Abstract
Background
Pyrethroid-based indoor residual spraying (IRS) and long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs) have been employed as key vector control measures against malaria in Namibia. However, pyrethroid resistance in Anopheles mosquitoes may compromise the efficacy of these interventions. To address this challenge, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the use of piperonyl butoxide (PBO) LLINs in areas where pyrethroid resistance is confirmed to be mediated by mixed function oxidase (MFO).
Methods
This study assessed the susceptibility of Anopheles gambiae sensu lato (s.l.) mosquitoes to WHO tube bioassays with 4% DDT and 0.05% deltamethrin insecticides. Additionally, the study explored the effect of piperonyl butoxide (PBO) synergist by sequentially exposing mosquitoes to deltamethrin (0.05%) alone, PBO (4%) + deltamethrin (0.05%), and PBO alone. The Anopheles mosquitoes were further identified morphologically and molecularly.
Results
The findings revealed that An. gambiae sensu stricto (s.s.) (62%) was more prevalent than Anopheles arabiensis (38%). The WHO tube bioassays confirmed resistance to deltamethrin 0.05% in the Oshikoto, Kunene, and Kavango West regions, with mortality rates of 79, 86, and 67%, respectively. In contrast, An. arabiensis displayed resistance to deltamethrin 0.05% in Oshikoto (82% mortality) and reduced susceptibility in Kavango West (96% mortality). Notably, there was reduced susceptibility to DDT 4% in both An. gambiae s.s. and An. arabiensis from the Kavango West region. Subsequently, a subsample from PBO synergist assays in 2020 demonstrated a high proportion of An. arabiensis in Oshana (84.4%) and Oshikoto (73.6%), and 0.42% of Anopheles quadriannulatus in Oshana. Non-amplifiers were also present (15.2% in Oshana; 26.4% in Oshikoto). Deltamethrin resistance with less than 95% mortality, was consistently observed in An. gambiae s.l. populations across all sites in both 2020 and 2021. Following pre-exposure to the PBO synergist, susceptibility to deltamethrin was fully restored with 100.0% mortality at all sites in 2020 and 2021.
Conclusions
Pyrethroid resistance has been identified in An. gambiae s.s. and An. arabiensis in the Kavango West, Kunene, and Oshikoto regions, indicating potential challenges for pyrethroid-based IRS and LLINs. Consequently, the data highlights the promise of pyrethroid-PBO LLINs in addressing resistance issues in the region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Malaria continues to pose a significant public health challenge in nine northern regions of Namibia: Zambezi, Kavango East, Kavango West, Kunene, Ohangwena, Oshikoto, Omusati, Oshana, and Otjozondjupa [1, 2]. In contrast, the southern regions of Namibia remain generally malaria-free [1, 2]. Namibia has relied on indoor residual spraying (IRS) as the primary vector control intervention since 1965 [1]. Initially, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) was the insecticide of choice, primarily applied to traditional mud and thatch structures. However, in 2005, the country shifted its approach to using deltamethrin, a pyrethroid insecticide, targeting modern cement structures [3]. This transition reflects Namibia's adaptability in response to changing malaria dynamics. The introduction of long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs) with pyrethroids to complement IRS in the mid-2000s marked another significant stride in malaria control [4, 5]. LLINs have demonstrated their high effectiveness in reducing malaria transmission throughout sub-Saharan Africa [6, 7].
Entomological surveillance in various regions has shown that approximately 30% of mosquito exposure occurs indoors [8]. This finding underscores the potential effectiveness of LLINs and IRS in reducing malaria transmission. The distribution of LLINs in Namibia has been substantial, with a target of one net for every two individuals at risk of malaria, following World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines [9]. The impact of LLINs on malaria transmission in sub-Saharan Africa, with significant reductions in malaria cases [6, 7], justifies ongoing efforts by the National Malaria Control Programmes (NMCPs) to increase LLIN ownership and usage in Africa [10,11,12]. Despite significant headway, malaria remains a public health problem in Namibia, with 13,633 reported cases in 2020 [12]. It is possible that pyrethroid resistance reduced the efficacy of IRS and LLINs. Using pyrethroid insecticides in IRS and LLINs in Africa, despite widespread pyrethroid resistance among Anopheles mosquito populations, may contribute to the increase in malaria cases [1]. Pyrethroid resistance has been detected in at least one malaria vector in more than two-thirds of the sites tested, with the highest in the WHO regions of Africa and the Eastern Mediterranean [13]. The WHO recommends annual monitoring of insecticide resistance in major malaria vectors to guide vector control strategies [13]. Local entomological surveillance of vector susceptibility to insecticides is crucial, as recommended by the WHO [14].
