Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to examine the fertility differential of women age 15 to 49 using data from Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey 2014- a survey of women who were born from 1963 to 1999.
Methods
The secondary data analysis was carried out using the BDHS 2014 in order to discuss differences in childbearing practices in Bangladesh. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze the data including education level, geographic location, and religion. A trend test used to assess the inferences.
Results
On average, women had 2.3 children in the BDHS 2014; more than 90% of them gave birth to at least one child by age 49 and the average age of first birth was 18 years. Fertility of women strongly differed by education (p < 0.001). The percentage of women with secondary education who had no child was 50.3% and never attended school 8.4%;those with secondary education were six times as likely as those who never attended school to have no child and this pattern was stronger among urban compared with rural women.
Conclusions
Fertility differential becomes robust as education increases. Women’s fertility is also related to religion and residence, but these factors were not strongly related as those educational attainments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Fertility is the major component of population dynamics that decide the size, structure, and composition of populations in any country of the world [1]. Fertility behaviors have changed in Bangladesh since 1975. Research has shown that women childbearing decsions are impacted by the increase in universal provision of family planning services, and rates of women’s educational attainment and urbanization. Differentials in fertility behavior and fertility levels in different population strata have been the most pervasive findings in the demography [2, 3]. Bangladesh has seen large improvements in reproductive health, such as reducing maternal and infant mortality, increases in contraceptive prevalence and health service use among married women [1].
The Total Fertility Rate (TFR) in Bangladesh was dropped markedly from 6.3 births each women in 1975 to 2.3 births each women in 2014. But, TFR was still high compared to other developing countries. Ahamed [4] examined differentials of fertility with selected demographic and socioeconomic characteristics for ever-married women and their husbands. He showed that a woman’s age has the highest effect on change in fertility. Ramesh [5] found that demographic, socioeconomic, and cultural causes affect fertility differentials in Nepal. Age at first marriage of women was a strong predictor of ever having children. Desalew Zelalem conducted a study about the level and patterns of fertility among women using the Kersa Demographic Surveillance [6]. This author used follow-up data 2008–2012 and found that the fertility rate was higher in rural illiterate women than urban literate women. Kasey [7] and Aughinbaugh [8] used the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth 1979 (NLSY79) to examine the wage-earning implications of delaying the first birth. This article found that an annual 3 % wage premium existed for each year of delayed motherhood. Delayed childbirth also correlated with high test scores, education, and professional status of the mother [9,10,11].
In the Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey (BDHS) 2014, early analyses were summary statistics with different characteristics such as marriage and sexuality, fertility preferences, fertility control, child health, nutrition, and female empowerment. However, they did not analyze this data for differences in childbearing practices and relationships with demographic factors. Our study focuses on differences in fertility patterns by educational attainment (no education, primary, secondary and higher), religion, and residence. Primary education is defined at completing grade 1 to 5, secondary education 6 to 10 grade, higher education 11 to 17 grade, and no education was those who never attended school. The analysis of this study is descriptive and does not try to discuss why fertility patterns differ among women.
Methods
To examine fertility differential change, this paper has used data from the Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey (BDHS) 2014. Details of the study design and data collection methods have been previously published [1]. Briefly, BDHS 2014 was a cross-sectional study designed to obtain information on key health indicators in Bangladesh i.e. fertility, family planning, maternal and child health, and women. The data used in this study is publicly available.
We conducted a secondary data analysis which examined fertility trend and differentials. Univariate and bivariate analyses have been performed to find out the sample characteristics and evaluate the differences in fertility patterns by following factors: educational attainment, religion, and residence. We also used a trend test to detect significant fertility differences.
Results
A total of 17,863 women participated in the BDHS 2014 between ages 15–49. 29.5% women were young whose age group 15 to 24. A rural area is defined by Upazilla and is divided into Union parishads and, within Union parishads, into Mouzas. Most women lived in rural areas (71.7%). Participants’ higher education level had 8.5%, 37.4% had secondary, and 24.9% had no education. At most one tenth participants were non-Muslim and 10.2% had no child. Among the participants, 29.3% had two children and 7.8% had five or more children. The wealth quintiles in BDHS 2014 are a composite measure of a household’s cumulative living standard. The wealth quintiles are calculated using data on a household’s ownership of selected assets, such as televisions and bicycles; materials used for housing construction, and types of water access and sanitation facilities. More than one-fifth of the population (21%) were in the richest cohort of women (see, Table 1).
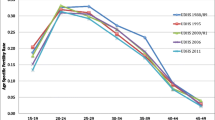
Table 2 shows the fertility outcomes of women age from 15 to 49, by educational attainment, religion, and residence. Among women with higher education, 19.9% have no child, 13.8% have one child, 8.5% have two children, 3.3% have three children, 0.9% have four children and 0.4% have five or more children. Of women with secondary education, 50.3% have no child, 49.9% have one child, 41.9% have two children, 28.2% have three children, 19.3% have four children, and 10.8% have five or more children. On the other hand, among women with no education, 8.4% have no child, 11.9% have one child, 20.1% have two children, 34.0% have three children, and 45.4% have four children and 56.4% have five or more children. Thus, examining the fertility pattern with education disclosed a key significant differences across the groups (p < 0.001). Non-Muslim more educated women were less likely to have five or more children compared with uneducated women (0.01% versus 48.1%, P < 0.001) and Muslim women with no children at the highest education had also significant differences (20.2% versus 8.3%) in the lowest education (P < 0.001). Minority groups were over-represented among those with secondary educational attainment and under-represented among that higher education. Urban women were more likely to have no children compared with rural women (11.7% versus 9.6%).Rural women were more likely to have five or more children than urban (8.9% versus 4.8%). The mean number of children was 2.23 in BDHS 2014, those with women having no education having the highest mean number of children (3.2) and the lowest (1.2) incidence of higher education (see, Fig. 1).
