Abstract
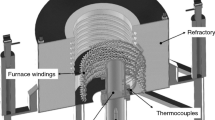
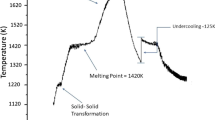
The Sn-Zn system has a eutectic structure of a broken lamellar type. Dependence of the broken-lamellar spacing λ and the undercooling ΔT on V and G were investigated, and the relationship between them was examined. A Sn-Zn (99.99%) high-purity eutectic alloy was melted in a graphite crucible under vacuum atmosphere. This eutectic alloy was directionally solidified upward with a constant growth rate V (8.30 µm/s) and different temperature gradients G (1.86–6.52 K/mm), and also with a constant temperature gradient (6.52 K/mm) and different growth rates (8.30–165.13 µm/s) in a Bridgman-type directional solidification furnace. The lamellar spacings λ were measured from both transverse and longitudinal sections of the specimen. The λ values from the transverse section were used for calculations and comparisons with the previous works. The undercooling values ΔT were obtained using growth rate and system parameters K 1 and K 2. It was found that the values of λ decreased while V and G increased. The relationships between lamellar spacing λ and solidification parameters V and G were obtained by linear regression analysis method. The λ2 V, ΔTλ, ΔTV −5, and λ3 G values were determined using λ, ΔT, V, and G values. The experimentally obtained values for the broken-lamellar growth (Sn-Zn eutectic system) were in good agreement with the theoretical and other experimental values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.W. Kraft and D.L.A. Albright: “Microstructure of Unidirectionally Solidified Al-CuAl2 Eutectic,” Trans. Met. Soc. AIME, 1961, 221, pp. 95–102.
H.E. Cline: Metall. Trans., 1971, 2, p. 189.
E.R. Thompson and F.D. Lemkey: Trans ASM, 1969, 62, p. 140.
M.F.X. Gigliotti, R. Melvin, F. Michael, A.David, S. Sherwin, and A. Charles: “Transverse Ductile Fiber Reinforced Eutectic Nickel-Base Superalloys,” U.S. Patent No. 4 292 076, 1981.
R. Caram and S. Milenkovic: “Microstructure of Ni-Ni3Si Eutectic Alloy Produced by Directional Solidification,” J. Cryst. Growth, 1999, 198/199, pp. 844–49.
F.S. Galasso: J. Metals, 1967, 19, p. 17.
M.N. Crocker, D. Baragar, and R.W. Smith: “Anamolous Eutectic Growth,” J. Cryst. Growth, 1975, 30, pp. 198–212.
R. Elliot, Eutectic Solidification Processings, Butterworths, London, UK, 1983, p. 136.
J.M. Liu, Z.G. Liu, and Z.C. Wu: “Spacing Selection for an Sn-Pb Lamellar Eutectic During Directional Solidified,” Mater. Sci. Eng. 1993, A167, p. 87.
M.R. Aguiar and R. Caram: “Directional Solidified of a Sn-Se Eutectic Alloy Using the Bridgman-Stockbarer Method,” J. Cryst. Growth, 1996, 166, pp. 398–401.
K.A. Jackson and J.D. Hunt: “Lamellar and Eutectic Growth,” Trans. Met. Soc. AIME, 1966, 236, pp. 1129–42.
J.M. Liu: “Dynamics of Spacing Selection of a Lamellar Eutectic During Directional Solidification,” Mater. Sci. Eng., 1992, A157, pp. 73–78.
H.E. Cline: “Strengthening of Lamellar vs Equiaxed Ag-Cu Eutectic,” Acta Metall., 1972, 18, pp. 315–23.
R.M. Jordan and J.D. Hunt: “The Growth of Lamellar Eutectic Structures in the Pb-Sn and Al-CuAl2 Systems,” Metall. Trans., 1971, 2, pp. 3401–10.
T. Sato and Y. Sayama: “Completely and Partially Co-operative Growth of Eutectic,” J. Cryst. Growth, 1974, 22, pp. 259–71.