This study was conducted as part of the annual entomological surveillance of the National Vector-borne Disease Control Programme (NVDCP) and aimed to assess the species-specific susceptibility of Anopheles gambiae sensu lato (s.l.) to DDT and deltamethrin insecticides. In addition to evaluating susceptibility to traditional insecticides, the NVDCP has been actively exploring innovative approaches to malaria vector control. Notably, the NVDCP has considered the distribution of novel pyrethroid piperonyl butoxide (PBO) LLINs, which have been shown to increase the mortality of malaria vectors with metabolic resistance involving monooxygenases [8]. These PBO LLINs combine a pyrethroid insecticide with the synergist PBO, increasing their effectiveness against pyrethroid-resistant Anopheles mosquitoes [15]. The PBO synergist inhibits metabolic enzymes, such as mixed function oxidases (MFO) of the cytochrome P450 family, preventing the sequestration of pyrethroids by mosquitoes before they become toxic [11, 16].
Methods
Study sites
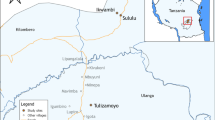
The insecticide susceptibility study in 2018 was conducted at sentinel sites in seven of the nine malaria-endemic regions. The seven regions (sentinel village sites in brackets) that were included in this study were Oshana (Onamutai), Oshikoto (Oniimwandi), Otjozondjupa (Otjituuo), Ohangwena (Okanghudi), Kunene (Otjimuhaka), Omusati (Omiindaba), and Kavango West (Mukekete) (Fig. 1). Thereafter, PBO synergist assays were conducted in sentinel sites from six malaria-endemic regions, which included the Oshana region (Onamutai), Oshikoto (Oniimwandi), Otjozondjupa (Otjituuo), Kavango West (Mukekete), Kavango East (Shadikongoro), and Zambezi (Sibbinda) (Fig. 1). A sentinel site in each region was a malaria hotspot determined by the NVDCP based on malaria risk maps generated from malaria surveillance data. Each sentinel site included a sampling area with a radius of approximately 10 km2 from the central location of the village.
Collection and rearing of larvae
Larvae and pupae were collected from the study sentinel sites from March to April 2018 for insecticide assays. For PBO synergist assays, larvae and pupae were only collected from sites in the Oshikoto and Oshana regions during the peak malaria season (March to May 2020). The larval collections were disrupted from March to April 2020 due to restrictions imposed by the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, collections from sites in the Oshikoto, Otjozondjupa, Kavango West, Kavango East, and Zambezi regions were not possible from March to April 2021, once again due to the ongoing COVID-19 restrictions. Larval sampling was performed by using larval scoops dipped at the edges of breeding sites [17, 18]. Specific sampling sites in each region were chosen by the NVDCP based on malaria risk maps generated from malaria surveillance data. Each sentinel site included a sampling area of approximately a 10 km radius from the central location of the village. Anopheles mosquito larvae and pupae were reared to adulthood at the NVDCP insectary in Oshakati. The larvae were fed a powdered mixture of dog biscuits and yeast, while the adults were fed on 10% sugar solution ad libitum. Insecticide susceptible An. arabiensis mosquitoes (KGB strain, Witwatersrand University) were used for the control assays. The temperature and humidity within the insectary were maintained between 28 °C and 29 °C and 70 and 80%, respectively. Female Anopheles mosquitoes aged 3–5 days that had never had a blood meal were used for the assays.
WHO insecticide susceptibility bioassays
Using WHO-recommended procedures [13, 17], a complete test included four replicates using 20 adult wild-caught specimens per tube and two control replicates each using 20 susceptible Anopheles arabiensis mosquitoes per tube. In total, 1680 female Anopheles were exposed to the WHO bioassays, while 280 mosquitoes were used as controls. Adult wild female mosquitoes (collected as larvae), 3–5 days old, were exposed to DDT (4%) and deltamethrin (0.05%) insecticide-impregnated papers in WHO tubes for one hour. Two control tubes, each lined with paper impregnated with silicone oil, were run concurrently with the insecticide assays testing. Following exposure, mosquitoes were provided with a 10% sugar solution and maintained at 28 °C to 29 °C with 70–80% humidity. Mosquito mortality was observed and recorded after 24 h. The observed mortality of the test sample was calculated by summing the number of dead mosquitoes across all exposure tubes and then expressing this as a percentage of the total number of exposed mosquitoes. Mosquitoes were stored separately on silica gel for molecular analysis.
