Abstract
This article reviews experimental and clinical data on the use of magnesium as a neuroprotective agent in various conditions of cerebral ischemia. Whereas magnesium has shown neuroprotective properties in animal models of global and focal cerebral ischemia, this effect could not be reproduced in a large human stroke trial. These conflicting results may be explained by the timing of treatment. While treatment can be started before or early after ischemia in experimental studies, there is an inevitable delay of treatment in human stroke. Magnesium administration to women at risk for preterm birth has been investigated in several randomized controlled trials and was found to reduce the risk of neurological deficits for the premature infant. Postnatal administration of magnesium to babies after perinatal asphyxia has been studied in a number of controlled clinical trials. The results are promising but the trials have, so far, been underpowered. In aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), cerebral ischemia arises with the onset of delayed cerebral vasospasm several days after aneurysm rupture. Similar to perinatal asphyxia in impending preterm delivery, treatment can be started prior to ischemia. The results of clinical trials are conflicting. Several clinical trials did not show an additive effect of magnesium with nimodipine, another calcium antagonist which is routinely administered to SAH patients in many centers. Other trials found a protective effect after magnesium therapy. Thus, it may still be a promising substance in the treatment of secondary cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal SAH. Future prospects of magnesium therapy are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Pathophysiology and molecular effects
The interruption of cerebral blood flow (CBF) is followed by a complex pathophysiological cascade which ultimately results in ischemic cell death. ATP-depletion and ischemic depolarization lead to excessive cellular calcium-entry. Under physiological conditions, calcium is an important second messenger whereas excessive calcium is toxic and induces mechanisms of cell destruction. Depending on the kind and severity of ischemia, tissue necrosis and/or apoptosis are the ultimate consequences [1]. Since the importance of calcium in ischemic cell death had been discovered, calcium antagonists have come into the focus of ischemic neuroprotection [2]. Magnesium has been called “nature’s physiologic calcium blocker” as it is a physiological mineral and interferes with calcium in a variety of ways [3]. The bivalent magnesium cation can compete with calcium ions for receptor binding or passage through ion channels. It dilates blood vessels by competitive inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle cells [4], improves rheological functions by inihibiton of platelet aggregation [5, 6], and increases the deformability of red blood cells [7]. Under experimental conditions, it prevents cellular calcium influx and excitatory amino acid release in neurons by blockade of N-type and L-type calcium channels [8], prevents cellular calcium entry through NMDA-receptor channels [9], reduces calcium-induced mitochondrial dysfunction [10] and preserves cellular energy metabolism [11]. By these mechanisms, magnesium may inhibit or delay ischemic cell death during and after cerebral ischemic events.
Physiological concentrations and side effects
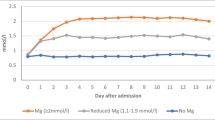
In human serum, the physiological magnesium concentration is 0.7 – 1.1 mmol/l [12]. Magnesium is almost completely renally excreted. Oral intake may result in diarrhea but does not markedly increase serum concentrations unless patients suffer from renal insufficiency. Intravenous magnesium has been used for a long time in obstetrics for the treatment of eclampsia and in cardiology for the treatment of supraventricular tachycardia. Therefore, side effects are well-defined. During magnesium treatment, hypocalcemia develops (Figure 1). With increasing serum concentrations, hypotension and bradycardia occur and tendon reflexes disappear. Serum concentrations over 6 mmol/l can result in coma, respiratory insufficiency and cardiac arrest. In patients with renal failure, magnesium may quickly accumulate and result in hazardous side effects.
Low blood pressure is a risk factor for aggravation of ischemic damage in states of cerebral ischemia reducing collateral flow in the ischemic penumbra. Therefore, magnesium doses must be kept low enough to ensure stable blood pressure if it is administered for the purpose of neuroprotection. In an experimental study of temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in rats, serum concentrations of 2.0 – 2.5 mmol/l showed the highest neuroprotective effect [13]. In higher doses, the cardiodepressive effect seemed to limit the extent of neuroprotection. In the clinical use in stroke and SAH, reports about side effects are diverse. Most authors did not find significant side effects apart from hypocalcemia, occasional flushing or a slight tendency to bradycardia [14–20], others reported significant hypotension and cardiorespiratory depression in spite of close surveillance of serum levels [21]. Co-treatment with other pharmaceutics with a antihypertensive potential may be a possible factor. The doses that are required to maintain certain target levels vary widely and depend on renal excretion [19]. Serum electrolyte concentrations are to be followed frequently with consequent adaptation of infusion rates. With a mean of 1.27 ± 0.15 mmol/l, physiological cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentrations are higher than serum concentrations suggesting an active transport through the blood–brain-barrier and blood-CSF-barrier. However, CSF concentrations increase only moderately even after several days of high-dose administration (1.50 ± 0.16 mmol/l at serum levels of 2.14 ± 0.21) indicating a saturation of transport capacity [19] (Figure 2).
Experimental data
The use of magnesium as a neuroprotective agent has been examined in various experimental models of cerebral ischemia with rather conflicting results. This may be explained by the variety of experimental models, the wide range of target parameters, and the different dosages, timing and routes of administration. Experimental data was collected by a Medline search for “magnesium”, “experimental” and “cerebral ischemia” or “cerebral hypoxia”.