G.E. Nash: “A Self Consistent Theory of Steady State Lamellar Solidification in Binary Eutectic Systems,” J. Cryst. Growth, 1977, 38, pp. 155–80.
H.E. Cline: “Growth of Eutectic Alloy, Tin Films,” J. Appl. Phys., 1979, 50, p. 4780; Mater. Sci. Eng. 1984, 65, pp. 93–100.
J.S. Langer: “Eutectic Solidification,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 1980, 44, p. 1023.
V. Dayte and J.S. Langer: “Stability of Thin Lamellar Eutectic Growth,” Phys. Rev. B, 1981, 24, p. 4155.
D.A. Kessler and H. Levine: “Computational Approach to Steady State Eutectic Growth,” J. Cryst. Growth, 1989, 94, p. 871.
A. Karma: “Wavelength Selection in Directional,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 1986, 57, p. 858.
A. Karma and P. Pelce: “Oscillatory of Deer Cels in Directional Solidification,” Phys. Rev. A, 1989, 39, p. 4162.
C. Zener: Trans. AIME, 1946, 167, p. 550.
V. Seetharaman and R. Trivedi: “Eutectic Growth,” Metall. Trans., 1988, 19A, pp. 2955–64.
R. Trivedi, J.T. Mason, J.D. Verhoeven, and W. Kurz: “Eutectic Spacing Selection in Lead-Based Alloy Systems,” Metall. Trans., 1991, 22A, pp. 2523–33.
H. Müller-Kurumbhaar and W. Kurz: in Material Science and Technology: A Comprehensive Treatment, Vol. 5, R.W. Chan, P. Haasen, and E.J. Kramer, ed., VCH, New York, 1991, p. 554.
R. Elliot: “Eutectic Solidification,” Mater. Sci. Eng., 1984, 65, pp. 85–92.
S.C. Gill and W. Kurz: “Rapid Solidification Al-Cu Alloys—I. Experiment Determination of the Microstructure Selection MAP,” Acta Metall., 1993, 41(12), pp. 3563–73.
A. Ourdjini, J. Liu, and R. Elliott: “Eutectic Spacing Selection in the Al-Cu System,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 1994, 10, pp. 312–18.
K.B. Kim, J. Liu, N. Maraşlı, and J.D. Hunt: “The Effect of Different Atomic Volumes in the Three Phases. During Lamellar Eutectic Growth. A Comparison of Experiment and Theory in the Al-Al2Cu System,” Acta Metall., 1995, 43(6), pp. 2143–47.
M. Tassa and J.D. Hunt: “The Measurement of Al-Cu Dendrite Tip and Eutectic Interface Temperatures and Their Use for Predicting the Extent of the Eutectic Range,” J. Cryst. Growth, 1976, 34, pp. 38–48.
E. Çadırlı and M. Gündüz: “The Dependence of Lamellar Spacing on Growth Rate and Temperature Gradient in the Lead-Tin Eutectic Alloy,” J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, 97, pp. 74–81.
E. Çadırlı, A. Ülgen, and M. Gündüz: “Directional Solidification of the Aluminium-Copper Eutectic Alloy,” Mater. Trans. JIM, 1999, 40(9), pp. 989–96.
H. Jones and W. Kurz: “Ration of Interphase Spacings and Growth Temperature to Growth Velocity in Fe-C and Fe-Fe3 Eutectic Alloys,” Z. Metalkd., 1981, 72, pp. 792–97.
P. Magnin, J.T. Mason, and R. Trivedi: “Growth of Irregular Eutectics and the Al-Si System,” Acta Metall. Mater., 1991, 39, pp. 469–80.
Y.X. Zhuang, X.M. Zhang, L.H. Zhu, and Z.Q. Hu: “Eutectic Spacing and Faults of Directionally Solidified Al-Al3Ni Eutectic,” Sci. and Tech. Adv. Mater., 2001, 2, pp. 37–39.