PBO synergist assays
WHO Whatman papers impregnated with the PBO synergist were used to perform the synergist assay. PBO-synergist assays were conducted using WHO-recommended procedures [13, 17]. A complete test included four holding tubes (each with 20 wild caught female mosquitoes) and five exposure tubes. The sample size was ~ 60 mosquitoes for sentinel sites and 20 An. arabiensis for the control replicates. A total of 120 female mosquitoes were used for the synergist-insecticide monitoring study from the Oshana (Onamutayi village) and Oshikoto regions (Oniimwandi and Omandongo village) in 2020. In 2021, 300 wild caught female mosquitoes were used from Oshikoto (Oniimwandi), Otjozondjupa (Otjituuo), Kavango West (Mukekete), Kavango East (Shadikongoro) and Zambezi (Sibbinda). For each sentinel site, a total of only 60 mosquitoes were exposed to the PBO synergist.
The mosquitoes were subjected to exposed in three WHO tubes under distinct conditions: (i) a dosage of 4% “PBO only”, (ii) pre-exposed to 4% “PBO” for one hour followed by exposure to 0.05% Deltamethrin for an additional hour (PBO + Deltamethrin), and (iii) exposure to 0.05% “Deltamethrin only”. Concurrently with the PBO assays, a control assay was conducted using a tube lined with paper impregnated with silicone oil. Test mosquitoes were maintained at 28°–29 °C and a relative humidity range of 70–80% during exposure and holding periods. Test mosquitoes were provided with 10% sugar solution ad libitum during the holding periods. Mosquito mortality was observed and recorded after 24 h. The observed mortality of the test sample was calculated by summing the number of dead mosquitoes across all exposure tubes and then expressing this as a percentage of the total number of exposed mosquitoes. This calculation was performed for each insecticide at each site.
Molecular identification of Anopheles gambiae
Dead and live mosquitoes were separated and labelled at the end of each assay. All mosquitoes were morphologically identified using keys [19] as An. gambiae s.l. All samples for 2018 and a subsample from 2020 underwent molecular species identification using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) diagnostic [20].
Analysis
WHO guidelines [13] were used to interpret the susceptibility status of An. gambiae s.l. mosquitoes after 24 h of exposure to insecticides. A mean mortality of > 98% indicated susceptibility to the insecticide, while a mean mortality between 90 and 98% indicated reduced susceptibility to the insecticide, and a mean mortality of < 90% indicated resistance to the insecticide. The Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare mosquito mortality between the sentinel sites using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 27 software. A Pearson's chi-square test was used to compare the Anopheles mosquito species composition between the regions in the R statistical package 4.1.2. WHO guidelines [13] were used to interpret the effect of the PBO synergist on mosquitoes. “If the mean mortality in the “insecticide only” samples is ≥ 90%, the effect of PBO cannot be reliably assessed. If the mean mortality in the “insecticide only” samples is < 90%, the effect of PBO can be interpreted according to the following criteria:
-
Complete restoration of susceptibility (mitigation of resistance) by pre-exposure to PBO (i.e., ≥ 98% mean mortality in the “PBO followed by insecticide” samples) implies that a monooxygenase-based resistance mechanism fully accounts for the expression of the resistant phenotype in the test population.
-
Partial restoration of susceptibility by pre-exposure to PBO (i.e., mean mortality in the “PBO followed by insecticide” samples is greater than mean mortality in the “insecticide only” samples but < 98%) implies that a monooxygenase-based resistance mechanism only partially accounts for expression of the resistant phenotype and that other resistance mechanisms are likely to be present in the test population.
All insecticide resistance analyses are presented for An. gambiae s.l., with the exclusion of non-amplifiers.
