Abstract
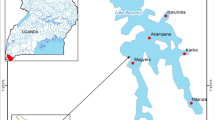
A wide-scale investigation providing insight into the spatial and temporal distribution of sanitary and microbiological indicators of water quality has been undertaken in the shallow nearshore zone of Lake Baikal. Water samples were collected along the entire lake perimeter from 2012 to 2016 and in 2020 (total number, n = 450). A comparison of the abundance of fecal indicator bacteria in the bottom and surface waters at a total depth of 1 m showed that the concentration of sanitary indicator bacteria was generally higher in the surface water layers. The dynamics of water quality indicators (as determined from May to November at the monitoring stations in the villages of Listvyanka and Bol’shie Koty) did not reveal, according to statistical calculations, any substantial differences in the number of fecal indicator bacteria in most cases for different months of this study. The results of four circum-Baikal surveys at the same stations in June and September 2015 and 2016 also showed no notable differences in terms of the period of sampling. The concentration gradient of the fecal indicator bacteria 100 m from the water edge exhibited a consistent decrease of these microorganisms with distance from the shore towards deeper parts of the lake. An area of sampling was revealed in which the concentrations of fecal indicator bacteria considerably exceeded the regulatory standards (SanPiN 1.2.3685-21). The village of Khuzhir was such a site. In the shallow water at the villages of Sakhyurta and Kultuk, the concentrations of fecal indicator bacteria were on the verge of the maximum permissible concentration. These data provided evidence of constant and significant water pollution in the nearshore zone adjacent to settlements characterized largely by touristic activities (recreational activity is increased).



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kravtsova, L.S., Izhboldina, L.A., Khanaev, I.V., Pomazkina, G.V., Domysheva, V.M., Kravchenko, O.S., and Grachev, M.A., Disturbances of the vertical zoning of green algae in the coastal part of the Listvennichnyi gulf of Lake Baikal, Dokl. Biol. Sci., 2012, vol. 447, no. 1, pp. 350–352.
Kravtsova, L.S., Izhboldina, L.A., Khanaev, I.V., Pomazkina, G.V., Rodionova, E.V., Domysheva, V.M., Sakirko, M.V., Tomberg, I.V., Kostornova, T.Ya., Kravchenko, O.S., and Kupchinsky, A.B., Nearshore benthic blooms of filamentous green algae in Lake Baikal, J. Great Lakes Res., 2014, vol. 40, pp. 441–448.
Timoshkin, O.A., Samsonov, D.P., Yamamuro, M., Moore, M.V., Belykh, O.I., Malnik, V.V., Sakirko, M.V., Shirokaya, A.A., Bondarenko, N.A., Domysheva, V.M., Fedorova, G.A., Kochetkov, A.I., Kuzmin, A.V., Lukhnev, A.G., Medvezhonkova, O.V., Nepokrytykh, A.V., Pasynkova, E.M., Poberezhnaya, A.E., Potapskaya, N.V., Rozhkova, N.A., Sheveleva, N.G., Tikhonova, I.V., Timoshkina, E.M., Tomberg, I.V., Volkova, E.A., Zaitseva, E.P., Zvereva, Yu.M., Kupchinsky, A.B., and Bukshuk, N.A., Rapid ecological change in the coastal zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia): Is the site of the world’s greatest freshwater biodiversity in danger?, J. Great Lakes Res., 2016, vol. 42, pp. 487–497.
Kobanova, G.I., Takhteev, V.V., Rusanovskaya, O.O., and Timofeyev, M.A., Lake Baikal ecosystem faces the threat of eutrophication, Int. J. Ecol., 2016, vol. 2016, pp. 1–7.
Malnik, V.V., Timoshkin, O.A., Suturin, A.N., Onishchuk, N.A., Sakirko, M.V., Tomberg, I.V., Gorshkova, A.S., and Zabanova, N.S., Anthropogenic changes in the hydrochemical and sanitary–microbiological characteristics of water quality in southern Baikal tributaries: Listvennichnyi Bay, Water Resour., 2019, vol. 46, no. 5, pp. 748–758.
Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation No. 552 “On approval of water quality standards for water bodies of fishery significance, including standards for maximum permissible concentrations of harmful substances in the waters of water bodies of fishery significance.” https://docs.cntd.ru/document/420389120. Cited April 7, 2021.
Guidelines 4.2.1884-04. Sanitary-microbiological and sanitary-parasitological analysis of surface water objects. http://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200039680/ (Cited April 7, 2021.
Sanitary rules and norms 1.2.3685-21. Hygienic standards and requirements for ensuring the safety and (or) harmlessness of environmental factors for humans. http://docs.cntd.ru /document/1200006938/. Cited April 7, 2021.
Cabelli, V.J., Dufour, A.P., McCabe, L., and Levin, M., Swimming association gastroenteritis and water quality, Am. J. Epidemiol., 1982, vol. 115, pp. 606–616.
Suturin A.N., Chebykin E.P., Mal’nik V.V., Khanaev I.V., Minaev A.V., and Minaev V.V. The role of anthropogenic factors in the development of ecological stress in Lake Baikal littoral (the Listvyanka settlement lakescape), Geogr. Prir. Resur., 2016, no. 6, pp. 43–54.
Baikal. Atlas (Baikal. Atlas), Galazii, G.I, Ed., Moscow: Sob. Otdel. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Roskartografiya, 1993.
GOST 31942-2012. Water. Sampling for microbiological analysis. http://docs.cntd.ru/document/gost-31942-2012/. Cited April 7, 2021.
Lukhnev, A.G., and Timoshkin, O.A., New sampler for near-bottom water of the coastal zone of reservoirs, Izv. Irk. Univ. Ser. Biol. Ekol., 2019, vol. 28, pp. 101–107.
GOST 24849-2014. Water. Methods of sanitary-bacteriological analysis for field conditions. http://docs. cntd.ru/document/1200115427/. Cited April 7, 2021.
Gorshkova, A.S., Mal’nik, V.V., Kostornova, T.Ya., Potapskaya, N.V., and Timoshkin, O.A., Distribution of bacteria – indicators of pollution in the splash zone of Lake Baikal, Geogr. Prir. Resur., 2020, no. 2, pp. 90–98.
Hatvani, I.G., Kirschner, A.T.K., Farnleitner, A.H., Tanos, and Herzig, A., Hotspots and main drivers of fecal pollution in Neusiedler See, a large shallow lake in central Europe, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2018, vol. 25, pp. 28884–28898.
Malnik V.V., Shtykova Yu.R., Suturin A.N., and Timoshkin O. A., Influence of settlements on the sanitary and microbiological state of small tributaries and coastal waters on the example of Listvennichny Bay (Southern Baikal), Geogr. Prir. Resur., 2019, no. 4, pp. 84–92.
Vorob’ev, N.V., Emel’yanova, N.V., Vorob’ev, A.N., and Valeeva, O.V., Settlement and population dynamics, Geogr. Prir. Resur., 2016, no. 5, pp. 168–178.
Tomberg, I.V., Sakirko, M.V., Molozhnikova, E.V., and Timoshkin, O.A., Ecological characteristics of the splash zone of Lake Baikal (by chemical components), Fundamental’nye problemy ekologii Rossii. Tezisy dokl. Vseros. nauch. konf. (Fundamental Problems of Ecology of Russia. Abstracts of the All-Russ. Scientific Conf.) (Irkutsk, Listvyanka, 2017) Irkutsk: Inst. Geogr. Sib. Otdel. Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2017, p. 193.
Hoyer, M.V., Donze, J.L., Schulz, E.J., Willis, D.J., and Canfield, Jr.D.E., Total coliform and Escherichia coli counts in 99 Florida lakes with relations to some common limnological factors, Lake Reservoir Manag., 2006, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 141–150.
Whitman, R.L. and Nevers, M.B., Microbes in beach sands: Integrating environment, ecology and public health, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 69, no. 9, pp. 5555–5562.