Global ischemia
Blair et al. did not find a reduction of hippocampal damage by a 5 mmol/kg intravenous bolus of magnesium chloride (MgCl2) immediately before 10 minutes of bilateral carotid occlusion in rats. Regarding the well-known concentration-related spectrum of side effects, it is remarkable that the authors did not observe any major side effects – especially regarding cardiovascular parameters - although the single intravenous bolus injection led to a tenfold elevation of plasma levels 10-fold [12, 22]. The animals’ heart-rate, the most sensitive parameter during magnesium treatment, however, was not measured so that a cardiodepressive effect cannot be finally excluded [19].
Studies with slower resorption of magnesium, in contrast, showed neuroprotective effects in global ischemia. The subcutaneous administration of the same amount (5 mmol/kg) of magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) 48 hours before a 15-minute period of forebrain ischemia in rats resulted in a 24% and 39% reduction of cell damage in the hippocampal CA1- and CA3-area, respectively [23]. Zhou et al. found a 50% reduction of hippocampal damage by an intraperitoneal administration of 16 mmol/kg MgSO4 30 minutes prior to 10 minutes of bilateral carotid artery occlusion [24]. However, neither body nor brain temperature were measured and regulated in these studies. In a series of studies using 8 minutes of bilateral carotid occlusion in rats, Zhu and coworkers found that a postischemic temperature drop could be the decisive factor for the neuroprotective effect of magnesium. When animals were kept strictly normothermic, magnesium did not reduce hippocampal damage. If body temperature was mildly reduced, hippocampal damage was significantly reduced after magnesium treatment compared to hypothermic controls [25, 26].
Permanent focal ischemia
Several groups investigated the protective efficacy in studies of permanent focal ischemia [27–30]. Apart from Roffe et al. [30], all authors reported reduced infarct volumes. In all of these studies, magnesium was administered either before or shortly after the onset of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Yang et al. evaluated the effect of magnesium administered 2, 6 or 8 hours after permanent MCAO. While the survival rate improved only in the 2-hour group, infarct volume decreased in the 2- and 6 hour groups and neurological outcome improved in all treatment groups [31]. This finding gave rise to the expectation that even delayed magnesium treatment might be effective in stroke patients.
Temporary focal ischemia
In a rat model of 90 minutes of MCAO, Marinov et al. found a nearly 60% reduction of infarct volume after 24 hours by a preischemic intraarterial bolus of 90 mg/kg MgSO4. The authors concluded that this superior protective effect was due to the intraarterial route of administration [32]. However, this overwhelming neuroprotective effect could not be reproduced in a direct comparison of intraarterial and intravenous administration of the same dose in the same model [33]. The infarct volume – assessed after 7 days - was reduced by 25% compared to saline treated animals in both the intraarteial and the intravenous groups. The difference between assessment of infarct volume after 1 day and after 7 days rather suggests that the neuroprotective effect of magnesium may, in part, be temporary [33]. The results of the latter study were rather consistent with previous results of the same group [34].
In most studies, the neuroprotective effect of magnesium in transient focal ischemia was moderate but reproducible. Magnesium has shown synergistic effects with other substances like radical scavengers and immunosuppressants, which makes it an interesting substance for the development of combination therapies [27, 34]. An experimental dose-finding study in transient MCAO in rats showed the highest neuroprotective effect in animals treated by a continuous elevation of serum levels to 2.0 – 2.5 mmol/l. Higher levels led to a cardiodepressive effect, probably limiting the neuroprotective efficacy [13].
Hypoxia/Ischemia
Several authors have studied the neuroprotective potential of magnesium in perinatal asphyxia in animal models. In an study of hypoxia/ischemia, Spandou and coworkers subjected newborn rats to permanent unilateral carotid occlusion and 1 or 2 hours of hypoxia by reduction of the inspired oxygen fraction to 8%. Treatment with 4 doses of 500 mg/kg MgSO4 resulted in a delay of energy depletion and a reduction of hippocampal damage compared to saline treated control animals [35]. Using the same species and experimental model, Thordstein et al. reported a neuroprotective effect of MgSO4 in combination with the oxygen scavengers L-Methionine and Mannitol determined as a less pronounced reduction of hemispheric weight than in placebo treated control anaimals [36].
In contrast, magnesium treatment did not show a neuroprotective effect in a model of hypoxia/ischemia in piglets [37, 38], where the animals were subjected to temporary bilateral carotid occlusion and a reduction of the inspiratory oxygen fraction to 0.12 until the ratio of phosphocratinine and inorganic phosphate, determined by magnetic resonance spectroscopy, had fallen to zero. The authors neither found a delay of energy depletion after MgSO4 treatment (400 mg/kg after 1 hour of resuscitation and 200 mg/kg after 24 and 48 hours) [38] nor a reduction of brain tissue damage [37]. In a model of 60 minutes of hypoxia without carotid ligation (inspiratory oxygen fraction 5 – 7%), in contrast, treatment with a bolus of 600 mg/kg MgSO4 followed by an infusion of 300 mg/kg through 1 hour of hypoxia did preserve cerebral energy stores in newborn piglets [39].
Experimental models of permanent and transient focal cerebral ischemia find their clinical counterparts in embolic stroke, events of temporary ischemia during neurosurgical operations or delayed vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage, respectively, models of hypoxia/ischemia in the clinical situation of perinatal asphyxia. Thus, a series of clinical studies has been performed during the last 15 years evaluating the neuroprotective potential of magnesium after embolic stroke, its ability to prevent ischemic deficits in secondary vasospasm after aneurysmal SAH and its potential to ameliorate ischemic/hypoxic damage after perinatal asphyxia.
Clinical trials
Clinical data was collected by a MEDLINE-search for “magnesium”, “clinical trial” and “stroke”, “subarachnoid hemorrhage” or “asphyxia”.