Anopheles species compositions
Morphologically, all species in the bioassays were identified as An. gambiae s.l. Of the mosquitoes tested for insecticide susceptibility (n = 1680), 1582 (94%) were successfully amplified using the An. gambiae s.l. diagnostic assay [20]. Anopheles gambiae sensu stricto (s.s.) made up the majority of amplified specimens (62%), and An. arabiensis came in second (38%). Non-amplified samples (n = 98) were not included in downstream analyses.
Due to capacity and funding limitations, only 72% (n = 309) of the PBO synergist assay samples from 2020 were subjected to molecular analysis. Approximately 84.3% (n = 200) of the samples molecularly identified from the Oshana region (n = 237) were An. arabiensis, 0.42% (n = 1) Anopheles quadriannulatus, and 15.2% (n = 36) did not amplify with PCR (non-amplifiers). From the Oshikoto region, 73.7% (n = 53) were An. arabiensis, and 26.4% (n = 19) were non-amplifiers. Samples from 2021 were not molecularly analysed. All results are presented for An. gambiae s.l. Overall, An. arabiensis (n = 253, 81.8%) was the dominant vector recorded.
A higher proportion of An. gambiae s.s. mosquitoes were sampled at most sites: 60.9% (n = 214) in Otjozondjupa, 80.3% (n = 196) in Oshana, 59.8% (n = 183) in Omusati, and 100% (n = 113) in Kunene. Approximately equal proportions of An. gambiae s.s. and An. arabiensis were observed in Oshikoto (50.3% (n = 72) and 49.7% (n = 71), respectively). Similarly, in Ohangwena, the proportions were 49.4% (n = 163) for An. gambiae s.s. and 50.6% (n = 167) for An. arabiensis, respectively), while in Kavango West, a higher proportion of An. arabiensis (56.8%; n = 54) was observed (Fig. 2). There was a significant difference in the species composition of the An. gambiae species complex between the regions (Pearson χ2, DF = 6, P = 0.001).
WHO Susceptibility bioassays
After conducting the WHO tube bioassays, molecular analyses were performed on a total of 1582 female An. gambiae s.l. mosquitoes. Of those, 980 were An. gambiae s.s. and 602 were An. arabiensis mosquitoes.
The results demonstrate that An. gambiae s.s. was resistant to deltamethrin 0.05% in Oshikoto, Kunene, and Kavango West (79, 86, and 67%, respectively) and that An. gambiae s.s. was less sensitive to deltamethrin in Omusati (97%) and Ohangwena (94%), as shown in Table 1. Anopheles gambiae s.s. showed reduced susceptibility to DDT in Kavango West (91%), while they showed full susceptibility (100%) in the rest of the regions. Anopheles arabiensis showed resistance to deltamethrin 0.05% in the Oshikoto region (82%), reduced susceptibility in Kavango West (96%), and full susceptibility (100%) in the rest of the regions. There is a reduced susceptibility of An. arabiensis to DDT 4% in the Kavango West (96%) region, whereas An. arabiensis vectors from the other regions showed full susceptibility (100%). A Kruskal-Wallis H test was performed for these data from 2018 and suggests that there is a difference in mean mortality by DDT and deltamethrin between the regions (P = 0.008; DF = 8).
PBO-synergist assay
In 2020, deltamethrin (0.05%) alone induced 93.3 and 95.0% mortality in Oshana and Oshikoto, respectively. After pre-exposure to the PBO synergist (4%) followed by exposure to deltamethrin (0.05%), the resistance status of mosquitoes in the Oshana and Oshikoto regions was completely restored to 100% susceptibility (Fig. 3). Mortality after pre-exposure to the PBO synergist increased by 6% in Oshana (from 93.3 to 100%) and by 5% in Oshikoto (from 95 to 100%). In 2021, deltamethrin (0.05%) alone induced 95.0, 90.0, 70.0, 80.0, and 75.0% mortality in Otjozondjupa, Oshikoto, Kavango East, Kavango West, and Zambezi, respectively. After pre-exposure to the PBO synergist (4%) followed by exposure to deltamethrin (0.05%), the resistance status of mosquitoes was completely restored to 100% susceptibility in all five regions (Otjozondjupa, Oshikoto, Kavango East, Kavango West, and Zambezi). The results also indicated that deltamethrin resistance in the Oshikoto region increased by 5% from 2020 to 2021 (from 95.0 to 90.0% mortality) (Fig. 3).
