Abstract
Introduction
Paramphistomosis is a disease caused by the rumen flukes which cause an acute gastroenteritis and anemia with high mortality particularly in young ruminants.
Materials and methods
In this study, we have investigated the anthelmintic effect of medicinal plant extracts from leaves and heartwoods of Cassia siamea L., roots of Plumbago zeylanica L. and Plumbago indica L., and leaves of Terminalia catappa L. against Carmyerius spatiosus.
Results
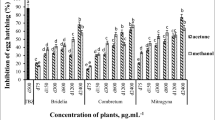
The highest anthelminthic effect on the flukes after 24 h of exposure was found in heartwood ethyl acetate extract of C. siamea (LC50 = 374.30; LC90 = 749.03 ppm), root n-butanol extract of P. zeylanica (LC50 = 1005.12; LC90 = 2411.55 ppm), root hexane, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol extract of P. indica (LC50 = 34.38, 211.34, 506.92; LC90 = 64.09, 496.05, 934.86 ppm), and leaf n-butanol and water extract of T. catappa (LC50 = 487.17, 470.28; LC90 = 913.27, 848.23 ppm). When observed by scanning electron microscopy, the tegument showed similar sequence of morphological changes after treatments with all plant extracts, comprising of swelling of ridges and folds, blebbing, rupturing of the blebs, erosion, lesion and disruption of the tegument.
Conclusion
This study is the first report on the anthelmintic activity of plant extracts to C. spatiosus; therefore, these plant extracts are highly effective in the elimination of adult rumen flukes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal R, Kaur K, Suri M, Bagai U (2016) Anthelmintic potential of Calotropis procera, Azadirachta indica and Punica granatum against Gastrothylax indicus. J Parasit Dis 40:1230–1238
Ahluwalia SS (1960) Gastrodiscoides hominis (Lewis and McConnell, 1876) Leiper, 1913-the amphistome parasite of man and pig. Indian J Med Res 48:315–325
Ajaiyeoba EO, Ashidi JS, Okpako LC, Houghton PJ, Wright CW (2008) Antiplasmodial compounds from Cassia siamea stem Bark extract. Phytother Res 22:254–255
Anuracpreeda P, Wanichanon C, Sobhon P (2008) Paramphistomum cervi: antigenic profile of adults as recognized by infected cattle sera. Exp Parasitol 118:203–207
Anuracpreeda P, Panyarachun B, Ngamniyom A, Tinikul Y, Chotwiwatthanakun C, Poljaroen J, Sobhon P (2012) Fischoederius cobboldi: a scanning electron microscopy investigation of surface morphology of adult rumen fluke. Exp Parasitol 130:400–407
Anuracpreeda P, Poljaroen J, Chotwiwatthanakun C, Tinikul Y, Sobhon P (2013) Antigenic components, isolation and partial characterization of excretion-secretion fraction of Paramphistomum cervi. Exp Parasitol 133:327–333
Anuracpreeda P, Phutong S, Ngamniyom A, Panyarachun B, Sobhon P (2015) Surface topography and ultrastructural architecture of the tegument of adult Carmyerius spatiosus Brandes, 1898. Acta Trop 143:18–28
Anuracpreeda P, Chawengkirttikul R, Sobhon P (2016) Antigenic profile, isolation and characterization of whole body extract of Paramphistomum gracile. Parasite Immunol 38:431–438
Anuracpreeda P, Chawengkirttikul R, Sobhon P (2016) Surface histology, topography, and ultrastructure of the tegument of adult Orthocoelium parvipapillatum (Stiles & Goldberger, 1910). Parasitol Res 115:2757–2769
Anuracpreeda P, Chankaew K, Puttarak P, Koedrith P, Chawengkirttikul R, Panyarachun B, Ngamniyom A, Chanchai S, Sobhon P (2016) The anthelmintic effects of the ethanol extract of Terminalia catappa L. leaves against the ruminant gut parasite, Fischoederius cobboldi. Parasitology 143:421–433
Anuracpreeda P, Chawengkirtikul R, Ngamniyom A, Panyarachun B, Puttarak P, Koedrith P, Intaratat N (2017) The in vitro anthelmintic activity of the ethanol leaf extracts of Terminalia catappa L. on Fasciola gigantica. Parasitology 144:1931–1942