Stroke
Promising results in experimental studies have raised high expectations that magnesium might be a valuable drug for the treatment of stroke patients. In 1984, a first clinical trial was launched investigating the tolerability of magnesium in human stroke [40]. In 1995, a randomized placebo-controlled pilot study was published [41], in which 30 patients were treated by a bolus infusion of 8 mmol MgSO4 followed by a continuous infusion of 65 mmol over 24 hours in order to double the physiological serum concentrations. 30 patients served as a control group. In the magnesium group, 30% of the patients were dead or disabled compared to 40% in the control group. The dose regimen had been chosen in accordance with previous studies on myocardial infarction [42] and because serum levels of approximately 1.5 mmol/l had shown a neuroprotective effect in experimental studies [32]. The initial bolus of 8 mmol, however, did not markedly elevate serum magnesium levels and target levels were only reached after 24 hours. A “dose optimization study” was conducted in 25 patients preparing a large clinical trial. Target levels were most rapidly reached by an initial bolus of 16 mmol MgSO4, still without cardiovascular side effects [16]. The IMAGES-trial (Intravenous Magnesium Efficacy in Stroke Trial) was launched in 1997 treating patients with ischemic stroke within 12 hours after the onset of symptoms and included 2598 patients [43]. After promising results of animal studies and small pilot trials, this large multicenter trial did not show an overall improvement of clinical outcome by magnesium treatment. Only a subgroup of patients with lacunar stroke profited from magnesium treatment [44] (Table 1).
It has been thoroughly discussed why the IMAGES trial failed to reproduce the positive results gained in experimental studies. The sample size might have still been too small or side effects might have been hazardous in some patients masking a positive effect in the majority. Moreover, the mean delay from the onset of clinical symptoms to the beginning of treatment was 7 hours. Since the efficacy of neuroprotective agents may decrease the longer their administration is delayed [31], this issue is given consideration to by the currently conducted FAST-MAG trial (“Field Administration of Stroke Therapy – Magnesium”) in which patients are enrolled within the first 2 hours after the onset of stroke symptoms [45]. One drawback of the IMAGES trial may have been the lack of proper preclinical testing of the dose-regimen and study-design before entering a large multicenter trial. It was proposed that a target serum concentration twice as high as the physiological concentration may be the optimum treatment for stroke patients [16, 41]. However, neither a preclinical dose-finding study using an established experimental stroke model nor a clinical (phase 2) dose-finding study had been conducted in advance to this large clinical trial.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Most cases of spontaneous SAH are caused by the rupture of an intracranial aneurysm. Aneurysmal SAH is followed by a sequence of different forms of cerebral ischemia: First, global ischemia arises due to an elevation of intracranial pressure (ICP). Starting immediately after SAH, a dissociation of cerebral perfusion pressure and CBF has been found which enhances and prolongs the early perfusion deficit after SAH. It is likely to be caused by an acute vasoconstriction, a disseminated cerebrovascular reaction [46, 47]. Finally, delayed vasospasm of subarachnoid vessels appears in a high percentage of SAH patients within the first 2 weeks after SAH. Subarachnoid vessels become increasingly spastic and cerebral blood flow (CBF) may fall below ischemic thresholds [48]. This feared complication affects 20 – 30% of SAH patients and may result in cerebral infarction, permanent morbidity or death. Delayed cerebral vasospasm after SAH is self-limiting after several days and, therefore, resembles a form of transient focal ischemia. This bears the opportunity to undertake neuroprotective measures prior to the onset of ischemia. In an animal model of temporary MCAO, a dose-finding study has demonstrated that the intra- and postischemic maintainance of serum concentrations between 2.0 and 2.5 mmol/l offered the highest neuroprotection [13].
The potential role for a treatment with magnesium was supported by the observation that hypomagnesemia is frequently found in SAH patients and correlates with the amount of blood in the subarachnoid space and with the patient’s neurological condition at the time of hospital admission. Hypomagnesemia arising during the course of treatment, in turn, correlates with the appearance of secondary neurological deficits and ischemic infarctions [49]. A series of clinical trials has been launched to assess the ability to reduce secondary neurological deficits after SAH (Table 2).
Luo and coworkers compared treatment with 100 – 200 mmol MgSO4 to a control group without giving other calcium antagonists. The authors reported a reduced incidence of secondary brain infarction and clinical deterioration [50]. In a randomized study, Veyna and colleagues raised serum magnesium levels to 1.7 – 2.3 mmol/l for 10 days in 20 SAH patients, reported no significant side effects and a non-significant reduction of delayed vasospasm and improvement of clinical outcome compared to 20 control patients [18].
Chia and colleagues compared 23 SAH patients with historical controls. Magnesium serum concentrations were kept between 1.0 and 1.5 mmol/l. The authors found a significant reduction of angiographic vasospasm [15].
Prevedello and coworkers reported a shorter hospitalization time by high dose magnesium therapy in a non-randomized study [53]. Muroi and coworkers treated patients with a loading-dose of 16 mmol MgSO4 followed by a continuous infusion of 64 mmol/day. In 16 patients, magnesium infusions had to be discontinued because of severe side effects, particularly hypotension, although mean magnesium serum levels in these patients were only 1.40 mmol/l. The authors reported a trend to better clinical outcome in magnesium treated patients [21].