Niyoyitungiye, L., Giri, A., and Ndayisenga, M., Assessment of coliforms bacteria contamination in lake tanganyika as bioindicators of recreational and drinking water quality, South Asian J. Res. Microbiol., 2020, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 9–16.
Amfo-Out, R., Wiafe, E.D., and Kocke, B.B., Assessment of water quality in Ahor Lake – Ghana, African J. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2011, vol. 5, n. 12, pp. 1093–1099.
Mitrukova, G.G., Kapustina, L.L., and Kurashov, E.A., Ecological assessment of the quality of waters in the littoral zone of Lake Ladoga based on the results of microbiological studies, Tr. Karel. Nauch. Tsentra Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2020, no. 9, pp. 88–100.
Hachich, E.M., Di Bari, M., Christ, A.P., Lamparelli, C.C., Ramos, S.S., and Sato, M.I., Comparison of thermotolerant coliforms and Escherichia coli densities in freshwater bodies, Braz. J. Microbiol., 2012. vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 675–681.
Odonkor, S.T. and Ampofo, J.K., Escherichia coli as an indicator of bacteriological quality of water: An overview, Microbiol. Res., 2013. vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–11.
Ge, Z., Nevers, M.B., Schwab, D.J., and Whitman, R.L., Coastal loading and transport of Escherichia coli at embayed beach in Lake Michigan, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 44, pp. 6731–6737.
Haack, S.K., Fogarty, L.R., and Wright, C., Escherichia coli and enterococci at beaches in the Grand Traverse Bay, Lake Michigan: Sources, characteristics, and environmental pathways, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, vol. 37, pp. 3275–3282.
Kinzelman, J., Ng, C., Jackson, E., Gradus, S., and Bagley, R., Enterococci as indicators of Lake Michigan recreational water quality: Comparison of two methodologies and their impacts on public health regulatory events, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2003, vol. 69, n 1, pp. 92–96.
Alm, E.W., Burke, J., and Spain, A., Fecal indicator bacteria are abundant in wet sand at freshwater beaches, Water Res., 2003, vol. 37, pp. 3978–3982.
Nevers, M.B., Byappanahalli, M.N., Nakatsu, C.H., Kinzelman, J.L., Phanikumar, M.S., Shively, D.A., and Spoljarich, A.M., Interaction of bacterial communities and indicators of water quality in shoreline sand, sediment, and water of Lake Michigan, Water Res., 2020, vol. 178, pp. 1–11.
Timoshkin, O.A., Moore, M.V., Kulikova, N.N., Tomberg, I.V., Malnik, V.V., Shimaraev, M.N., Troitskaya, E.S., Shirokaya, A.A., Synyukovich, V.N., Zaitseva, E.P., Domysheva, V.M., Yamamuro, M., Poberezhnaya, A.E., and Timoshkina, E.M., Groundwater contamination by sewage causes benthic algal outbreaks in the littoral zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia), J. Great Lakes Res., 2018, vol. 44, pp. 230–244.
Palmer, J.A., Law, Ji-Y., and Soupir, M.L., Spatial and temporal distribution of E. coli contamination on three inland lake and recreational beach systems in the upper Midwestern United States, Sci. Total Environ., 2020, vol. 722, pp. 1–9.
Funding
This work was carried out as part of state tasks of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation and the topic “Comprehensive Studies of the Coastal Zone of Lake Baikal: Long-Term Dynamics of Communities under the Influence of Various Environmental Factors and Biodiversity; Causes and Consequences of Negative Environmental Processes” (0279-2021-0007). The collection and analysis of field data was supported by the projects “Large-Scale Changes in the Ecology and Biodiversity of Communities in the Coastal Zone of Lake Baikal: Interdisciplinary Research, Identification of Causes, and Development Forecast” (0345-2019-0009) and “Influence of Changing Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on Biogeochemical Processes on the Rocky Littoral of Baikal” (0345-2019-0010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Translated by S. Avodkova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malnik, V.V., Suturin, A.N., Gorshkova, A.S. et al. Water Quality in the Shallow Zone of Lake Baikal as Deduced from Sanitary and Microbiological Indicators. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 43, 141–148 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S187537282202007X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S187537282202007X