Abstract
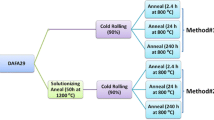
The micro- and nanostructure of 40Kh13 stainless steel is studied by optical, scanning electron, and atomic-force microscopy. The images of the steel’s structure and phase composition in three different states (after annealing, quenching, and high-temperature tempering) are compared. The optical images of the ferrite–pearlite structure with considerable content of (Cr, Fe)23C6 globular carbides obtained after annealing are compared with the results of scanning electron and atomic-force microscopy. It is found that the qualitative conclusions regarding the microstructure of the steel obtained by atomic-force and scanning electron microscopy not only agree with the results of optical microscopy but also provide greater detail. Data from the scanning electron microscope indicate that large carbides are located at the boundaries of ferrite grains. Some quantity of carbides may be found within the small ferrite grains. The size of the inclusions may be determined. The structure formed after quenching consists of coarse acicular martensite. Images from the atomic-force microscope show the acicular structure with greater clarity; three-dimensional images may be constructed. The undissolved carbides are also globular. The size of the martensite plates may be determined. The structure of the steel after high-temperature tempering (tempering sorbite) is formed as a result of the decomposition of martensite to ferrite–carbide mixture, with the deposition of regular rounded carbides. As confirmed by spectral analysis, the individual and row carbides (Cr, Fe)23C6 that appear contain chromium, which rapidly forms carbides. This structure is stronger than martensite. Data from uniaxial tensile tests are presented for all the states; the hardness HB is determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eksner, G.E., Quality and quantity surface microscopy, in Fizicheskoe metallovedenie (Physical Metallurgy), Kan, R.U. and Khaazen, P.T., Eds., Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1987, vol. 1, pp. 50–111.
Knechtel, H.E., Kindle, W.F., McCall, J.L., and Buchheit, R.D., Metallography, in Metallography. Tools and Techniques in Physical Metallurgy, Weinberg, F., Ed., New York: McGraw-Hill, 1970, vol. 1, pp. 329–400.
Binnig, G., Quate, C.F., and Gerber, Ch., Atomic force microscope, Phys. Rev. Lett., 1986, vol. 56, no. 9, pp. 930–933.
Mironov, V.L., Osnovy skaniruyushchei zondovoi mikroskopii (Principles of Scanning Probe Microscopy), Moscow: Tekhnosfera, 2004.
Lapshin, R.V., Feature-oriented scanning methodology for probe microscopy and nanotechnology, Nanotechnology, 2004, vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 1135–1151.
Zuev, L.B. and Shlyakhova, G.V., On possibilities of atomic force microscopy in metallography of carbon steels, Materialovedenie, 2014, no. 7, pp. 7–12.
Dobrotvorskii, A.M., Maslikova, E.I., Shevyakova, E.P., Ul’yanov, P.G., Usachev, D.Y., Senkovskiy, B.V., Adamchuk, V.K., Pushko, S.V., Mal’tsev, A.A., and Balizh, K.S., Metallographic study of construction materials with atomic force microscopy method, Inorg. Mater., 2014, vol. 50, no. 15, pp. 1487–1494.
Ulyanov, P.G., Usachov, D.Yu., Fedorov, A.V., Bondarenko, A.S., Senkovskiy, B.V., Vyvenko, O.F., Pushko, S.V., Balizh, K.S., Maltsev, A.A., Borygina, K.I., Dobrotvorskii, A.M., and Adamchuk, V.K., Microscopy of carbon steels: combined AFM and EBSD study, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, vol. 267, pp. 216–218.
Bykov, I.V., Methods of point-by-point relief measurements, action forces and local properties: new approach for complex analysis in atomic force microscopy, Nauch. Priborostr., 2009, no. 4 (19), pp. 38–43.
Danilov, V.I., Shlyakhova, G.V., and Semukhin, B.S., Plastic deformation macrolocalization. Local stress and fracture in ultrafine grain titanium, Appl. Mech. Mater., 2014, vol. 682, pp. 351–356.
Shlyakhova, G.V., Barannikova, S.A., and Zuev, L.B., Nanostructure of superconducting Nb–Ti cable, Steel Transl., 2013, vol. 43, no. 10, pp. 640–643.
Zuev, L.B., Shlyakhova, G.V., Barannikova, S.A., and Kolosov, S.V., Microstructure of the elements of a superconducting alloy Nb–Ti cable, Russ. Metall. (Engl. Transl.), 2013, vol. 2013, no. 3, pp. 229–234.
Afonin, V.K., Ermakov, B.S., Lebedev, E.L., et al., Metally i splavy: spravochnik (Metals and Alloys: Handbook), Solntsev, Yu.P., Ed., St. Petersburg: Professional, 2007.
Pelleg, J., Mechanical Properties of Materials, Dordrecht: Springer-Verlag, 2013.
Wiesendanger, R., Scanning Probe Microscopy and Spectroscopy. Methods and Applications, Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1994.
Beckert, M. and Klemm, H., Handbuch der Metallographischen Ätzverfahren, Leipzig: Dtsch. Verlag Grundstoffind., 1976.
Barannikova, S.A., Bochkareva, A.V., Lunev, A.G., Shlyakhova, G.V., and Zuev, L.B., Changes in ultrasound velocity in the plastic deformation of high-chromium steel, Steel Transl., 2016, vol. 46, no. 8, pp. 552–557.
Trefilov, V.I., Moiseev, V.F., and Pechkovskii, E.P., Deformatsionnoe uprochnenie i razrushenie polikristallicheskikh metallov (Mechanical Hardening and Destruction of Polycrystalline Metals), Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1989.
Metallografiya zheleza. Atlas stalei (Iron Metallography. Atlas of Steels), Tavadze, F.N., Ed., Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1972.
GOST (State Standard) 8233-56: Steel. Microstructure Standards, Moscow: Izd. Standartov, 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © G.V. Shlyakhova, A.V. Bochkareva, S.A. Barannikova, L.B. Zuev, E.V. Martusevich, 2017, published in Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Chernaya Metallurgiya, 2017, No. 2, pp. 133–139.
About this article
Cite this article
Shlyakhova, G.V., Bochkareva, A.V., Barannikova, S.A. et al. Microstructure of stainless steel after heat treatment: Data from atomic-force microscopy. Steel Transl. 47, 99–104 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091217020103
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0967091217020103