Discussion
The results of this study provide a comprehensive view of the Anopheles species compositions at the end of the rainy season, shedding light on critical implications for malaria control in Namibia. Notably, the analysis revealed that the Anopheles population consisted predominantly of Anopheles gambiae s.l., with An. arabiensis accounting for 38% and An. gambiae s.s. for 62% of the specimens. Remarkably, the presence of An. gambiae s.s. in Namibia, thought to have disappeared in the mid-2000s [21], suggests a resurgence of this vector species, potentially driven by factors such as low-quality indoor residual spraying (IRS) and inadequate coverage. This resurgence carries significant implications for the region’s malaria control efforts.
Anopheles gambiae s.s. has also been reported as the primary vector in neighbouring Angola [22] and, when compared to Anopheles funestus, is the most prevalent vector in Zimbabwe [23]. This underscores its potential for cross-border re-invasion and its adaptability to drier regions, such as Otjozondjupa, challenging previous assumptions [5, 24]. Consequently, scaling up IRS with effective insecticides, considering insecticide resistance, becomes imperative, particularly in malaria hotspots, with a recommended coverage of 85% or more [21]. In contrast, An. arabiensis, typically associated with lower rainfall floodplains, was unexpectedly abundant in the wetter and more humid Kavango West and Ohangwena regions, mirroring findings by Kamwi [21]. This uneven distribution of An. gambiae s.l. species underscores the influence of microenvironmental factors on vector presence [5]. Notably, the confirmation of both An. gambiae s.s. and An. arabiensis as a primary vector in Namibia, linked to malaria transmission in some parts of Africa [25, 26], raises concerns about year-round transmission with seasonal peaks [1, 12].
Moreover, parallel studies highlight the presence of other potential malaria vectors, such as Anopheles coustani s.l., Anopheles squamosus, Anopheles pharoensis, and An. funestus [27]. The non-amplifiers in this study point to the presence of non-An. gambiae s.l. samples—and probably include these species. Their inclusion in insecticide resistance tests, particularly for An. funestus, is essential for a comprehensive understanding of the impact of insecticides. Regarding the insecticide resistance aspect, the data reveal concerning trends. Some WHO insecticide resistance bioassays did not meet the required mosquito density due to operational constraints. Nevertheless, the results indicate reduced mortality (< 90%), signifying resistance to deltamethrin (0.05%) in both An. gambiae s.s. and An. arabiensis in specific regions. This resistance extends to the extensively used insecticide deltamethrin, mirroring trends observed in other countries [28, 29]. Insecticide resistance emerges as a significant threat to malaria control efforts [30].
Furthermore, the findings underscore the need for a shift in Namibia's IRS policy, advocating for insecticides other than pyrethroids and DDT. Given the increasing pyrethroid resistance in areas with high agricultural activity, such as Oshikoto and Kavango West, the role of agricultural insecticide uses in exerting selective pressure on Anopheles mosquitoes becomes evident [14]. Resistance to DDT is also observed, possibly due to knockdown resistance (kdr)-based cross-resistance between pyrethroids and DDT [31]. Such resistance can disrupt control efforts, leading to sporadic malaria outbreaks. Preserving the efficacy of pyrethroid-impregnated bed nets, a widely used vector control method, becomes crucial. The introduction of mosquito nets incorporating the PBO synergist, designed to counter metabolic resistance to pyrethroids [15, 32, 33], presents a potential solution. Notably, this study points to MFO-detoxifying enzymes as a likely resistance mechanism in An. gambiae s.l. populations [15], aligning with findings from Ghana. PBO synergist exposure successfully restored susceptibility to pyrethroids, demonstrating its operational potential.
However, it is important to note that PBO LLINs should ideally increase mortality by at least 10% [16], which was not consistently achieved across all regions. Nonetheless, the complete restoration of susceptibility in all tested sites with a ≥ 10% increase in mortality confirms the involvement of MFO enzymes in deltamethrin resistance [16].