In a randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter study conducted by van den Bergh et al. [17], patients received a daily dose of 64 mmol MgSO4 for 14 days. The results of this trial were promising as magnesium reduced the risk of delayed cerebral ischemia by 34% and the risk for poor outcome by 23%. Including 283 patients, however, the study was still underpowered. In 2006, Stippler and coworkers administered 50 mmol MgSO4 in 38 patients and compared them to 38 matched controls in a matched cohort study [54]. They found a reduced incidence of secondary neurological deterioration and a tendency to better neurological outcome. In a south-east Asian/Australian trial, 327 patients were randomized to receive a daily dose of 80 mmol/l MgSO4 or placebo. The authors reported no significant benefit of magnesium-treatment regarding clinical outcome after 6 months or clinical vasospasm [20]. The results of the largest clinical trial have just recently been published by Mees and coworkers. In this European/South American multicenter study, 1,204 patients with aneurysmal SAH were enrolled and assigned to one of two study arms to either receive 64 mmol MgSO4 per day or serve as controls. The administration of MgSO4 did not improve clinical outcome assessed 3 months after SAH [52].
The results of these clinical trials regarding the efficacy of magnesium require a critical analysis. Except for the very first clinical study by Luo et al. [50], who compared magnesium treatment to a true placebo group, all patients enrolled in these trials were co-treated with nimodipine. Nimodipine, a pyrrolopyrimidine-type calcium antagonist, has been intensively tested in various clinical studies in the 1980s and 1990s. All trials but one [55] failed to find a significant improvement of patient outcome. Analyzing the pooled data for nimodipine trials, a Cochrane review still revealed an advantage of nimodipine treatment, so that this treatment is routinely used in many centers. The Cochrane article concludes, however, that the evidence for nimodipine “is not beyond any doubt” since the benefit of treatment is largely determined by one trial [55, 56]. Schmid-Elsaesser et al. compared nimodipine treatment to magnesium treatment and found no marked and significant difference in the incidence of vasospasm and clinical outcome [51].
In our own placebo-controlled study 107 patients were randomized to either receive a placebo infusion or to receive a variable dose of intravenous MgSO4 in order to maintain serum concentrations of 2.0 – 2.5 mmol/l for 10 days or – if there was clinical, angiographic and/or ultrasonographic vasospasm – until the signs of vasospasm had disappeared or to receive a placebo infusion [19]. The patients were not treated with other calcium antagonists. The incidence of ultrasonographic/angiographic vasospasm and of secondary ischemic infarction was lower in magnesium-treated patients. The improvement of outcome and mortality did not reach the level of significance.
Perinatal asphyxia
Magnesium has for a long time been used for the treatment of eclampsia [57]. For the treatment of eclamptic seizures, it has been found to be more effective than phenytoin and nimodipine [58, 59]. Due to its reported neuroprotective effect, observational studies have been performed assessing the protective effect for the child. In very low birth weight children, Nelson et al. [60] and Schendel et al. [61] reported a lower incidence of cerebral palsy. Randomized trials for prenatal magnesium administration were called for [62]. In large randomized placebo-controlled trials, Marret et al. found a non-significant improvement of infant mortality and white-matter injury [63], Crowther et al. a significant improvement of motor function [64] and Rouse et al. a reduced rate of cerebral palsy [65]. In the MAGPIE trial, less children had neurosensory deficits assessed by questionnaires, however, without statistical significance [66] (Table 3a). The results of these clinical trials were analyzed in a meta-analysis that concluded that magnesium administration to women at risk of preterm birth is neuroprotective for the preterm fetus [67].
Several authors have assessed the neuroprotective efficacy of magnesium administered after delivery to neonates with asphyxia. Levene et al. [68] and Gathwala et al. [71] assessed the safety of intravenous administrations of 250 mg/kg. Whereas Groenendaal and coworkers found no effect on pathological EEG patterns [69], Ishiba et al. reported less pathological EEG- and CT-findings, a higher rate of oral feeding and better short-term outcome [70]. Bath et al. [72] and Gathwala et al. [73] included developmental and neurological outcome measures as endpoints of their randomized placebo-controlled trials. Both groups reported a reduction of neurological deficits and abnormal CT-findings. However, both trials included only 40 patients and were underpowered to provide definitive evidence for the effectiveness of postpartum administration in perinatal asphyxia (Table 3b).
Conclusion and future prospects
Magnesium can be beneficial in cerebral ischemia. The range of results suggests that its effect depends on the timing of treatment, route of administration, and co-medication. Different forms of ischemia are likely to require different dose regimens. Magnesium levels in serum and CSF are well controllable because they are easy to measure and follow. Compared to other calcium antagonists, magnesium may be more suitable as a component of a combination therapy [74].
Stroke
In spite of a reproducible neuroprotective effect in experimental models of cerebral ischemia no randomized clinical trial has, to date, confirmed the neuroprotective effect in human stroke. The FAST-MAG trial, which is currently being conducted, follows a novel concept as it is the first clinical study which starts treatment before hospital admission. This trial conception considers that the delay from the onset of ischemia to the start of infusion may have been too long in the IMAGES trial to result in a neuroprotective effect. Another interesting approach for stroke therapy could be the combination of intravenous magnesium with mild systemic hypothermia as recently proposed by Zhu and Meloni after positive results in experimental studies [26, 75].
