Abstract
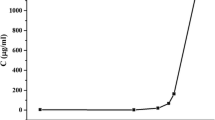
The aim of the present study was to enhance the dissolution rate of gliclazide using its solid dispersions (SDs) with polyethylene glycol (PEG) 6000. The phase solubility behavior of gliclazide in presence of various concentrations of PEG 6000 in 0.1 N HCl was obtained at 37 °C. The solubility of gliclazide increased with increasing amount of PEG 6000 in water. Gibbs free energy (\(\Delta G_{{\text{tr}}}^{\text{o}} \)) values were all negative, indicating the spontaneous nature of gliclazide solubilization and they decreased with increase in the PEG 6000 concentration, demonstrating that the reaction conditions became more favorable as the concentration of PEG 6000 increased. The SDs of gliclazide with PEG 6000 were prepared at 1:1, 1:2 and 1:5 (gliclazide/PEG 6000) ratio by melting-solvent method and solvent evaporation method. Evaluation of the properties of the SDs was performed by using dissolution, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies. The SDs of gliclazide with PEG 6000 exhibited enhanced dissolution rate of gliclazide, and the rate increased with increasing concentration of PEG 6000 in SDs. Mean dissolution time (MDT)of gliclazide decreased significantly after preparation of SDs and physical mixture with PEG 6000. The FTIR spectroscopic studies showed the stability of gliclazide and absence of well-defined gliclazide–PEG 6000 interaction. The DSC and XRD studies indicated the microcrystalline or amorphous state of gliclazide in SDs of gliclazide with PEG 6000.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Leuner, and J. Dressman. Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersion. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 50:47–60 (2000).
G. V. Betageri, and K. R. Makarla. Enhancement of dissolution of glyburide by solid dispersion and lyophilization techniques. Int. J. Pharm. 126:155–160 (1995).
G. V. Mooter, R. Kinget, N. Blaton, and F. Damian. Physical stability of solid dispersion of anti-viral agent UC-781 with PEG 6000, Gelucire®44/14 and PVK 30. Int. J. Pharm. 244:87–98 (2002).
G. V. Betageri, and K. R. Makarla. Characterization of glyburide-polyethylene by solid dispersions. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 22(7):731–734 (1996).
L. S. Law, and W. Y. Lo. Dissolution behavior of griseofulvin solid dispersions using polyethylene glycol, talc, and their combination as dispersion carriers. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 32(3):231–236 (1996).
P. Mura, A. Manderioli, G. Bramanti, and L. Ceccarelli. Properties of solid dispersions of naproxen in various polyethylene glycols. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 22(9&10):909–916 (1996).
G. Trapani, M. Franco, A. Latrofa, M. R. Pantaleo, M. R. Provenzano, E. Sanna, E. Maciocco, and G. Liso. Physicochemical characterization and in vivo properties of Zolpidem in solid dispersions with polyethylene glycol 4000 and 6000. Int. J. Pharm. 184:121–130 (1999).
G. Trapani, M. Franco, A. Latrofa, C. Tullio, M. R. Provenzano, M. Serra, M. Muggironi, G. Biggio, and G. Liso. Dissolution properties and anticonvulsant activity of phenytoin–polyethylene glycol 6000 and –polyvinylpyrrolidone K-30 solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 225:63–73 (2001).
H. Valizadeh, A. Nokhodchi, N. Qarakhani, P. Zakeri-Milani, S. Azarmi, D. Hassanzadeh, and R. Lobenberg. Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersions of indomethacin with PEG 6000, Myrj 52, Lactose, Sorbitol, Dextrin, and Eudragit E100. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 30(3):303–317 (2004).
M. B. Tashtoush, S. Z. Al-Qashi, and M. N. Najib. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of glibenclamide in solid dispersion system. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 30(6):601–607 (2004).
J. E. F. Reynolds, (Ed.), Martindale: The Extra Pharmacopoiea, 30th ed. The Pharmaceutical Press, London, P-279–280.
A. D. Harrower. Comparison of efficacy, secondary failure rate and complications of sulfonylurea. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 8:201–203 (1994).
K. J. Palmer, and R. N. Brogden. Gliclazide, an update of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in NIDDM. Drugs. 46:92–125 (1993).
R. Lobenberg, and G. L. Amidon. Modern bioavailability, bioequivalence and biopharmaceutics classification system: new scientific approaches to international regulatory standards. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 50:3–12 (2000).
K. G. H. Desai, A. R. Kulkarni, and T. M. Aminabhavi. Solubility of rofecoxib in presence of methanol, ethanol and sodium lauryl sulfate at (298.15, 303.15 and 308.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 48:942–945 (2003).
J. L. Ford. The current status of solid dispersions. Pharm. Acta Helv. 61:69–88 (1986).
L. Chengsheng, G. H. D. Kashappa, and L. Chenguang. Enhancement of dissolution rate of valdecoxib using solid dispersions with PEG-4000. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 31:1–10 (2005).
