Abstract
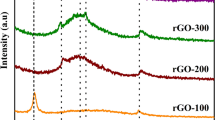
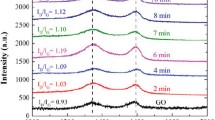
Among various methods used for the reduction of graphene oxide (GO) into a purer form of graphene, the thermal reduction method provides a simpler, safer, and economic alternative, compared to other techniques. Thermal reduction of GO causes significant weight loss and volume expansion of the material. Current work investigates the onset temperature where reduction in terms of exfoliation takes place, which is determined to be 325 °C at standard atmospheric pressure. Reduction temperature plays the most crucial role as it controls the quality of reduced graphene oxide in terms of weight percentage of carbon and lattice defect. The study leads to achieving highest content with a minimum defect in the graphene lattice at the optimum temperature, which is found to be 350 °C at standard atmospheric pressure. The thermal reduction process has been analyzed with the help of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and thermal degradation kinetics. From thermal degradation kinetics of GO, the rate of reaction has been found to be independent of concentration and is a sole function of temperature.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.K. Geim and K.S. Novoselov: The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6, 183 (2007).
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S.V. Dubonos, I.V. Grigorieva, and A.A. Firsov: Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306, 666 (2004).
C. Berger, X. Wu, N. Brown, C. Naud, X. Li, Z. Song, D. Mayou, T. Li, J. Hass, A. Marchenkov, E.H. Conrad, P.N. First, and W.A. De Heer: Electronic confinement and coheraence in patterned epitaxial graphene. Science 312, 1191 (2006).
R.B. Patel, C. Yu, T. Chou, and Z. Iqbal: Novel synthesis route to graphene using iron nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. 29, 1522 (2014).
A. Lerf, H. He, M. Forster, and J. Klinowski: Structure of graphite oxide revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 4477 (1998).
A. Bagri, C. Mattevi, M. Acik, Y.J. Chabal, M. Chhowalla, and V.B. Shenoy: Structural evolution during the reduction of chemically derived graphene oxide. Nat. Chem. 2, 581 (2010).
T. Szabó, O. Berkesi, P. Forgó, K. Josepovits, Y. Sanakis, D. Petridis, and I. Dékány: Evolution of surface functional groups in a series of progressively oxidized graphite oxides evolution of surface functional groups in a series of progressively oxidized graphite oxides. Chem. Mater. 18, 2740 (2006).
B.C. Brodie: On the atomic weight of graphite. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London 149, 249 (1859).
L. Staudenmaier: Procedure for the preparation of graphitic acid. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 32, 1394 (1899).
W.S. Hummers and R.E. Offeman: Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80, 1339 (1958).
D.C. Marcano, D.V. Kosynkin, J.M. Berlin, A. Sinitskii, Z. Sun, A. Slesarev, L.B. Alemany, W. Lu, and J.M. Tour: Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 4, 4806 (2010).
H. Yu, B. Zhang, C. Bulin, R. Li, and R. Xing: High-efficient synthesis of graphene oxide based on improved hummers method. Sci. Rep. 6, 36143 (2016).
Y. Si and E.T. Samulski: Synthesis of water soluble graphene. Nano Lett 8, 1679 (2008).
J. Lu, J. Yang, J. Wang, A. Lim, S. Wang, and K.P. Loh: One-pot synthesis of fluorescent carbon graphene by the exfoliation of graphite in ionic liquids. ACS Nano 3, 2367 (2009).
W. Chen, L. Yan, and P.R. Bangal: Preparation of graphene by the rapid and mild thermal reduction of graphene oxide induced by microwaves. Carbon 48, 1146 (2010).
Y. Zhu, S. Murali, M.D. Stoller, A. Velamakanni, R.D. Piner, and R.S. Ruoff: Microwave assisted exfoliation and reduction of graphite oxide for ultracapacitors. Carbon 48, 2118 (2010).
Y.M. Shulga, S.A. Baskakov, E.I. Knerelman, G.I. Davidova, E.R. Badamshina, N.Y. Shulga, E.A. Skryleva, A.L. Agapov, D.N. Voylov, A.P. Sokolov, and V.M. Martynenko: Carbon nanomaterial produced by microwave exfoliation of graphite oxide: New insights. RSC Adv. 4, 587 (2014).