Perinatal asphyxia
The administration of magnesium to women in preterm labor has been studied in various randomized placebo-controlled trials. A meta-analysis has found a benefit for this treatment with respect to the neurological outcome for the infant [67]. The effect of magnesium adminstration to chidren born at term that suffered parinatal asphyxia is not clear. Two randomized clinical studies have reported a beneficial effect of magnesium therapy but were underpowered. To date, no larger randomized trial has been published.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Similar to the prophylactic preterm magnesium administration to infants at risk to suffer perinatal hypoxia, neuroprotective drugs can be administered prior to delayed vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Large clinical trials assessing the efficacy of magnesium in combination with nimodipine, another calcium antagonist which is, in many centers, used as a standard treatment for all patients, found no additional, synergistic effect. Pharmacologically, the co-administration of magnesium and other calcium-antagonists is the attempt to enhance neuroprotection by two similar substances. Thus, it is not surprising that magnesium and nimodipine do not exert a synergistic neuroprotective effect while specific side effects may be enhanced [21]. The results of Schmid-Elsaesser et al. showing no significant difference between nimodipine treatment and magnesium treatment, challenge the routine use of nimodipine in aneurysmal SAH [51]. The comparison of magnesium treatment to a true placebo group to prevent secondary neurological deficits after SAH showed promising results [19, 50] The bioavailability may still be improved by a clinical dose-finding study. Even after continuous high-dose treatment, however, CSF levels remain markedly lower than serum levels [19] (Figure 2). For a direct – topical - dilatory effect on subarachnoid vessels, however, much higher concentrations are required [76, 77]. Those are not achievable by intravenous administration without serious side effects [12]. Intrathecal administration of MgSO4 by a microcatheter placed directly into the subarachnoid space has been examined by Mori et al. in experimental models of SAH in rats and dogs and has demonstrated a CBF-enhancing [78] and spasmolytic effect [79]. First experiences in SAH patients suffering clinical deterioration due to cerebral vasospasm showed an attenuation of cerebral vasoconstriction [80]. Thus, an intracisternal therapy could be an interesting and promising approach for a more efficient therapy of delayed cerebral vasospasm.
References
Siesjo BK: Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia. Part I: Pathophysiology. J Neurosurg 1992,77(2):169–184.
Ginsberg MD: Neuroprotection for ischemic stroke: past, present and future. Neuropharmacology 2008,55(3):363–389. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.12.007
Iseri LT, French JH: Magnesium: nature’s physiologic calcium blocker. Am Heart J 1984,108(1):188–193. 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90572-6
Altura BM, Altura BT, Carella A, Gebrewold A, Murakawa T, Nishio A: Mg2+−Ca2+ interaction in contractility of vascular smooth muscle: Mg2+ versus organic calcium channel blockers on myogenic tone and agonist-induced responsiveness of blood vessels. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 1987,65(4):729–745. 10.1139/y87-120
Dong JF, Cruz MA, Aboulfatova K, Martin C, Choi H, Bergeron AL, Martini SR, Kroll MH, Kent TA: Magnesium maintains endothelial integrity, up-regulates proteolysis of ultra-large von Willebrand factor, and reduces platelet aggregation under flow conditions. Thromb Haemost 2000,99(3):586–593.
Kh R, Khullar M, Kashyap M, Pandhi P, Uppal R: Effect of oral magnesium supplementation on blood pressure, platelet aggregation and calcium handling in deoxycorticosterone acetate induced hypertension in rats. J Hypertens 2000,18(7):919–926. 10.1097/00004872-200018070-00014
Schauf B, Becker S, Abele H, Klever T, Wallwiener D, Aydeniz B: Effect of magnesium on red blood cell deformability in pregnancy. Hypertens Pregnancy 2004,24(1):17–27.
Peruche B, Krieglstein J: Mechanisms of drug actions against neuronal damage caused by ischemia–an overview. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1993,17(1):21–70. 10.1016/0278-5846(93)90032-N
Nowak L, Bregestovski P, Ascher P, Herbet A, Prochiantz A: Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature 1984,307(5950):462–465. 10.1038/307462a0
Kristal BS, Dubinsky JM: Mitochondrial permeability transition in the central nervous system: induction by calcium cycling-dependent and -independent pathways. J Neurochem 1997,69(2):524–538.
Schanne FA, Gupta RK, Stanton PK: 31P-NMR study of transient ischemia in rat hippocampal slices in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 1993,1158(3):257–263. 10.1016/0304-4165(93)90023-2
Mohr K: Therapeutic drugs. Magnesium. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 1994,119(48):1669–1670.
Westermaier T, Zausinger S, Baethmann A, Schmid-Elsaesser R: Dose finding study of intravenous magnesium sulphate in transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2005,147(5):525–532. 10.1007/s00701-005-0496-4
Boet R, Mee E: Magnesium sulfate in the management of patients with Fisher Grade 3 subarachnoid hemorrhage: a pilot study. Neurosurgery 2000,47(3):602–606.
Chia RY, Hughes RS, Morgan MK: Magnesium: a useful adjunct in the prevention of cerebral vasospasm following aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Clin Neurosci 2002,9(3):279–281. 10.1054/jocn.2001.1039
Muir KW, Lees KR: Dose optimization of intravenous magnesium sulfate after acute stroke. Stroke 1998,29(5):918–923. 10.1161/01.STR.29.5.918
van den Bergh WM, Algra A, van Kooten F, Dirven CM, van Gijn J, Vermeulen M, Rinkel GJ: Magnesium sulfate in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2005,36(5):1011–1015. 10.1161/01.STR.0000160801.96998.57
Veyna RS, Seyfried D, Burke DG, Zimmerman C, Mlynarek M, Nichols V, Marrocco A, Thomas AJ, Mitsias PD, Malik GM: Magnesium sulfate therapy after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 2002,96(3):510–514. 10.3171/jns.2002.96.3.0510
Westermaier T, Stetter C, Vince GH, Pham M, Tejon JP, Eriskat J, Kunze E, Matthies C, Ernestus RI, Solymosi L, Roosen K: Prophylactic intravenous magnesium sulfate for treatment of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical study. Crit Care Med 2010,38(5):1284–1290.