Athanasiadou S, Githiori J, Kyriazakis I (2007) Medicinal plants for helminth parasite control: facts and fiction. Animal 1:1392–1400
Chen PS, Li JH, Liu TY, Lin TC (2000) Folk medicine Terminalia catappa and its major tannin component, punicalagin, are effective against bleomycin-induced genotoxicity in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Lett 152:115–122
Chen PS, Li JH (2005) Chemopreventive effect of punicalagin, a novel tannin component isolated from Terminalia catappa, on H-ras-transformed NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol Lett 163:44–53
Chin HF, Enoch IC (1988) Malaysian trees in colour. Tropical Press Sdn. Bhd, Kuala
Chu SC, Yang SF, Liu SJ, Kuo WH, Chang YZ, Hsieh YS (2007) In vitro and in vivo antimetastatic effects of Terminalia catappa L. Leaves on lung cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol 45:1194–1201
Corner EJH (1988) Wayside trees of malaysia, vol. 1, 3rd Edn. Malayan Nature Society, Kuala Lumpur, pp. 476
Dutt SC, Srivastava HD (1972) The life history of Gastrodiscoides hominis (Lewis and McConnel, 1876) Leiper, 1913, the amphistome parasite of man and pig. J Helminthol 46:35–46
Elango G, Rahuman AA (2011) Evaluation of medicinal plant extracts against ticks and fluke. Parasitol Res 108:513–519
Fan YM, Xu LZ, Gao J, Wang Y, Tang XH, Zhao XN, Zhang ZX (2004) Phytochemical and antiinflammatory studies on Terminalia catappa. Fitoterapia 75:253–260
Finney DJ, Stevens WL (1948) A table for the calculation of working probits and weights in probit analysis. Biometrika 35:191–201
Fyhrquist P, Mwasumbi L, Haeggström CA, Vuorela H, Hiltunen R, Vuorela P (2002) Ethnobotanical and antimicrobial investigation on some species of Terminalia and Combretum (Combretaceae) growing in Tanzania. J Ethnopharmacol 79:169–177
Geary TG, Chibale K, Abegaz B, Andrae-Marobela K, Ubalijoro E (2012) A new approach for anthelminthic discovery for human. Trends Parasitol 28:176–181
Gupta PP, Singh B, Dutt SC (1978) A note on amphistomiasis in an adult buffalo. Indian Vet J 55:491–492
Hanna REB, Williamson DS, Mattison RG, Nizami WA (1988) Seasonal reproduction in Paramphistomum epiclitum and Gastrothylax crumenifer, rumen paramphistomes of the indian water buffalo, and comparison with the biliary paramphistome Gigantocotyle explanatum. Int J Parasitol 18:513–521
Harinasuta T, Bunnag D, Radomyos P (1987) Intestinal fluke infections. Baillieres Clin Trop Med Commun Dis 2:695–721
Hossain E, Chandra G, Nandy AP, Mandal SC, Gupta JK (2012) Anthelmintic effect of a methanol extract of Bombax malabaricum leaves on Paramphistomum explanatum. Parasitol Res 110:1097–1102
Ilha MR, Loretti AP, Reis AC (2005) Wasting and mortality in beef cattle parasitized by Eurytrema coelamaticum in the state of Parana, southern Brazil. Vet Parasitol 133:49–60
Jeyachandran R, Mahesh A, Cindrella L, Sudhakar S, Pazhanichamy K (2009) Antibacterial activity of plumbagin and root extracts of Plumbago Zeylanica L. Acta Biol Crac Ser Bot 51:17–22
Jiangsu (1979) Zhongyao dictionary (Encyclopedia of Chinese materia medica). Shanghai Scientific & Technological Press, Shanghai. pp. 711–712
Kamagaté M, Koffi C, Kouamé NM, Akoubet A, Yao NAR, Die-Kakou HM (2014) Ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology profiles of Cassia siamea Lam. J Phytopharmacol 3:57–76
Kamaraj C, Rahuman AA, Bagavan A, Elango G, Rajakumar G, Zahir AA, Marimuthu S, Santhoshkumar, Jayaseelan C (2010) Evaluation of medicinal plant extracts against blood-sucking parasites. Parasitol Res 106:1403–1422