T. Higuchi, and K. Connors. Phase solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 4:17–123 (1965).
M. J. Arias, J. M. Gines, J. R. Moyano, and A. M. Rabasco. Dissolution properties and in vivo behavior of triamterene in solid dispersions with polyethylene glycols. Pharm. Acta Helv. 71:229–235 (1996).
F. Damian, N. Blaton, L. Naesens, J. Balzarini, R. Kinget, P. Augustinjns, and G. V. Mooter. Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersions of the antiviral agent UC-781 with polyethylene glycol 6000 and Gelucire 44/14. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 10:311–322 (2000).
S. Okonogi, T. Oguchi, E. Yonemochi, S. Puttipipatkhachorn, and K. Yamamoto. Improved dissolution of ofloxacin via solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 156:175–180 (1997a).
J. E. Polli, G. S. Rekhi, L. L. Augsburger, and V. P. Shah. Methods to compare dissolution profiles and a rationale for wide dissolution specification for metoprolol tartrate tablets. J. Pharm. Sci. 8:690–700 (1997).
C. A. Khan, and C. T. Rhodes. The concept of dissolution efficiency. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 27:48–49 (1975).
A. T. M. Serajudin, P. C. Sheen, and M. A. Augustine. Improved dissolution of poorly water soluble drug from solid dispersions in poly ethylene:polysorbste 80 mixtures. J. Pharm. Sci. 79:463–464 (1990).
A. T. M. Serajuddin, P. C. Sheen, D. Mufson, D. F. Bernstein, and M. A. Augustine. Effect of vehicle amphiphilicity on the dissolution and bioavailability of a poorly water-soluble drug from solid dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 77:414–417 (1988).
P. Costa, and J. M. S. Lobo. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 13:123–133 (2001).
R. W. Korsemeyer, R. Gurney, E. Doelker, P. Buri, and N. A. Peppas. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 15:25–35 (1983).
G. V. Betageri, H. D. Doshi, and R. W. Ravis. Carbamazepine and polyethylene glycol solid dispersions: preparation, in vitro dissolution and characterization. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 23(12):1167–1176 (1997).
O. I. Corrigan, C. A. Murphy, and R. F. Timoney. Dissolution properties of polyethylene glycols and polyethylene-drug systems. Int. J. Pharm. 4:67–74 (1979).
J. L. Dubois, and J. L. Ford. Similarities in the release rates of different drugs from polyethylene glycol 6000 dispersions. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 37:494–495 (1985).
D. Q. M. Craig, and J. M. Newton. The dissolution of nortriptyline HCl from polyethylene glycol solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 78:175–182 (1992).
S. E. Saers, and D. Q. M. Craig. An investigation into the mechanisms of dissolution of alkyl p-aminobenzoates from polyethylene glycol solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 83:211–219 (1992).
G. V. Mooter, P. Augustijns, N. Blaton, and R. Kinget. Physico-chemical characterization of solid dispersions of temazepam with polyethylene glycol 6000 and PVP K 30. Int. J. Pharm. 164:67–80 (1998).
Y. Özkan, T. Atay, N. Díkman, A. Isimer, and Y. H. Aboul-Enein. Improvement of water solubility and in vitro dissolution rate gliclazide by complexation with b-cyclodextrin. Pharm. Acta Helv. 74:365–370 (2000).
S. Winters, P. York, and P. Timmins. Solid state examination of a gliclazide:beta-cyclodextrin complex. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 5:209–214 (1997).
B. C. Hancock, and G. Zografi. Characteristics and significance of the amorphous state in pharmaceutical systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 86:1–12 (1997).
S. C. Shin, and J. Kim. Physicochemical characterization of solid dispersion of furosemide with TPGS. Int. J. Pharm. 251:79–84 (2003).
S. Okonogi, E. Yonemochi, T. Oguchi, S. Puttipipatkhachorn, and K. Yamamoto. Enhanced dissolution of ursodeoxycholic acid from the solid dispersion. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 23:1115–1121 (1997b).
K. Yamashita, T. Nakate, K. Okimoto, A. Ohike, Y. Tokunaga, R. Ibuki, K. Higaki, and T. Kimura. Establishment of new preparation method for solid dispersion formulation of tacrolimus. Int. J. Pharm. 267:79–91 (2003).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Aristo pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd, Mumbai, India and Clariant GmbH, Sulzbach, Germany for supply of gliclazide and various grades of polyethylene glycol respectively. Mr. S. Biswal acknowledges All India Council for Technical Education, New Delhi, India for the scholarship granted.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biswal, S., Sahoo, J., Murthy, P.N. et al. Enhancement of Dissolution Rate of Gliclazide Using Solid Dispersions with Polyethylene Glycol 6000. AAPS PharmSciTech 9, 563–570 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9079-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9079-z