis with competitive and noncompetitive substrate and product inhibition; it is necessary that the endo-β-1.4-glucanase with competitive product inhibition is also taken into account.
The enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose (Avicel) was described with a mathematical model by using the results of the decomposition of cellobiose by the same enzyme mixture.
the identified model parameters are presented. A sensitivity analysis of the parameter was carried out also.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binder A, Ghose TK (1978) Adsorption of cellulose by Trichoderma viride. Biotechnol Bioeng 20: 1187–1199
Bisaria VS, Ghose TK (1977) Sorption characteristics of cellulases on cellulose substances. Proc Bioconversion Symposium III, Delhi 155–164
Brown DE, Waluzzaman M (1977) Kinetics of enzymatic hydrolysis of waste newspaper. Proc Bioconversion Symposium III, Delhi 351–372
Buchholz K, Gödelmann J (1981) Hydrolysis of cellulosic wastes. 2nd European Congress on Biotechnology, Eastbourne
Castonen M, Wilke C (1980) Adsorption and recovery of cellulases during hydrolysis of newspaper. Biotechnol Bioeng 22: 1073–1053
Fliess A, Schügerl K (1983) Characterization of cellulases by HPLC separation. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 17: 314–318
Frank PM (1976) Empfindlichkeitsanalyse dynamischer Systeme. In: Föllinger O, Sartorius H (eds) Methoden der Regelungstechnik R. Oldenburg, München
Ghose TK, Bisaria VS (1972) Studies on the mechanism of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic substances. Biotechnol Bioeng 21: 131–146
Hong H, Ladisch MR, Gong CS, Wankat PC, Tsao GT (1981) Combined product and substrate inhibition equations for cellobiase. Biotechnol Bioeng 23: 2779–2788
Ladisch MR, Gong CS, Tsao GT (1980) Cellobiose hydrolysis by endoglucanase (glucan glucanohydrolase) from Trichodermareesei: Kinetics and mechanism. Biotechnol Bioeng 22: 1107–1126
Langmuir I (1961) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Am Chem Soc 38: 2221–2295
Lee SB, Shin HS, Ryu DDY, Mandels M (1982) Adsorption of cellulase on cellulose: effect of physicochemical properties of cellulose on adsorption and rate of hydrolysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 24: 2137–2153
Mandels J, Andreotti R (1976) Measurement of saccharofying cellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 6: 21–33
Mandels M, Sternberg D, Andreotti RE (1975) Growth and cellulase production by Trichoderma. Sitra 81: 81–109
Moreira AR, Phillips JA, Humphrey AE (1981) Utilization of carbohydrates by Thermomonospora sp grown on glucose, cellobiose and cellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng 23: 1325–1338
Nelson N (1944) A photometric adaptation of the somogy method for the determination of glucose. J Biol Chem 153: 375–380
Pörtner K (1982) Untersuchungen des enzymatischen Celluloseabbaus mit mathematischen Modellen. Diplomarbeit, Universität Hannover: hierauf verwiesen in Scheiding (1983)
Ross A (1982) Die Produktion von Cellulasen mit Trichoderma reesei. Dissertation, Universität Hannover
Ross A, Schügerl K, Scheiding W (1983) Cellulase production by Trichoderma reesei. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 18: 29–37
Scheiding W (1983) Modelltechnische Untersuchungen zur enzymatischen Hydrolyse von Cellulose. Dissertation, Universität Hannover
Tagnu SK, Blanch HW, Wilke CR (1981) Enhances production of cellulase, hemicellulase and β-glucosidase by Trichoderma reesei (Rut C-30). Biotechnol Bioeng 23: 1837–1849
Thoma M (1973) Theorie linearer Systeme. In: Pestel (Hrsg) Theorie geregelter Systeme, Viehweg, Braunschweig
Wood TM (1968) Cellulolytic enzyme system of Trichoderma koningii, Biochem J 104: 217–227
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheiding, W., Thoma, M., Ross, A. et al. Modelling of the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellobiose and cellulose by a complex enzyme mixture of Trichoderma reesei QM 9414. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 20, 176–182 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253727
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253727