Further research and replication of studies on PBO synergist are needed to ascertain their impact, as the efficacy of PBO LLINs may vary depending on local resistance levels and other resistance mechanisms [16, 33,34,35]. Overall, this study contributes to the growing body of evidence supporting the potential of PBO LLINs for malaria control in areas where resistance, although not assessed for intensity, has been confirmed. While specific resistance intensity assays were not performed in this study, the findings align with the broader context of resistance challenges, suggesting that PBO LLINs could be valuable tools in regions with reported moderate-to-high pyrethroid resistance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study underscores the pressing issue of insecticide resistance in malaria vectors in Namibia. Pyrethroid resistance is evident in two important vector species and is more pronounced in the predominant species, Anopheles. gambiae s.s., which is anthropophagic and endophilic. This finding raises concerns about the potential impact on the effectiveness of indoor residual spraying (IRS) and long-lasting insecticidal nets (LLINs), both critical components of malaria control efforts. It also poses a challenge to achieving the goal of malaria elimination. Addressing insecticide resistance demands a multifaceted approach, such as integrated vector management (IVM) strategies that encompass a range of interventions, including IRS, LLINs, larviciding, and personal protective tools such as repellents. Such a comprehensive approach can help reduce human-vector contact and disrupt the vector's life cycle at multiple stages [36]. One unexpected finding was the predominance of An. gambiae s.s. over An. arabiensis in arid regions, suggesting that the bionomics of Namibian Anopheles vectors of malaria may vary significantly across different ecological niches. This calls for further site-specific research to better understand the dynamics of malaria vectors in these dry areas.
Nonetheless, the study also revealed a promising avenue for overcoming pyrethroid resistance through pre-exposure to PBO synergists. This preexposure restored susceptibility, leading to 100% mortality among pyrethroid-resistant An. gambiae s.l. mosquitoes. This finding suggests the potential efficacy of pyrethroid-impregnated PBO LLINs in Namibia. It is important to note that PBO synergistic tests were conducted on wild An. gambiae s.l. complex mosquitoes, collected as larvae. Therefore, it will be important to complete the PCR assays to distinguish species-specific insecticide susceptibility to provide valuable insights into the dynamics of resistance among different vector species. Continued surveillance and monitoring of resistance, along with the inclusion of other vectors such as An. funestus, are vital components of Namibia’s malaria elimination strategy.
Data availability
The data supporting this study's findings is available from the Ministry of Health and Social Services, Namibia. However, restrictions apply to the availability of this data, as it was used under license for the current study and is not publicly available. Nonetheless, the authors can provide the data upon reasonable request and with permission from the MoHSS.
Abbreviations
- CHAI:
-
Clinton health access initiative
- DDT:
-
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane
- EHP:
-
Environmental health practitioners
- IRS:
-
Indoor residual spraying
- IVM:
-
Integrated vector management
- kdr :
-
Knockdown resistance
- LLIN:
-
Long-lasting insecticidal net
- MFO:
-
Mixed-function oxidases
- MoHSS:
-
Ministry of health and social services
- NMCP:
-
National malaria control programme
- NVDCP:
-
National vector-borne disease control programme
- PBO:
-
Piperonyl butoxide
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- RDT:
-
Rapid diagnostic test
- s.l. :
-
Sensu lato
- s.. :
-
Sensu stricto
- UNAM:
-
University of Namibia
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
MoHSS. National vector-borne diseases control programme annual report 2017 Namibia. Windhoek: MoHSS; 2017.
Smith JL, Mumbengegwi D, Haindongo E, Cueto C, Roberts KW, Gosling R, et al. Malaria risk factors in northern Namibia: the importance of occupation, age and mobility in characterizing high-risk populations. PLoS ONE. 2021;16: e0252690.
Noor AM, Uusiku P, Kamwi RN, Katokele S, Ntomwa B, Alegana VA, et al. The receptive versus current risks of Plasmodium falciparum transmission in northern Namibia: implications for elimination. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13:184.
malERA Consultative Group on Vector Control. A research agenda for malaria eradication: vector control. PLoS Med. 2011;8: e1000401.
Smith Gueye C, Gerigk M, Newby G, Lourenco C, Uusiku P, Liu J. Namibia’s path toward malaria elimination: a case study of malaria strategies and costs along the northern border. BMC Publ Health. 2014;14:1190.
Ng’ang’a PN, Aduogo P, Mutero CM. Long lasting insecticidal mosquito nets (LLINs) ownership, use and coverage following mass distribution campaign in Lake Victoria basin. BMC Publ Health. 2021;21:1046.
Pryce J, Richardson M, Lengeler C. Insecticide-treated nets for preventing malaria. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000363.pub3.