I. Jung, D.A. Dikin, R.D. Piner, and R.S. Ruoff: Tunable electrical conductivity of individual graphene oxide sheets reduced at “low” temperatures. Nano Lett. 8, 4283 (2008).
S. Pei and H.M. Cheng: The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon 50, 3210 (2012).
R. Larciprete, S. Fabris, T. Sun, P. Lacovig, A. Baraldi, and S. Lizzit: Dual path mechanism in the thermal reduction of graphene oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 17315 (2011).
H-K. Jeong, Y.P. Lee, M.H. Jin, E.S. Kim, J.J. Bae, and Y.H. Lee: Thermal stability of graphite oxide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 470, 255 (2009).
S. Xu, Z. Zhang, J. Liu, Y. Wang, and J. Hu: Facile preparation of reduced graphene by optimizing oxidation condition and further reducing the exfoliated products. J. Mater. Res. 32, 383 (2017).
D. Yang, A. Velamakanni, G. Bozoklu, S. Park, M. Stoller, R.D. Piner, S. Stankovich, I. Jung, D.A. Field, C.A. Ventrice, and R.S. Ruoff: Chemical analysis of graphene oxide films after heat and chemical treatments by X-ray photoelectron and micro-Raman spectroscopy. Carbon 47, 145 (2009).
C. Mattevi, G. Eda, S. Agnoli, S. Miller, K.A. Mkhoyan, O. Celik, D. Mastrogiovanni, G. Granozzi, E. Carfunkel, and M. Chhowalla: Evolution of electrical, chemical, and structural properties of transparent and conducting chemically derived graphene thin films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 2577 (2009).
M.C. Kim, G.S. Hwang, and R.S. Ruoff: Epoxide reduction with hydrazine on graphene: A first principles study. J. Chem. Phys. 131, 1 (2009).
X. Gao, J. Jang, and S. Nagase: Hydrazine and thermal reduction of graphene oxide: Reaction mechanisms and design. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 832 (2010).
C.M. Chen, Q. Zhang, M.G. Yang, C.H. Huang, Y.G. Yang, and M.Z. Wang: Structural evolution during annealing of thermally reduced graphene nanosheets for application in supercapacitors. Carbon 50, 3572 (2012).
S. Mao, H. Pu, and J. Chen: Graphene oxide and its reduction: Modeling and experimental progress. RSC Adv. 2, 2643 (2012).
H.C. Schniepp, J.L. Li, M.J. McAllister, H. Sai, M. Herrera-Alonson, D.H. Adamson, R.K. Prud’homme, R. Car, D.A. Seville, and I.A. Aksay: Functionalized single graphene sheets derived from splitting graphite oxide. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 8535 (2006).
G. Wang, J. Yang, J. Park, X. Gou, B. Wang, H. Liu, and J. Yao: Facile synthesis and characterization of graphene nanosheets. J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 8192 (2008).
R. Simões and V. Neto: Graphene oxide nanocomposites for potential wearable solar cells—A review. J. Mater. Res. 31, 1633 (2016).
A. Jorio, E.H.M. Ferreira, M.V.O. Moutinho, F. Stavale, C.A. Achete, and R.B. Capaz: Measuring disorder in graphene with the G and D bands. Phys. Status Solidi B 247, 2980 (2010).
Y. Hu: A simple reduction route to carbon hollow spheres. Indian J. Chem. 44, 2259 (2005).
A.W. Coats and J.P. Redfern: Kinetic parameters from thermogravimetric data. Nature 201, 68 (1964).
S. Chakraborty, M. Kumar, K. Suresh, and G. Pugazhenthi: Investigation of structural, rheological and thermal properties of PMMA/ONi-Al LDH nanocomposites synthesized via solvent blending method: Effect of LDH loading. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 34, 739 (2016).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors express their gratitude to the DST-FIST funded XPS laboratory at the Department of Physics and Meteorology, IIT Kharagpur, for their help in conducting the XPS analysis. The authors also acknowledge FESEM and XRD laboratory and Departmental Research Facility at the Department of Chemical Engineering, IIT Kharagpur, for their co-operation in carrying out the experiments and analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sengupta, I., Chakraborty, S., Talukdar, M. et al. Thermal reduction of graphene oxide: How temperature influences purity. Journal of Materials Research 33, 4113–4122 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.338
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2018.338