Wong GK, Poon WS, Chan MT, Boet R, Gin T, Ng SC, Zee BC: Intravenous magnesium sulphate for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (IMASH): a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, multicenter phase III trial. Stroke 2010,41(5):921–926. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.571125
Muroi C, Terzic A, Fortunati M, Yonekawa Y, Keller E: Magnesium sulfate in the management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-adapted trial. Surg Neurol 2008,69(1):33–39. 10.1016/j.surneu.2007.07.015
Blair JL, Warner DS, Todd MM: Effects of elevated plasma magnesium versus calcium on cerebral ischemic injury in rats. Stroke 1989,20(4):507–512. 10.1161/01.STR.20.4.507
Sirin BH, Coskun E, Yilik L, Ortac R, Sirin H, Tetik C: Neuroprotective effects of preischemia subcutaneous magnesium sulfate in transient cerebral ischemia. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1998,14(1):82–88. 10.1016/S1010-7940(98)00140-7
Zhou H, Ma Y, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Wang K, Chen G: Effects of magnesium sulfate on neuron apoptosis and expression of caspase-3, bax and bcl-2 after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin Med J (Engl) 2003,116(10):1532–1534.
Zhu H, Meloni BP, Bojarski C, Knuckey MW, Knuckey NW: Post-ischemic modest hypothermia (35 degrees C) combined with intravenous magnesium is more effective at reducing CA1 neuronal death than either treatment used alone following global cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp Neurol 2005,193(2):361–368. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.01.022
Zhu H, Meloni BP, Moore SR, Majda BT, Knuckey NW: Intravenous administration of magnesium is only neuroprotective following transient global ischemia when present with post-ischemic mild hypothermia. Brain Res 2004,1014(1–2):53–60.
Chung SY, Lin JY, Lin MC, Liu HM, Wang MF, Cheng FC: Synergistic efficacy of magnesium sulfate and FK506 on cerebral ischemia-induced infarct volume in gerbil. Med Sci Monit 2004,10(4):BR105-BR108.
Izumi Y, Roussel S, Pinard E, Seylaz J: Reduction of infarct volume by magnesium after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1991,11(6):1025–1030. 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.170
Lee EJ, Ayoub IA, Harris FB, Hassan M, Ogilvy CS, Maynard KI: Mexiletine and magnesium independently, but not combined, protect against permanent focal cerebral ischemia in Wistar rats. J Neurosci Res 1999,58(3):442–448. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19991101)58:3<442::AID-JNR10>3.0.CO;2-4
Roffe C, Thomas L, Fotheringham A, Davies I: The effect of megnesium on infarct size and oedema after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Cerebrovasc Dis 1996,6(Suppl. 2):42.
Yang Y, Li Q, Ahmad F, Shuaib A: Survival and histological evaluation of therapeutic window of post-ischemia treatment with magnesium sulfate in embolic stroke model of rat. Neurosci Lett 2000,285(2):119–122. 10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01048-X
Marinov MB, Harbaugh KS, Hoopes PJ, Pikus HJ, Harbaugh RE: Neuroprotective effects of preischemia intraarterial magnesium sulfate in reversible focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosurg 1996,85(1):117–124. 10.3171/jns.1996.85.1.0117
Westermaier T, Hungerhuber E, Zausinger S, Baethmann A, Schmid-Elsaesser R: Neuroprotective efficacy of intra-arterial and intravenous magnesium sulfate in a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2003,145(5):393–399.
Schmid-Elsaesser R, Zausinger S, Hungerhuber E, Baethmann A, Reulen HJ: Neuroprotective effects of combination therapy with tirilazad and magnesium in rats subjected to reversible focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosurgery 1999,44(1):163–171. 10.1097/00006123-199901000-00100
Spandou E, Soubasi V, Papoutsopoulou S, Augoustides-Savvopoulou P, Loizidis T, Pazaiti A, Karkavelas G, Guiba-Tziampiri O: Neuroprotective effect of long-term MgSO4 administration after cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in newborn rats is related to the severity of brain damage. Reprod Sci 2007,14(7):667–677. 10.1177/1933719107305864
Thordstein M, Bagenholm R, Thiringer K, Kjellmer I: Scavengers of free oxygen radicals in combination with magnesium ameliorate perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Pediatr Res 1993,34(1):23–26. 10.1203/00006450-199307000-00006
Greenwood K, Cox P, Mehmet H, Penrice J, Amess PN, Cady EB, Wyatt JS, Edwards AD: Magnesium sulfate treatment after transient hypoxia-ischemia in the newborn piglet does not protect against cerebral damage. Pediatr Res 2000,48(3):346–350. 10.1203/00006450-200009000-00014
Penrice J, Amess PN, Punwani S, Wylezinska M, Tyszczuk L, D’Souza P, Edwards AD, Cady EB, Wyatt JS, Reynolds EO: Magnesium sulfate after transient hypoxia-ischemia fails to prevent delayed cerebral energy failure in the newborn piglet. Pediatr Res 1997,41(3):443–447. 10.1203/00006450-199703000-00024
Hoffman DJ, Marro PJ, McGowan JE, Mishra OP, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M: Protective effect of MgSO4 infusion on nmda receptor binding characteristics during cerebral cortical hypoxia in the newborn piglet. Brain Res 1994,644(1):144–149. 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90357-3
Wester PO, Asplund K, Eriksson S, Hagg E, Lithner F, Strand T: Infusion of magnesium in patients with acute brain infarction. Acta Neurol Scand 1984,70(2):143.
