Abstract
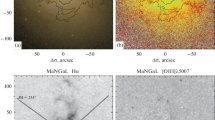
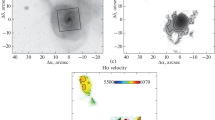
We investigate in detail the kinematics and morphology of the Seyfert galaxy NGC 6104 in order to identify the mechanism of gas transportation to the active galactic nucleus (AGN). Our observational data were obtained at the 6-m Special Astrophysical Observatory telescope with the MPFS integral-field spectrograph and the SCORPIO universal device in three modes: direct imaging, a scanning Fabry—Perot interferometer, and long-slit spectroscopy. Images from the HST archive were invoked to study the structure of the circumnuclear region. An analysis of deep images has shown for the first time that NGC 6104 is in the phase of active merging with a companion galaxy. We have been able to study the detailed picture of ionized gas motions up to galactocentric distances of 14 kpc and to construct the stellar velocity field for the inner region. The radial gas motions toward the AGN along the central bar play a significant role at galactocentric distances of 1–5 kpc. In addition, we have detected an outflow of ionized gas from the nucleus that presumably resulted from the intrusion of a radio jet into the ambient interstellar medium. Using diagnostic diagrams, we estimate the contributions from the AGN and star formation to the galactic gas ionization. We estimate the bar pattern speed by the Tremaine-Weinberg method and show that the inner ring observed in the galaxy’s images has a resonant nature. Two possible ring formation scenarios, before and during the interaction with a companion, are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. L. Afanasiev, S. N. Dodonov, and A. V. Moiseev, Stellar Dynamics: From Classic to Modern, Ed. by L. P. Osipkov and I. I. Nikiforov (St. Petersburg, 2001), p. 103.
V. L. Afanasiev and A. V. Moiseev, Pis’ma Astron. Zh. 31, 214 (2005) [Astron. Lett. 31, 194 (2005)]; astroph/0502095.
J. A. L. Aguerri, V. P. Debattista, and E. M. Corsini, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 338, 465 (2003).
R. Buta, Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 61, 609 (1986).
R. Buta and F. Combes, Fundam. Cosm. Phys. 17, 95 (1996).
A. Capetti, D. J. Axon, F. D. Macchetto, et al., Astrophys. J. 516, 187 (1999).
S. Ciroi, V. Afanasiev, A. Moiseev, et al., Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 360, 253 (2005).
F. Combes, Advanced Lectures on the Starburst-AGN Connection (World Sci., Singapore, 2001), p. 223.
F. Combes and M. Gerin, Astron. Astrophys. 150, 327 (1985).
O. Dahari, Astron. J. 90, 1772 (1985).
V. P. Debattista, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 342, 1194 (2003).
S. Garcia-Burillo, F. Combes, E. Schinnerer, et al., Astron. Astrophys. 441, 1011 (2005).
P. Hall and G. Richards, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 116, 593 (2004).
O. Hernandez, Wozniak, C. Carignan, et al., Astrophys. J. 632, 253 (2005).
L. Ho and C. Peng, Astrophys. J. 555, 650 (2001).
L. Jimenez-Benito, A. Diaz, R. Terlevich, and E. Terlevich, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 317, 907 (2000).
S. Jogee, J. D. P. Kenney, and B. J. Smith, Astrophys. J. 526, 665 (1999).
G. Kauffmann, S. White, T. Heckman, et al., Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 353, 713 (2004).
R. Kennicutt, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 36, 189 (1998).
J. Knapen, Astrophys. Space Sci. 295, 85 (2005).
J. Kormendy, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 27, 235 (1989).
S. Laine, I. Shlosman, J. Knapen, and R. Peletier, Astrophys. J. 567, 97 (2002).
M. Malkan, V. Gorjian, and R. Tam, Astrophys. J., Suppl. Ser. 117, 25 (1998).
P. Martini, The Interplay among Black Holes, Stars and ISM in Galactic Nuclei, Ed. by L. Storchi-Bergmann et al. (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2004), p. 222.
P. Martini, M. Regan, J. Mulchaey, and R. Pogge, Astrophys. J. 589, 774 (2003).
A. V. Moiseev, Bull. Spec. Astrophys. Obs. 51, 11 (2001); astro-ph/0111219.
A. V. Moiseev, Bull. Spec. Astrophys. Obs. 54, 74 (2002a); astro-ph/0211104.
A. V. Moiseev, Pis’ma Astron. Zh. 28, 840 (2002b) [Astron. Lett. 28, 755 (2002b)].
A. V. Moiseev, J. R. Valdés, and V. H. Chavushyan, Astron. Astrophys. 421, 433 (2004).
H. Mouri and Y. Taniguchi, Astrophys. J. 565, 786 (2002).
I. I. Pasha, Pis’ma Astron. Zh. 11, 3 (1985) [Sov. Astron. Lett. 11, 1 (1985)].
P. Rafanelli, M. Violato, and A. Baruffolo, Astron. J. 109, 1546 (1995).
R. Rand and J. Wallin, Astrophys. J. 614, 142 (2004).
M. W. Regan, K. Sheth, and S. N. Vogel, Astrophys. J. 482, 143L (1997).
M. de Robertis, H. Yee, and K. Hayhoe, Astrophys. J. 496, 93 (1998).
H. Schmitt, Astron. J. 122, 2243 (2001).
M. P. Schwarz, Proc. Astron. Soc. Aust. 6, 202 (1984).
F. Schweizer and P. Seitzer, Astrophys. J. 326, 88 (1988).
F. Simien and G. de Vaucouleurs, Astrophys. J. 302, 564 (1986).
A. Tomita, H. Maehara, T. Takeuchi, et al., Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 51, 285 (1999).
S. Tremaine and D. Weinberg, Astrophys. J. 282, L5 (1984).
S. Veilleux, Astron. Soc. Pac. Conf. Proc. 284, 111 (2002).
K. Wada, Coevolution of Black Holes and Galaxies, Ed. by C. Ho (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 2004), p. 187; astro-ph/0308134.
P. Zimmer, R. J. Rand, and J. T. McGraw, Astrophys. J. 607, 285 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.A. Smirnova, A.V. Moiseev, V.L. Afanasiev, 2006, published in Pis’ma v Astronomicheskiĭ Zhurnal, 2006, Vol. 32, No. 8, pp. 577–591.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smirnova, A.A., Moiseev, A.V. & Afanasiev, V.L. Observational evidence for AGN fueling: I. The case of NGC 6104—Merging with a companion. Astron. Lett. 32, 520–533 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063773706080032
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063773706080032