Katiki LM, Gomes ACP, Barbieri AME, Pacheco PA, Rodrigues L, Veríssimo CJ, Gutmanis G, Piza AM, Louvandini H, Ferreira JFS (2017) Terminalia catappa: chemical composition, in vitro and in vivo effects on Haemonchus contortus. Vet Parasitol 246:118–123
Keiser J, Morson G (2008) Fasciola hepatica: tegumental alterations in adult flukes following in vitro and in vivo administration of artesunate and artemether. Exp Parasitol 118:228–237
Khan UJ, Tanveer A, Maqbool A, Masood S (2008) Epidemiological studies of paramphistomosis in cattle. Veterinarski Arhiv 78:243–251
Kumar V (1980) The digenetic trematodes, Fasciolopsis buski, Gastrodiscoides hominis and Artyfechinostomum malayanum, as zoonotic infections in South Asian countries. Annales de la Société belge de médecine tropicale 60:331–339
Lin CC, Chen YL, Lin JM, Ujiie T (1997) Evaluation of the antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of Terminalia catappa. Am J Chin Med 25:153–161
Lin CC, Hsu YF, Lin TC (1999) Effects of punicalagin and punicalin on carrageenan-induced inflammation in rats. Am J Chin Med 27:371–376
Lorsuwannarat N, Saowakon N, Ramasoota P, Wanichanon C, Sobhon P (2013) The anthelmintic effect of plumbagin on Schistosoma mansoni. Exp Parasitol 133:18–27 Lumpur, Malaysia, pp. 180
Lorsuwannarat N, Piedrafita D, Chantree P, Sansri V, Songkoomkrong S, Bantuchai S, Sangpairot K, Kueakhai P, Changklungmoa N, Chaichanasak P, Chansela P, Sobhon P (2014) The in vitro anthelmintic effects of plumbagin on newly excysted and 4-weeks-old juvenile parasites of Fasciola gigantica. Exp Parasitol 136:5–13
Magalhes LG, Kapadia GJ, da Silva Tonuci LR, Caixeta SC, Parreira NA, Rodrigues V, Da Silva Filho AA (2010) In vitro schistosomicidal effects of some phloroglucinol derivatives from Dryopteris species against Schistosoma mansoni adult worms. Parasitol Res 56:395–401
Masuda T, Yonemori S, Oyama Y, Takeda Y, Tanaka T, Andoh T, Shinohara A, Nakata M (1999) Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of environmental plants: activity of the leaf extracts from seashore plants. J Agric Food Chem 47:1749–1754
Mininel FJ, Leonardo Junior CS, Espanha LG, Resende FA, Varanda EA, Leite CQ, Vilegas W, Dos Santos LC (2014) Characterization and quantification of compounds in the hydroalcoholic extract of the leaves from Terminalia catappa Linn. (Combretaceae) and their mutagenic activity. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 2014:1–11
Mishra BB, Gour JK, Kishore N, Singh RK, Tripathi V, Tiwari VK (2013) An antileishmanial prenyloxy-naphthoquinone from roots of Plumbago zeylanica. Nat Prod Res 27:480–485
Morita H, Oshimi S, Hirasawa Y, Koyama K, Honda T, Ekasari W, Indrayanto, Zaini NC (2007) Cassiarins A and B, novel antiplasmodial alkaloids from Cassia siamea. Org Lett 9:3691–3693
Nagappa AN, Thakurdesai PA, Venkat Rao N, Singh J (2003) Antidiabetic activity of Terminalia catappa Linn fruits. J Ethnopharmacol 88:45–50
Nikitin VF (1979) The course of acute enzootic amphistomiasis in claves in the lower Volga region. Helminthol Abstr Ser A 48:463
Pandya NB, Tigari P, Dupadahalli K, Kamurthy H, Nadendla RR (2013) Antitumor and antioxidant status of Terminalia catappa against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma in Swiss albino mice. Indian J Pharmacol 45:464–469
Panyarachun B, Sobhon P, Yotsawan T, Chotwiwatthanakun C, Anupunpisit V, Anuracpreeda P (2010) Paramphistomum cervi: surface topography of thetegument of adult fluke. Exp Parasitol 125:95–99
Panyarachun B, Ngamniyom A, Sobhon P, Anuracpreeda P (2013) Morphology and histology of the adult Paramphistomum gracile Fischoeder, 1901. J Vet Sci 14:425–432
