Abstract
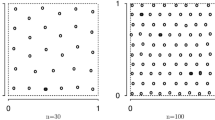
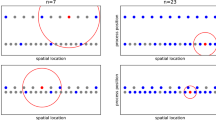
We study spatial sampling design for prediction of stationary isotropic Gaussian processes with estimated parameters of the covariance function. The key issue is how to incorporate the parameter uncertainty into design criteria to correctly represent the uncertainty in prediction. Several possible design criteria are discussed that incorporate the parameter uncertainty. A simulated annealing algorithm is employed to search for the optimal design of small sample size and a two-step algorithm is proposed for moderately large sample sizes. Simulation results are presented for the Matérn class of covariance functions. An example of redesigning the air monitoring network in EPA Region 5 for monitoring sulfur dioxide is given to illustrate the possible differences our proposed design criterion can make in practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowitz, M., and Stegun, I. (1965), Handbook of Mathematical Functions (9th ed.), New York: Dover.
Abt, M. (1999), “Estimating the Prediction Mean Squared Error in Gaussian Stochastic Processes With Exponential Correlation Structure,” Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 26, 563–578.
Banjevic, M., and Switzer, P. (2002), “Bayesian Netoork Designs for Fields with Variance as a Function of the Location,” in Proceedings of the 2002 JSM Conference.
Baumgardner, R. E., Isil, S. S., Bowser, J. J., and Fitzgerald, K. M. (1999), “Measurements of Rural Sulfur Dioxide and Particle Sulfate: Analysis of CASTNet Data, 1987 through 1996,” Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 49, 1266–1279.
Baumgardner, R. E., Lavery, T. F., Rogers, C. M., and et al. (2002), “Estimates of the Atmospheric Deposition of Sulfur and Nitrogen Species: Clean Air Status and Trends Network, 1990–2000,” Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 2614–2629.
Benhenni, K., and Cambanis, S. (1992), “Sampling Designs for Estimating Integrals of Stochastic Processes,” The Annals of Statistics, 20, 161–194.
Caselton, W. F., and Zidek, J. V. (1984), “Optimal Monitoring Network Designs,” Statistics and Probability Letters, 2, 223–227.
Caselton, W. F., Kan, L., and Zidek, J. V. (1992), “Quality Data Networks that Minimize Entropy,” in Statistics in the Environmental and Earth Sciences, eds. A. T. Walden and P. Guttorp, London: Edward Arnold, pp. 10–38.
Cressie, N. (1993), Statistics for Spatial Data (rev. ed.), New York: Wiley.
Cressie, N., and Lahiri, S. N. (1993), “The Asymptotic Distribution of REML Estimators,” Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 45, 217–233.
Davison, A. C., and Hinkley, D. V. (1997), Bootstrap Methods and Their Application, New York: Cambridge University Press.
Diggle, P. J., and Ribeiro, P. J. (2002), “Bayesian Inference in Gaussian Model Based Geostatistics,” Geographical and Environmental Modeling, 6, 129–146.
Diggle, P. J., Tawn, J. A., and Moyeed, R. A. (1998), “Model-Based Geostatistics,” Applied Statistics, 47, 299–326.
Guttorp, P., Le, N. D., Sampson, P. D., and Zidek, J. V. (1993), “Using Entropy in the Redesign of an Environmental Monitoring Network,” in Multivariate Environmental Statistics, eds. G. P. Patil and C. R. Rao, Amsterdam: Elsevier, pp. 175–202.
Handcock, M. S., and Wallis, J. R. (1994), “An Approach to Statistical Spatial-Temporal Modeling of Meteorological Fields,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 89, 368–378.
Harville, D. A., and Jeske, D. R. (1992), “Mean Squared Error of Estimation or Prediction Under a General Linear Model,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 87, 724–731.
Holland, D. M., Caragea, P., and Smith, S. L. (2004), “Regional Trends in Rural Sulfur Concentrations,” Atmospheric Environment, 38, 1673–1684.
Kackar, R. N., and Harville, D. A. (1984), “Approximations for Standard Errors of Estimators of Fixed and Random Effects in Mixed Linear Models,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 79, 853–862.
Ko, C., Lee, J., and Queyranne, M. (1995), “An Exact Algorithm for Maximum Entropy Sampling,” Operations Research, 43, 684–691.