L.M. Hogan and H. Song: “Interparticle Spacings and Undercooling in Al-Si Eutectic Microstructure,” Metall. Trans., 1987, 18A, pp. 707–13.
P. Magnin and W. Kurz: “An Analytical Model of Irregular Eutectic Growth and Its Application to Fe-C,” Acta Metall., 1987, 35, pp. 1119–28.
P. Magnin and R. Trivedi: “Eutectic Growth: A Modification of the Jackson-Hunt Theory,” Acta Metall. Mater., 1991, 39, pp. 453–67.
P.H. Shingu: J. Appl. Phys., 1979, 50, p. 5743.
Y. Wang, H. Jones, and P. V. Evans: “Eutectic Solidification Characteristics of Bridgman Growth Al-3Fe-0.1V Alloy,” J. Mater. Sci., 1998, 33, pp. 5205–20.
M.R. Aguiar and R. Caram: “Lamellar Spacing Selection in a Directional Solidified Sn-Se Eutectic Alloy,” J. Cryst. Growth, 1997, 174, pp. 70–75.
S. Guldberg and N. Ryum: “Microstructure and Crystallographic Orientation Relationship in Directionally Solidified Mg-Mg17Al12-Eutectic,” Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, A289, p. 143.
M. Gündüz: The Measurement of the Solid-Liquid Surface Energy, Ph.D. Thesis, Oxford University, Oxford, UK, 1984, p. 60.
D.G. McCartney: Studies on Cellular and Dendritic Solidification, Ph.D. Thesis, Oxford University, Oxford, UK, 1981, p. 95.
T. Lyman, ed.: Metals Handbook—Fractograph and Atlas of Fractographs, Vol. 8, 8th ed., American Society for Metals (ASM Handbook Committee), Metals Park, OH, 1973, p. 336
F. Vnuk, M. Sahoo, D. Baragor, and R.W. Smith: “Mechanical Properties of Sn-Zn Eutectic Alloys,” J. Mater. Sci., 1980, 15, pp. 2573–80.
B. Toloui and A. Hellawell: “Phase Separation and Undercooling in Al-Si Eutectic Alloy—The Influence of Freezing Rate and Temperature Gradient,” Acta Metall. 1976, 24, pp. 565–73.
R. Elliott and S.M.D. Glenister: “Strontium Modification of Al-12.7 wt.% Si Alloys,” Metal Sci., 1981, 4, pp. 181–84.
S. Li, S. Zhao, M. Pan, D. Zhao, X. Chan, O.M. Barabash, and R.I. Barabash: “Solidification and Structural Characteristics of α (Al)-Mg2Si Eutectic,” Mater. Trans. JIM, 1997, 38, pp. 553–59.
B. Saatci: The Measurement of the Solid-Liquid Surface Energy, D. Phil. Thesis, University of Erciyes, Kayseri, Turkey, 2000, p. 167.
D. Bouchhard and J.S. Kirkaldy: “Prediction of Dendrite Arm Spacings in Unsteady and Steady-State Heat Flow of Unidirectionally Solidified Binary Alloys,” Metall. Mater. Trans., 1997, 28B, pp. 651–63.
D.J. Fisher and W. Kurz: “A Theory of Branching Limited Growth of Irregular Eutectics,” Acta Metall., 1980, 28, pp. 777–94.
E. Schürman and H. Löblich: Giessereiforschung, 1977, 29, p. 67.
E. Schürman and H. Löblich: 43rd Int. Foundry Congress, Bucharest, 1976, p. 17.
D.J. Fisher: Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne, Sc.D. Thesis, 1978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaya, H., Çadırlı, E. & Gündüz, M. Effect of growth rates and temperature gradients on the spacing and undercooling in the broken-lamellar eutectic growth (Sn-Zn eutectic system). J. of Materi Eng and Perform 12, 456–469 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1361/105994903770343024
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/105994903770343024