Phiri IK, Phiri AM, Ziela M, Chota A, Masuku M, Monrad J (2007) Prevalence and distribution of gastrointestinal helminths and their effects on weight gain in free-range chickens in Central Zambia. Trop Anim Health Prod 39:309–315
Prasitirat P, Nithiuthai S, Ruengsuk K, Kitwan P, Bunmatid C, Roopan S, Itagaki H (1997) Efficacy of bithionol sulfoxide, niclosamide and fenbendazole against natural rumen fluke infection in cattle. Helminthologia 34:155–157
Ratnasooriya WD, Dharmasiri MG (2000) Effects of Terminalia catappa seeds on sexual behaviour and fertility of male rats. Asian J Androl 2:213–219
Robinson RD, Williams LAD, Linda JF, Terzy SI, Mansingh A (1990) Inactivation of Strongyloides stercoralis larvae in vitro by six Jamaican plant extracts and three commercial anthelmintics. West Indian Med J 39:213–217
Rolfe PE, Boray JC, Nichols P, Collins GH (1991) Epidemiology of paramphistomosis in cattle. Aust Vet J 21:813–819
Rolfe PF, Boray JC (1988) Chemotherapy of paramphistomosis in sheep. Aust Vet J 65:148–150
Saowakon N, Tansatit T, Wanichanon C, Chanakul W, Reutrakul V, Sobhon P (2009) Fasciola gigantica: anthelmintic effect of the aqueous extract of Artocarpus lakoocha. Exp Parasitol 122:289–298
Saowakon N, Lorsuwannarat N, Changklungmoa N, Wanichanon C, Sobhon P (2013) Paramphistomum cervi: the in vitro effect of plumbagin on motility, survival and tegument structure. Exp Parasitol 133:179–186
Sundaramoorthy S, Gunasekaran S, Arunachalam S, Sathiavelu M (2016) A phytopharmacological review on Cassia species. J Pharm Sci Res 8:260–264
Tandon V, Pal P, Roy B, Rao HSP, Reddy KS (1997) In vitro anthelmintic activity of root-tuber extract of Flemingia vestita, an indigenous plant in Shillong, India. Parasitol Res 83:492–498
Tang X, Gao J, Wang Y, Fan YM, Xu LZ, Zhao XN, Xu Q, Qian ZM (2006) Effective protection of Terminalia catappa L. leaves from damage induced by carbon tetrachloride in liver mitochondria. J Nutr Biochem 17:177–178
Thomson, L.A.J. and Evans, B. (2006). Terminalia catappa (tropical almond), 2.2. In: Elevitch, C.R. (Ed.). Species profiles for pacific Island agroflorestry: permanent agriculture resources (PAR), 2006
Wongsawad C, Wongsawad P, Luangphai P, Kumchoo K (2005) In vitro effects of aqueous extract from Artocarpus takoocha Roxb on tegumental surface of Haplorchis taichui. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 36(Suppl. 4):112–116
Yeh CB, Hsieh MJ, Hsieh YS, Chien MH, Lin PY, Chiou HL, Yang SF (2012) Terminalia catappa exerts antimetastatic effects on hepatocellular carcinoma through transcriptional inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 by modulating NF-κB and AP-1 activity. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med 2012:1–11
Zahir AA, Rahuman AA, Bagavan A, Geetha K, Kamaraj C, Elango G (2012) Evaluation of medicinal plant extracts and isolated compound epicatechin from Ricinus communis against Paramphistomum cervi. Parasitol Res 111:1629–1635
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Research Grants from Agricultural Research Development Agency (ARDA), National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT) and TRF Research Career Development Grant co-funded by The Thailand Research Fund and Mahidol University (RSA6080071) to Panat Anuracpreeda.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minsakorn, S., Nuplod, K., Puttarak, P. et al. The Anthelmintic Effects of Medicinal Plant Extracts Against Paramphistome Parasites, Carmyerius spatiosus. Acta Parasit. 64, 566–574 (2019). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-019-00072-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-019-00072-6