Abstract
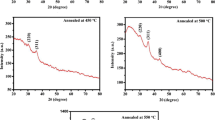
The effects of annealing temperatures on the structure and photocurrent response of nanoporous iron oxide film prepared by anodization of iron foil in an ethylene glycol, NH4F, and H2O electrolyte were studied. The as-anodized anodic film was found to be rather amorphous and crystallized to predominantly α-Fe2O3 upon annealing in nitrogen. Nitrogen was used as to reduce the thickening of the barrier layer which affects the photocurrent response of the oxide. However, annealing must be done above 300 °C to produce crystalline oxide but must be kept lower than 500 °C since high temperature promotes grain growth, destroying the nanoporous structure and also thickens the barrier layer, which significantly reduce the photocurrent of the film. Sample annealed at 450 °C in nitrogen has the highest photocurrent of 1.04 mA/cm2 (0.5 V versus Ag/AgCl in 1 M NaOH) compared to 0.13 mA/cm2 at 0.5 V for air-annealed sample.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Barroso, S.R. Pendlebury, A.J. Cowan, and J.R. Durrant: Charge carrier trapping, recombination and transfer in hematite (α-Fe2O3) water splitting photoanodes. Chem. Sci. 4, 2724–2734 (2013).
J.H. Kennedy and K.W. Frese: Photooxidation of water at α-Fe2O3 electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 125, 709–714 (1978).
S. Shen: Toward efficient solar water splitting over hematite photoelectrodes. J. Mater. Res. 29(01), 29–46 (2014).
H. Nishikiori, W. Qian, M.A. El-Sayed, N. Tanaka, and T. Fujii: Change in titania structure from amorphousness to crystalline increasing photoinduced electron-transfer rate in dye-titania system. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 9008–9011 (2007).
N. Uekawa and K. Kaneko: Nonstoichiometric properties of nanoporous iron oxide films. J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 8719–8724 (1998).
S.P. Albu, A. Ghicov, and P. Schmuki: High aspect ratio, self-ordered iron oxide nanopores formed by anodization of Fe in ethylene glycol/NH4F electrolytes. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 3, 64–66 (2009).
H. Habazaki, Y. Konno, Y. Aoki, P. Skeldon, and G.E. Thompson: Galvanostatic growth of nanoporous anodic films on iron in ammonium flouride-ethylene glycol electrolytes with different water contents. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 18853–18859 (2010).
A. Jagminas, K. Mazeika, N. Bernotas, V. Klimas, A. Selskis, and D. Baltrunas: Compositional and structural characterization of nanoporous produced by iron anodizing in ethylene glycol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 3893–3897 (2011).
Y. Konno, E. Tsuji, P. Skeldon, G.E. Thompson, and H. Habazaki: Factors influencing the growth behaviour of nanoporous anodic films on iron under galvanostatic anodizing. J. Solid State Electrochem. 16, 3887–3896 (2012).
H.E. Prakasam, O.K. Varghese, M. Paulose, G.K. Mor, and C.A. Grimes: Synthesis and photoelectrochemical properties of nanoporous iron (III) oxide by potentiostatic anodization. Nanotechnology 17, 4285–4291 (2006).
H. Cheng, L. Zheng, C.K. Tsang, J. Zhang, H.E. Wang, Y. Dong, H. Li, F. Liang, J.A. Zapien, and Y.Y. Li: Electrochemical fabrication and optical properties of periodically structured porous Fe2O3 films. Electrochem. Commun. 20, 178–181 (2012).
Z. Zhang, M.F. Hossain, and T. Takahashi: Fabrication of shape-controlled α-Fe2O3 nanostructures by sonoelectrochemical anodization for visible light photocatalytic application. Mater. Lett. 64, 435–438 (2010).
M. Rozana, M.A. Azhar, D.M. Anwar, G. Kawamura, A.R. Khairunisak, A. Matsuda, and Z. Lockman: Effect of applied voltage on the formation of self-organized iron oxide nanoporous film in organic electrolyte via anodic oxidation process and their photocurrent performance. Adv. Mater. Res. 1024, 99–103 (2014).
U. Schwertmann and R. Cornell: The Iron Oxides (Wiley-VCH GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinhem, 2003).
C.Y. Lee, L. Wang, Y. Kado, M.S. Killian, and P. Schmuki: Anodic nanotubular/porous hematite photoanode for solar water splitting: Substantial effect of iron substrate purity. ChemSusChem 7, 934–940 (2014).
M.I. Nagayama and M. Cohen: The anodic oxidation of iron in a neutral solution: I. The nature and composition of the passive film. J. Electrochem. Soc. 109, 781–790 (1962).
Z. Szklarska-Smialowska: Mechanism of pit nucleation by electrical breakdown of the passive film. Corros. Sci. 44, 1143–1149 (2002).
D. Regonini, C.R. Bowen, A. Jaroenworaluck, and R. Stevens: A review of growth mechanism, structure and crystallinity of anodized TiO2 nanotubes. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 74, 377–406 (2013).
P. Schmuki: From Bacon to barriers: A review on the passivity of metals and alloys. J. Solid State Electrochem. 6, 145–164 (2002).
K. Yasuda, J.M. Macak, S. Berger, A. Ghicov, and P. Schmuki: Mechanistic aspects of the self-organization process for oxide nanotube formation on valve metals. J. Electrochem. Soc. 154, C472–C478 (2007).
R.Y. Chen and W.Y.D. Yeun: Review of the high-temperature oxidation of iron and carbon steels in air or oxygen. Oxid. Met. 59, 433–468 (2003).
D. Bersani, P.P. Lottici, and A. Montenero: Micro-Raman investigation of iron oxide films and powders produced by sol–gel syntheses. J. Raman Spectrosc. 30, 355–360 (1999).
D.L.A. de Faria, S. Venâncio Silva, and M.T. de Oliveira: Raman microspectroscopy of some iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. J. Raman Spectrosc. 28, 873–878 (1997).
M. Hanesch: Raman spectroscopy of iron oxides and (oxy)hydroxides at low laser power and possible applications in environmental magnetic studies. Geophys. J. Int. 177, 941–948 (2009).
M.K. Nieuwoudt, J.D. Comins, and I. Cukrowski: The growth of the passive film on iron in 0.05 M NaOH studied in situ by Raman micro-spectroscopy and electrochemical polarisation. Part I: Near-resonance enhancement of the Raman spectra of iron oxide and oxyhydroxide compounds. J. Raman Spectrosc. 42, 1335–1339 (2011).
S. Oh, D.C. Cook, and H.E. Townsend: Characterization of iron oxides commonly formed as corrosion products on steel. Hyperfine Interact. 112, 59–66 (1998).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful for support by the ASEAN University Network/Southeast Asia Engineering Education Development Network (AUN/SEED-Net), Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). Nanomaterials development is supported by OneBAJA Long Term Research Grant Scheme (LRGS), Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia, Project 2, 304/PBAHAN/6050235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rozana, M., Razak, K.A., Yew, C.K. et al. Annealing temperature-dependent crystallinity and photocurrent response of anodic nanoporous iron oxide film. Journal of Materials Research 31, 1681–1690 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.206
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.206