Muir KW, Lees KR: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial of intravenous magnesium sulfate in acute stroke. Stroke 1995,26(7):1183–1188. 10.1161/01.STR.26.7.1183
Woods KL, Fletcher S, Roffe C, Haider Y: Intravenous magnesium sulphate in suspected acute myocardial infarction: results of the second Leicester Intravenous Magnesium Intervention Trial (LIMIT-2). Lancet 1992,339(8809):1553–1558. 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91828-V
Muir KW, Lees KR, Ford I, Davis S: Magnesium for acute stroke (Intravenous Magnesium Efficacy in Stroke trial): randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2004,363(9407):439–445.
Aslanyan S, Weir CJ, Muir KW, Lees KR: Magnesium for treatment of acute lacunar stroke syndromes: further analysis of the IMAGES trial. Stroke 2007,38(4):1269–1273. 10.1161/01.STR.0000259628.94421.09
Saver JL, Kidwell C, Eckstein M, Starkman S: Prehospital neuroprotective therapy for acute stroke: results of the Field Administration of Stroke Therapy-Magnesium (FAST-MAG) pilot trial. Stroke 2004,35(5):106–108. 10.1161/01.STR.0000124458.98123.52
Bederson JB, Germano IM, Guarino L: Cortical blood flow and cerebral perfusion pressure in a new noncraniotomy model of subarachnoid hemorrhage in the rat. Stroke 1995,26(6):1086–1091. 10.1161/01.STR.26.6.1086
Westermaier T, Jauss A, Vince GH, Raslan F, Eriskat J, Roosen K: Impact of various extents of experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage induced by the endovascular filament model on mortality and changes of cerebral blood flow. J Exp Stroke Transl Med 2011,4(1):8–15. 10.6030/1939-067X-4.1.8
Jones TH, Morawetz RB, Crowell RM, Marcoux FW, FitzGibbon SJ, DeGirolami U, Ojemann RG: Thresholds of focal cerebral ischemia in awake monkeys. J Neurosurg 1981,54(6):773–782. 10.3171/jns.1981.54.6.0773
van den Bergh WM, Algra A, van der Sprenkel JW, Tulleken CA, Rinkel GJ: Hypomagnesemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2003,52(2):276–281. 10.1227/01.NEU.0000043984.42487.0E
Luo W, Qiu S, Ma W: Clinical study of magnesium sulphate on delayed cerebral vasospasmafter subarachnoid haemorrhage. Journal of Clinical Neurology 1996,9(4):244–245.
Schmid-Elsaesser R, Kunz M, Zausinger S, Prueckner S, Briegel J, Steiger HJ: Intravenous magnesium versus nimodipine in the treatment of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a randomized study. Neurosurgery 2006,58(6):1054–1065. 10.1227/01.NEU.0000215868.40441.D9
Mees SM, Algra A, Vandertop WP, van Kooten F, Kuijsten HA, Boiten J, van Oostenbrugge RJ, Salman RA, Lavados PM, Rinkel GJ, van den Bergh WM: Magnesium for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (MASH-2): a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012,380(9836):44–9. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60724-7
Prevedello DM, Cordeiro JG, de Morais AL, Saucedo NSJ, Chen IB, Araujo JC: Magnesium sulfate: role as possible attenuating factor in vasospasm morbidity. Surg Neurol 2006,65(Suppl 1):14–20.
Stippler M, Crago E, Levy EI, Kerr ME, Yonas H, Horowitz MB, Kassam A: Magnesium infusion for vasospasm prophylaxis after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 2006,105(5):723–729. 10.3171/jns.2006.105.5.723
Pickard JD, Murray GD, Illingworth R, Shaw MD, Teasdale GM, Foy PM, Humphrey PR, Lang DA, Nelson R, Richards P: Effect of oral nimodipine on cerebral infarction and outcome after subarachnoid haemorrhage: British aneurysm nimodipine trial. BMJ 1989,298(6674):636–642. 10.1136/bmj.298.6674.636
Dorhout MS, Rinkel GJ, Feigin VL, Algra A, van den Bergh WM, Vermeulen M, van Gijn J: Calcium antagonists for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007., 3: CD000277
Pritchard JA: The use of the magnesium ion in the management of eclamptogenic toxemias. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1955,100(2):131–140.
Belfort MA, Anthony J, Saade GR, Allen JCJ: A comparison of magnesium sulfate and nimodipine for the prevention of eclampsia. N Engl J Med 2003,348(4):304–311. 10.1056/NEJMoa021180
Lucas MJ, Leveno KJ, Cunningham FG: A comparison of magnesium sulfate with phenytoin for the prevention of eclampsia. N Engl J Med 1995,333(4):201–205. 10.1056/NEJM199507273330401
Nelson KB, Grether JK: Can magnesium sulfate reduce the risk of cerebral palsy in very low birthweight infants? Pediatrics 1995,95(2):263–269.
Schendel DE, Berg CJ, Yeargin-Allsopp M, Boyle CA, Decoufle P: Prenatal magnesium sulfate exposure and the risk for cerebral palsy or mental retardation among very low-birth-weight children aged 3 to 5 years. JAMA 1996,276(22):1805–1810. 10.1001/jama.1996.03540220029026
Blair E, Palmer L, Stanley F: Cerebral palsy in very low birth weight infants, pre-eclampsia and magnesium sulphate. Pediatrics 1996,97(5):780–782.
