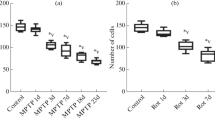
Abstract
The behavioral effects following intrastriatal MPP+, the neurotoxic metabolite of MPTP, were evaluated in mice. Bilateral injections of 10 ίcro;g MPP+ to mice previously trained in the shuttle box paradigm produced a 66% decrease in striatal dopamine and significant deficits in all measures of conditioned avoidance responding. In addition, although these mice showed no deficits in baseline rotorod performance, challenge with the cholinergic agonist oxotremorine revealed that MPP+-treated mice exhibited an increased sensitivity to the disruptive effects of the drug at each dose and time point. Finally, MPP+-treated mice also exhibited an increase in tremor induced by 0.1 and 0.15 mg/kg oxotremorine. These observations are discussed in reference to idiopathic parkinsonism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballard P, Tetrud J, Langston JW (1985) Permanent human parkinsonism due to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine(MPTP)-Seven cases. Neurology 35:949–956
Burns RS, Chiueh C, Markey S, Ebert M, Jacobowitz D, Kopin I (1983) A primate model of parkinsonism: Selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra by n-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4546–4550
Chiba K, Trevor A, Castagnoli N (1984) Metabolism of the neurotoxic tertiary amine, MPTP, by brain monoamine oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120 (2):574–578
Chiueh CC, Markey SP, Burns RS, Johannessen JN, Jacobowitz D, Kopin I (1983) I-N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine, a parkinsonian syndrome causing agent in man and monkey, produces different effects in guinea pig and rat. The Pharmacologist 25:131
Davis G, Williams A, Markey S, Ebert M, Caine E, Reichert C, Kopin I (1979) Chronic parkinsonism secondary to intravenous injection of meperidine analogues. Psychiatr Res 1:249–254
Duvoisin R (1967) Cholinergic-anticholinergic antagonism in parkinsonism. Arch Neurol 17:124–136
Heikkila R, Hess A, Duvoisin R (1984) Dopaminergic neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine in mice. Science 224:1451–1453
Izumi K, Nomoto M, Koja T, Shimuzu T, Kishita C, Fukuda T (1984) Phenytoin potentiates methamphetamine induced behavior in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:803–806
Jarvis MF, Wagner GC (1985) Neurochemical and functional consequences following 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and methamphetamine. Life Sci 36:249–254
Lang AE (1984) Treatment of Parkinson's disease with agents other than levodopa and dopamine agonists: Controversies and new approaches. Can J Neurol Sci 11:210–220
Langston JW (1985) MPTP Neurotoxicity: An overview and characterization of phases of toxicity. Life Sci 36:201–206
Langston JW, Ballard P, Tetrud JW, Irwin I (1983) Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219:979–980
Lenard LG, Beer B (1975) Relationship of brain levels of norepinephrine and dopamine to avoidance behavior in rats after intraventricular administration of 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 3:895–899
Lloyd KG, Davidson L, Hornykiewicz O (1975) The neurochemistry of Parkinson's disease: Effect of L-dopa. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 195:453–464
Neill DB, Boggan WO, Grossman SP (1974) Impairment of avoidance performance by intrastriatal administration of 6-hydroxydopamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:97–103
Seiden LS, Carlsson A (1963) Temporary and partial antagonism by L-dopa of reserpine induced suppression of a conditioned avoidance response. Psychopharmacologia 4:418–423
Wagner GC, Gardener I, Tsigas DJ, Masters DB (1984) Tolerance following the repeated administration of phencyclidine: No relation to central catecholamine depletion. Drug Alcohol Depend 13:225–234
Wagner GC, Jarvis MF, Rubin JG (1986) L-Dopa reverses the effects of MPP+ toxicity. Psychopharmacology 88:401–402
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, G.C., Walsh, S.L. Increased sensitivity of mice to tremorogenic agents following MPP+ . Psychopharmacology 92, 470–472 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176480
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176480