Abstract
Background
Management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) has been transformed with tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). While data on optimal duration of adjuvant imatinib remains elusive, guidelines for administration of neoadjuvant TKIs remain unknown.
Methods
Under an institutional review board-approved protocol, patients at our institution with a diagnosis of GIST treated with neoadjuvant TKIs and surgical resection were identified. Clinical and pathologic characteristics were obtained from medical records.
Results
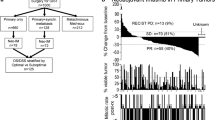
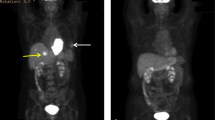
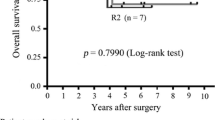
Ninety-three patients underwent surgical resection after neoadjuvant TKI therapy; 41 had primary and 52 had recurrent/metastatic GIST. Median follow-up was 2.4 years. Median duration of neoadjuvant therapy was 315 (range 3–1,611) days for primary and 537 (range 4–3,257) days for recurrent/metastatic GIST (p = 0.001). Two-year, recurrence-free survival (RFS) was 85 and 44 % for primary and recurrent/metastatic disease, respectively, whereas 2-year overall survival (OS) was 97 % for primary and 73 % for recurrent/metastatic GIST. For primary GIST, duration of neoadjuvant therapy >365 days (p = 0.02) was associated with higher risk of recurrence on univariate analysis, whereas none of the clinicopathologic factors impacted OS. For recurrent/metastatic disease, disease progression was associated with a shorter OS (p = 0.001), but no factors were found to impact RFS. Lastly, when examining all patients, KIT mutations (p = 0.03) and multivisceral resection (p = 0.011) predicted shorter RFS.
Conclusions
Neoadjuvant TKIs can be effectively used for the treatment of primary and recurrent/metastatic GIST. While duration of neoadjuvant therapy, KIT mutation status, and the need for multivisceral resection can help to predict higher risk for recurrence, progression on neoadjuvant TKIs can aid in selection of patients with recurrent/metastatic disease for surgical resection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, et al. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a consensus approach. Hum Pathol. 2002;33(5):459–65.
Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: review on morphology, molecular pathology, prognosis, and differential diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2006;130(10):1466–78.
Dematteo RP, Ballman KV, Antonescu CR, et al. Adjuvant imatinib mesylate after resection of localised, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373(9669):1097–104.
van Oosterom AT, Judson I, Verweij J, et al. Safety and efficacy of imatinib (STI571) in metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours: a phase I study. Lancet. 2001;358(9291):1421–3.
van Oosterom AT, Mouridsen HT, Nielsen OS, et al. Results of randomised studies of the EORTC Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group (STBSG) with two different ifosfamide regimens in first- and second-line chemotherapy in advanced soft tissue sarcoma patients. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38(18):2397–406.
Eisenberg BL, Harris J, Blanke CD, et al. Phase II trial of neoadjuvant/adjuvant imatinib mesylate (IM) for advanced primary and metastatic/recurrent operable gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST): early results of RTOG 0132/ACRIN 6665. J Surg Oncol. 2009;99(1):42–7.
Joensuu H, Eriksson M, Sundby Hall K, et al. One vs three years of adjuvant imatinib for operable gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2012;307(12):1265–72.
Wang D, Zhang Q, Blanke CD, et al. Phase II trial of neoadjuvant/adjuvant imatinib mesylate for advanced primary and metastatic/recurrent operable gastrointestinal stromal tumors: long-term follow-up results of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 0132. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19(4):1074–80.
Andtbacka RH, Ng CS, Scaife CL, et al. Surgical resection of gastrointestinal stromal tumors after treatment with imatinib. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14(1):14–24.
DeMatteo RP, Maki RG, Singer S, Gonen M, Brennan MF, Antonescu CR. Results of tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy followed by surgical resection for metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Ann Surg. 2007;245(3):347–52.
Fiore M, Palassini E, Fumagalli E, et al. Preoperative imatinib mesylate for unresectable or locally advanced primary gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009;35(7):739–45.
McAuliffe JC, Hunt KK, Lazar AJ, et al. A randomized, phase II study of preoperative plus postoperative imatinib in GIST: evidence of rapid radiographic response and temporal induction of tumor cell apoptosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(4):910–9.
Rubin BP, Heinrich MC, Corless CL. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Lancet. 2007;369(9574):1731–41.
Tielen R, Verhoef C, van Coevorden F, et al. Surgical treatment of locally advanced, non-metastatic, gastrointestinal stromal tumours after treatment with imatinib. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2013;39(2):150–5.
Rutkowski P, Gronchi A, Hohenberger P, et al. Neoadjuvant imatinib in locally advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST): the EORTC STBSG experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2013;20(9):2937–43.
Kang HJ, Ryu MH, Kim KM, et al. Imatinib efficacy by tumor genotype in Korean patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST): the Korean GIST Study Group (KGSG) study. Acta Oncol. 2012;51(4):528–36.
Lasota J, Miettinen M. Clinical significance of oncogenic KIT and PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Histopathology. 2008;53(3):245–66.
Wozniak A, Rutkowski P, Piskorz A, et al. Prognostic value of KIT/PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST): Polish Clinical GIST Registry experience. Ann Oncol. 2012;23(2):353–60.
Debiec-Rychter M, Sciot R, Le Cesne A, et al. KIT mutations and dose selection for imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42(8):1093–103.
Wozniak A, Floris G, Debiec-Rychter M, Sciot R, Schoffski P. Implications of mutational analysis for the management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors and the application of targeted therapies. Cancer Investig. 2010;28(8):839–48.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Fig. 1
(DOCX 111 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bednarski, B.K., Araujo, D.M., Yi, M. et al. Analysis of Prognostic Factors Impacting Oncologic Outcomes After Neoadjuvant Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 21, 2499–2505 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3632-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3632-7