Table 3 also presents descriptive statistics on women’s age and birth spacing children, educational attainment, religion, and residence. More educated women had children at the later ages. The average age at first birth was 19.0 years for women with one child, 18.0 years for women with two children, and 17.2 years for women with three children. The births of women in the latter group were spaced more closely than those of women with two children. On average, the time between first and second births were 5.7 years for women with two children, compared with 4.7 years for those with three children. Evaluation of birth spacing in women with no education by two and three children-women, found the mean time between first and second births to be 6.2 years for women with two children, compared with 4.9 years for those with three children.
There were also birth spacing differences related to higher education,, residence, and religion. Education strongly correlates with age at first birth. Women with a higher education tend to have first birth at older ages. These ages are 22.3 for women with one child, 21.9 for women with two children, and 20.9 for women with three children. At first birth, for a given number of children, women with a higher education are 3.9 to 4.9 years older than those with primary education and 3.4 to 4.0 years older than those with secondary education.
However, the age at first birth for urban women falls more steeply as total fertility increases. On average, urban women who have only one child are 19.7 years old at the birth of their child. Urban women who have two children are 18.6 and three children are 17.5 at their first birth. Moreover, on average, rural women who have only one child are age 18.5 at the first birth of their child and women who have two children are 17.7 and three children are 17.1 at their first birth.
Discussion
The major finding of our study are that education and residential area impact the fertility of women age 15–49. More than 90% of women in the BDHS 2014 had at least one child by age 49 and 2.3 children was the average in this cross-sectional data set. Women from 15 to 49 who had higher education had the lowest fertility compared with women with only secondary, primary and no education, which means that fertility was delayed as education increased in Bangladesh.
These findings are similar to a previous study of demographic, socioeconomic, and cultural factors affecting fertility differentials in Nepal [5] which found strong relationships between fertility and demographic factors. Bangladesh, however, is quite similar to Nepal with regard to cultural activities and socioeconomic status. Globalization and regionalization supported by the revolution in technology have changed the socioeconomic landscape.
We was also found that the average age at first birth in urban areas was older, and that urban dwelling women were more likely to have lower fertility than rural women.
The present study has some limitations. The study included subjects from BDHS 2014. We did not include subjects from Sample vital registration system (SVRS). This population may not be representative of all classes of women in Bangladesh. The analysis in this study is only descriptive and did not try to explain why fertility patterns differ among women.
Conclusions
Fertility patterns mostly differ by educational attainment rather than other factors, i.e. religion and residence. The mean number of living children in women with higher education is lower than women with less education. Fertility rates are higher in rural women than urban women with no education. Overall, women in rural areas and those with less advanced levels of education had more children, and women with higher education were older at the age of birth of their first child. We conclude that the education level contributes most to fertility differential in Bangladesh.
Abbreviations
- BDHS:
-
Bangladesh demographic and health survey
- NIPORT:
-
National institute of population research and training
- NLSY79:
-
National longitudinal survey of youth 1979
- Q1:
-
First quantile
- Q2:
-
Second quantile
- Q3:
-
Third quantile
- Q4:
-
Fourth quantile
- Q5:
-
Fifth quantile
- SVRS:
-
Sample vital registration system
- TFR:
-
Total fertility rate
References
NIPORT, Mitra and Associates, and ICF International. Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey 2014, Dhaka, Bangladesh, and Rockville, Maryland, USA; 2016.
Cochrane SH. Fertility and education. Baltimore: The John Hopkins University Press; 1979.
Majumder N, Ram F. Explaining the role of proximate determinants on fertility decline among poor and non-poor in Asian countries. PLoS One. 2015;10(2):e0115441.
Ahamed, MMU: Fertility differentials in Bangladesh. https://cardinalscholar.bsu.edu/handle/handle/184485 (1992). Accessed 10 Feb 2017.
Adhikari R. Demographic, socio-economic, and cultural factors affecting fertility differentials in Nepal. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2010;10:19.
Zelalem, et al. The level and patterns of fertility among women in Kersa demographic surveillance and Health Research Center (KDS-HRC) field site, Kersa District, East Ethiopia. Fertil Res Prac. 2015;1:18.
Kasey SB. Understanding the returns to delayed childbearing for working women. American. Econ Rev. 2008;98(2):403–7.
Aughinbaugh A, Sun H. Fertility of women in the NLSY79, Monthly Labor review; 2016. p. 1–19.
East PL, Felice ME. Outcomes of parent-child relationships of former adolescent mothers and their 12-year-old children. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1990;11:175–83.
Buros OK. The mental measurements yearbook. Highland Park, NJ: Mental Measurements Yearbook; 1940.
Kunz PR, Peterson ET. Family size, birth order and academic achievement. Social Bio. 1977;24:144–8.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thanks Editor and two anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions. This manuscript presented in the International Statistical Institute Regional Statistics Conference 2017, Bali, Indonesia, and authors also thanks to the participants comments to improve the manuscript.
Funding
No financial support was received for this manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Demographic and Health Survey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SR produced the study, planned its design and its coordination, and drafted the manuscript. SMIH review the manuscript. SR also organized and built the database and performed the statistical analyses. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, S., Hossain, S.M.I. Fertility differential of women in Bangladesh demographic and health survey 2014. Fertil Res and Pract 3, 16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40738-017-0043-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40738-017-0043-z