MoHSS. National vector-borne diseases control programme annual report 2018/2019 Namibia. Windhoek: MoHSS; 2019.
WHO. Achieving and maintaining universal coverage with long-lasting insecticidal nets for malaria control. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017.
Bhatt S, Weiss DJ, Cameron E, Bisanzio D, Mappin B, Dalrymple U, et al. The effect of malaria control on Plasmodium falciparum in Africa between 2000 and 2015. Nature. 2015;526:207–11.
Oumbouke WA, Rowland M, Koffi AA, Alou LPA, Camara S, N’Guessan R. Evaluation of an alpha-cypermethrin + PBO mixture long-lasting insecticidal net VEERALIN® LN against pyrethroid resistant Anopheles gambiae s.s.: an experimental hut trial in M’bé, central Côte d’Ivoire. Parasit Vectors. 2019;12:544.
MoHSS. Namibia Malaria Strategic Plan 2017–20222020. 2017, Windhoek.
WHO. Global plan for IR management in malaria vectors. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
Fodjo BK, Koudou BG, Tia E, Saric J, N’Dri PB, Zoh MG, et al. Insecticides resistance status of An. gambiae in areas of varying agrochemical use in Côte d’Ivoire. Biomed Res Int. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2874160.
Dadzie SK, Chabi J, Asafu-Adjaye A, Owusu-Akrofi O, Baffoe-Wilmot A, Malm K, et al. Evaluation of piperonyl butoxide in enhancing the efficacy of pyrethroid insecticides against resistant Anopheles gambiae s.l. in Ghana. Malar J. 2017;16:342.
WHO. Conditions for deployment of mosquito nets treated with a pyrethroid and piperonyl butoxide: recommendations. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017.
WHO. Test procedures for IR monitoring in malaria vector mosquitoes Switzerland. 2nd ed. Geneva: WHO; 2016.
Williams J, Pinto J. Training manual on malaria entomology for entomology and vector control technicians (basic level). Washington: USAID; 2012.
Gillies MT, Coetzee M. A supplement to the anophelinae of Africa south of the Sahara (Afro-tropical region). Johannesburg: South African Institute for Medical Research; 1987. https://doi.org/10.4236/wja.2014.41008.
Scott JA, Brogdon WG, Collins FH. Identification of single specimens of the Anopheles gambiae complex by the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1993;49:520–9.
Kamwi RC. Malaria situation in Namibia: a study of vector species and effectiveness of the past and current control strategies in selected parts of Namibia Namibia. University of Namibia; 2005.
Cuamba N, Choi KS, Townson H. Malaria vectors in Angola: distribution of species and molecular forms of the Anopheles gambiae complex, their pyrethroid insecticide knockdown resistance (kdr) status and Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite rates. Malar J. 2006;5:2.
Wiebe A, Longbottom J, Gleave K, Shearer FM, Sinka ME, Massey NC, et al. Geographical distributions of African malaria vector sibling species and evidence for insecticide resistance. Malar J. 2017;16:85.
Sinka ME, Bangs MJ, Manguin S, Coetzee M, Mbogo CM, Hemingway J, et al. The dominant Anopheles vectors of human malaria in Africa, Europe and the middle east: occurrence data, distribution maps and bionomic précis. Parasit Vectors. 2010;3:117.
Okwa O, Rasheed A, Adeyemi A, Omoyeni M, Fayemi A, Ogunwomoju A. Anopheles species abundances, composition and vectoral competence in six areas of Lagos: Nigeria. J Cell Anim Biol. 2007;1:19–23.
Oringanje C, Alaribe AA, Oduola AO, Oduwole OA, Adeogun AO, Meremikwu MM, et al. Vector abundance and species composition of Anopheles mosquito in Calabar. Nigeria J Vector Borne Dis. 2011;48:171–3.
Mwema T, Lukubwe O, Joseph R, Maliti D, Iitula I, Katokele S, et al. Human and vector behaviors determine exposure to Anopheles in Namibia. Parasit Vectors. 2022;15:436.
Kanyangarara M, Mamini E, Mharakurwa S, Munyati S, Gwanzura L, Kobayashi T, et al. Reduction in malaria incidence following indoor residual spraying with actellic 300 CS in a setting with pyrethroid resistance: Mutasa district Zimbabwe. PLoS ONE. 2016;11: e0151971.