Marret S, Marpeau L, Zupan-Simunek V, Eurin D, Leveque C, Hellot MF, Benichou J: Magnesium sulphate given before very-preterm birth to protect infant brain: the randomised controlled PREMAG trial. BJOG 2007,114(3):310–318.
Crowther CA, Hiller JE, Doyle LW, Haslam RR: Effect of magnesium sulfate given for neuroprotection before preterm birth: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2003,290(20):2669–2676. 10.1001/jama.290.20.2669
Rouse DJ, Hirtz DG, Thom E, Varner MW, Spong CY, Mercer BM, Iams JD, Wapner RJ, Sorokin Y, Alexander JM, Harper M, Thorp JMJ, Ramin SM, Malone FD, Carpenter M, Miodovnik M, Moawad A, O’Sullivan MJ, Peaceman AM, Hankins GD, Langer O, Caritis SN, Roberts JM: A randomized, controlled trial of magnesium sulfate for the prevention of cerebral palsy. N Engl J Med 2008,359(9):895–905. 10.1056/NEJMoa0801187
Magpie Trial Follow-Up Collaborative Group: The Magpie Trial: a randomised trial comparing magnesium sulphate with placebo for pre-eclampsia. Outcome for children at 18 months. BJOG 2007,114(3):289–299.
Doyle LW, Crowther CA, Middleton P, Marret S, Rouse D: Magnesium sulphate for women at risk of preterm birth for neuroprotection of the fetus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009., 1: CD004661
Levene M, Blennow M, Whitelaw A, Hanko E, Fellman V, Hartley R: Acute effects of two different doses of magnesium sulphate in infants with birth asphyxia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1995,73(3):174–177. 10.1136/fn.73.3.F174
Groenendaal F, Rademaker CM, Toet MC, de Vries LS: Effects of magnesium sulphate on amplitude-integrated continuous EEG in asphyxiated term neonates. Acta Paediatr 2002,91(10):1073–1077. 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2002.tb00102.x
Ichiba H, Tamai H, Negishi H, Ueda T, Kim TJ, Sumida Y, Takahashi Y, Fujinaga H, Minami H: Randomized controlled trial of magnesium sulfate infusion for severe birth asphyxia. Pediatr Int 2002,44(5):505–509. 10.1046/j.1442-200X.2002.01610.x
Gathwala G, Khera A, Singh I: Magnesium therapy in birth asphyxia. Indian J Pediatr 2006,73(3):209–212. 10.1007/BF02825482
Bhat MA, Charoo BA, Bhat JI, Ahmad SM, Ali SW, Mufti MU: Magnesium sulfate in severe perinatal asphyxia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Pediatrics 2009,123(5):e764-e769. 10.1542/peds.2007-3642
Gathwala G, Khera A, Singh J, Balhara B: Magnesium for neuroprotection in birth asphyxia. J Pediatr Neurosci 2010,5(2):102–104. 10.4103/1817-1745.76094
Zausinger S, Westermaier T, Plesnila N, Steiger HJ, Schmid-Elsaesser R: Neuroprotection in transient focal cerebral ischemia by combination drug therapy and mild hypothermia: comparison with customary therapeutic regimen. Stroke 2003,34(6):1526–1532. 10.1161/01.STR.0000070841.31224.29
Zausinger S, Scholler K, Plesnila N, Schmid-Elsaesser R: Combination drug therapy and mild hypothermia after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 2003,34(9):2246–2251. 10.1161/01.STR.0000083622.65684.21
Kimura T, Yasue H, Sakaino N, Rokutanda M, Jougasaki M, Araki H: Effects of magnesium on the tone of isolated human coronary arteries. Comparison with diltiazem and nitroglycerin. Circulation 1989,79(5):1118–1124. 10.1161/01.CIR.79.5.1118
Pyne GJ, Cadoux-Hudson TA, Clark JF: Magnesium protection against in vitro cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid haemorrhage. Br J Neurosurg 2001,15(5):409–415. 10.1080/02688690120082413
Mori K, Miyazaki M, Iwata J, Yamamoto T, Nakao Y: Intracisternal infusion of magnesium sulfate solution improved reduced cerebral blood flow induced by experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in the rat. Neurosurg Rev 2008,31(2):197–203. 10.1007/s10143-008-0122-z
Mori K, Yamamoto T, Nakao Y, Miyazaki M, Iwata J, Tamura M, Shiroishi T: Novel neuroprotective effect of cisternal and intra-cerebral magnesium sulfate solution infusion on delayed cerebral death in rat hippocampal neurons after transient global ischemia. Brain Res 2012,22(1480):72–80.
Mori K, Yamamoto T, Nakao Y, Osada H, Hara Y, Oyama K, Esaki T: Initial clinical experience of vasodilatory effect of intra-cisternal infusion of magnesium sulfate for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Med Chir 2009,49(4):139–144. 10.2176/nmc.49.139
Funding
This publication was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the University of Wuerzburg in the funding program Open Access Publishing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
None of the authors has a financial or other conflicts of interest to declare.
Authors’ contributions
TW – Design and writing of manuscript and literature work ischemia. CS – Creation of figures and literature work subarachnoid hemorrhage. EK – Literature work subarachnoid hemorrhage. NW – Literature work asphyxia experimental and clinical. FR – Literature work ischemia experimental and clinical. GHV – Design of review, drafting of the manuscript, RIE – Design of review, drafting of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Westermaier, T., Stetter, C., Kunze, E. et al. Magnesium treatment for neuroprotection in ischemic diseases of the brain. Exp & Trans Stroke Med 5, 6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-7378-5-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-7378-5-6