Abstract
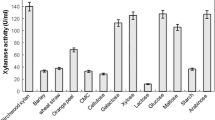
Thermophilic, aerobic bacteria isolated from Icelandic hot springs were screened for xylanase activity. Of 97 strains tested, 14 were found to be xylanase positive. Xylanase activities up to 12 nkat/ml were produced by these strains in shake flasks on xylan medium. The xylanases of the two strains producing the highest activities (ITI 36 and ITI 283) were similar with respect to temperature and pH optima (80°C and pH 8.0). Xylanase production of strain ITI 36 was found to be induced by xylan and xylose. Xylanase activity of 24 nkat/ml was obtained with this strain in a laboratory-scale-fermentor cultivation on xylose medium. β-Xylosidase activity was also detected in the culture filtrate. The thermal half-life of ITI 36 xylanase was 24 h at 70°C. The highest production of sugars from hydrolysis of beech xylan was obtained at 70°C, although xylan depolymerization was detected even up to 90°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey MJ, Poutanen K (1989) Production of xylanolytic enzymes by strains of Aspergillus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 30:5–10
Bailey MJ, Biely P, Poutanen K (1992) Interlaboratory testing of methods for assay of xylanase activity. J Biotechnol 23:257–270
Berenger J-F, Frixon C, Bigliardi J, Creuzet N (1985) Production, purification and properties of thermostable xylanase of Clostridium stercorarium. Can J Microbiol 31:635–643
Bragger JM, Daniel RM, Coolbear T, Morgan HW (1989) Very stable enzymes from extremely thermophilic archaebacteria and eubacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:556–561
Degryse E, Glansdorff N, Pierard A (1978) A comparative analysis of extreme thermophilic bacteria belonging to the genus Thermus. Arch Microbiol 117:189–196
Grüninger H, Fiechter A (1986) A novel, highly thermostable d-xylanase. Enzyme Microb Technol 8:309–314
IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) (1987) Measure of cellulase activities. Pure Appl Chem 59:257–268
Lenz J, Schurz J (1986) Neue Wege zur Verwertung von Hemicellulosen. Oesterr Chem Ztg 11:318–321
Lüthi E, Jasmat NB, Bergquist PL (1990) Xylanase from the extremely thermophilic bacterium Caldocellum saccharolyticum: overexpression of the gene in Escherichia coli and characterization of the gene product. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2677–2683
McCarthy AJ, Peace E, Broda P (1985) Studies on the extracellular xylanase activity of some thermophilic actinomycetes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 21:238–244
Nakanishi K, Yasui T (1980) Production of xylanase by Streptomyces sp. using non-metabolizable inducer. Agric Biol Chem 44:2729–2730
Paice MG, Jurasek L (1984) Removing hemicellulose from pulps by specific enzyme hydrolysis. J Wood Chem Technol 4:187–198
Poutanen K (1988) An α-l-arabinofuranoside of Trichoderma resei. J Biotechnol 7:271–282
Poutanen K, Puls J (1988) Characteristics of Trichoderma reesei β-xylosidase and its use in hydrolysis of solubilized xylans. Appl Microb Biotechnol 28:425–432
Poutanen K, Rättö M, Puls J, Viikari L (1987) Evaluation of different microbial xylanolytic systems. J Biotechnol 6:49–60
Ristroph DL, Humprey AH (1985) Kinetic characterization of extracellular xylanases of Thermomonospora sp. Biotechnol Bioeng 27:832–835
Summer JB, Somers GF (1949) Dinitrosalisylic method for glucose. In: Laboratory experiments for biological chemistry, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 38–39
Viikari L, Ranua M, Kantelinen A, Sundquist J, Linko M (1986) Bleaching with enzymes. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Biotechnology in the Pulp and Paper Industry, Stockholm, 16–19 June 1986. pp 66–69
Viikari L, Ranua M, Kantelinen A, Linko M, Sundquist J (1987) Application of enzymes in bleaching. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Congress on Wood and Pulping Chemistry, Paris, 27–30 April 1987, vol 1. pp 151–154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: M. Rättö
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perttula, M., Rättö, M., Kondradsdottir, M. et al. Xylanases of thermophilic bacteria from Icelandic hot springs. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 592–595 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182794
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182794