WHO. Indoor residual spraying: An operational manual for IRS for malaria transmission, control and elimination. 2nd ed. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.
Hemingway J, Ranson H, Magill A, Kolaczinski J, Fornadel C, Gimnig J, et al. Averting a malaria disaster: will insecticide resistance derail malaria control? Lancet. 2016;387:1785–8.
Matiya DJ, Philbert AB, Kidima W, Matowo JJ. Dynamics and monitoring of insecticide resistance in malaria vectors across mainland Tanzania from 1997 to 2017: a systematic review. Malar J. 2019;18:102.
Sovi A, Keita C, Sinaba Y, Dicko A, Traore I, Cisse MBM, et al. Anopheles gambiae (s.l.) exhibit high intensity pyrethroid resistance throughout southern and central Mali (2016–2018): PBO or next generation LLINs may provide greater control. Parasit Vectors. 2020;13:239.
Toe KH, Müller P, Badolo A, Traore A, Sagnon N, Dabiré RK, et al. Do bednets including piperonyl butoxide offer additional protection against populations of Anopheles gambiae s.l. that are highly resistant to pyrethroids? An experimental hut evaluation in Burkina Fasov. Med Vet Entomol. 2018;32:407–16.
Churcher TS, Lissenden N, Griffin JT, Worrall E, Ranson H. The impact of pyrethroid resistance on the efficacy and effectiveness of bednets for malaria control in Africa. Elife. 2016. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.16090.
Gleave K, Lissenden N, Chaplin M, Choi L, Ranson H. Piperonyl butoxide (PBO) combined with pyrethroids in insecticide-treated nets to prevent malaria in Africa. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD012776.pub3.
Cisse MBM, Sangare D, Oxborough RM, Dicko A, Dengela D, Sadou A, et al. A village level cluster-randomized entomological evaluation of combination long-lasting insecticidal nets containing pyrethroid plus PBO synergist in southern Mali. Malar J. 2017;16:477.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the University of Namibia (UNAM) Multidisciplinary Research, Science, Technology and Innovation Division, the Malaria Elimination Initiative–University of California, and the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI), which provided funds for this work. Thanks to the Ministry of Health and Social Services (MoHSS) Namibia–National Vector-borne Diseases Control Programme (NVDCP) for providing the facilities for this work and the Environmental Health Practitioners (EHPs) who assisted with larval collections.
Funding
The insecticide resistance study was funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (Gates Grant # Inv-009652) through the Malaria Elimination Initiative, University of California. The PBO synergist study was funded by the Clinton Health Access Initiative (Grant # CHGMALMELIM5/BMGFMELIM4) and Global Fund (Grant #NAM-Z-NVDCP 2021–2023). It was also partially funded by UNAM and MoHSS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RNJ, PNU, II, DVM, DW, STK, SBO, ÉAV, AT, CS, NFL, and DRM conceived and designed the study. DRM, SJE and SBO supervised the study. PNU, II, OL, SBO, DW and STK were responsible for project oversight and management. RNJ, II, DVM, OL, and STK led the entomology field activities for larval collection. RNJ, TM, II, and DVM raised the mosquitoes in the insectary. RNJ, TM and DVM conducted the WHO tube bioassays. RNJ conducted the PBO synergist assays. RNJ, TM, MT, LE, OL, and DRM performed the molecular tests. RNJ, DRM, and NFL performed the data analysis and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was part of a larger study being conducted by the Ministry of Health and Social Services (MoHSS), National Vector-borne Disease Control Programme (NVDCP). This study was authorized by the MoHSS Biomedical Research Ethics Committee and the University of Namibia Health Research Ethics Committee. Informed consent forms were provided to all the blood volunteers, and they were required to read and understand the content of the consent and ask questions and clarification. The volunteers were tested for malaria each Monday of the week; all the rapid diagnostic tests (RDT) for malaria were conducted by a qualified nurse from the MoHSS. The participants were also compensated for their time and effort.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Joseph, R.N., Mwema, T., Eiseb, S.J. et al. Insecticide susceptibility status of Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes and the effect of pre-exposure to a piperonyl butoxide (PBO) synergist on resistance to deltamethrin in northern Namibia. Malar J 23, 77 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-024-04898-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-024-04898-y