Lark, R. M. (2002), “Optimized Spatial Sampling of Soil for Estimation of the Variogram by Maximum Likelihood,” Geoderma, 105, 49–80.
Lee, J. (1998), “Constrained Maximum-Entropy Sampling,” Operations Research, 46, 655–664.
Malm, W. C., Schichtel, B. A., Ames, R. B., and et al. (2002), “A 10-year Spatial and Temporal Trend of Sulfate Across the United States,” Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 107(D22), 4627.
Mardia, K. V., and Marshall, R. J. (1984), “Maximum Likelihood Estimation of Models for Residual Covariance in Spatial Regression,” Biometrika, 71, 135–146.
McBratney, A. B., Webster, R., and Burgess, T. M. (1981), “The Design of Optimal Sampling Schemes for Local Estimation and Mapping of Regionalized Variables, I—Theory and Method,” Computers and Geosciences, 7, 331–334.
McCullagh, P., and Nelder, J. A. (1989), Generalized Linear Models (2nd ed.), London: Chapman & Hall.
Mueller, S. F. (2003), “Seasonal Aerosol Sulfate Trends for Selected Regions of the United States,” Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 53, 168–184.
Müller-Gronbach, T., and Ritter, K. (1998), “Spatial Adaption for Predicting Random Functions,” The Annals of Statistics, 26, 2264–2288.
Patterson, H. D., and Thompson, R. (1971), “Recovery of Inter-Block Information When Block Sizes are Unequal,” Biometrika, 58, 545–554.
Ritter, K. (1996), “Asymptotic Optimality of Regular Sequence Designs,” The Annals of Statistics, 24, 2081–2096.
Sacks, J., Welch, W. J., Mitchell, T. J., Wynn, H. P. (1989), “Design and Analysis of Computer Experiments,” Statistical Science, 4, 409–423.
Smith, R. L., and Zhu, Z. (2004), “Asymptotic Theory for Kriging with Estimated Parameters and its Application to Network Design,” available online at: http://www.unc.edu/depts/statistics/postscript/rs/supp5.pdf.
Stein, M. L. (1995), “Locally Lattice Sampling Designs for Isotropic Random Fields,” The Annals of Statistics, 23, 1991–2012.
— (1999), Interpolation of Spatial Data: Some Theory for Kriging, New York: Springer-Verlag.
van Groenigen, J. W., and Stein, A. (1998), “Constrained Optimization of Spatial Sampling using Continuous Simulated Annealing,” Journal of Environomental Quality, 43, 684–691.
Wiens, D. P. (2004), “Robustness in Spatial Studies I: Minimax Design,” Environmetrics, in press.
Wikle, C. K., and Royle, J. A. (1999), “Space-Time Dynamic Design of Environmental Monitoring Networks,” Journal of Agricultural, Biological, and Environmental Statistics, 4, 489–507.
Yfantis, E. A., Flatman, G. T., and Behar, J. V. (1987), “Efficiency of Kriging Estimation for Square, Triangular, and Hexagonal Grids,” Mathematical Geology, 19, 183–205.
Zhu, Z., and Stein, M. L. (2005), “Spatial Sampling Design for Parameter Estimation of the Covariance Function,” Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 134, 583–603.
Zidek, J. V., Sun, W. M., and Le, N. D. (2000), “Designing and Integrating Composite Networks for Monitoring Multivariate Gaussian Pollution Fields,” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Ser. C, 49, 63–79.
Zimmerman, D. L. (2005), “Optimal Network Design for Spatial Prediction, Covariance Parameter Estimation, and Empirical Prediction,” Environmetrics, in press.
Zimmerman, D. L., and Cressie, N. (1992), “Mean Squared Prediction Error in the Spatial Linear Model with Estimated Covariance Parameters,” Annals of the Institute of Statistical Mathematics, 44, 27–43.
Zimmerman, D. L., and Zimmerman, M. B. (1991), “A Comparison of Spatial Semivariogram Estimators and Corresponding Ordinary Kriging Predictors,” Technometrics, 33, 77–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z., Stein, M.L. Spatial sampling design for prediction with estimated parameters. JABES 11, 24–44 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1198/108571106X99751
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1198/108571106X99751