Abstract
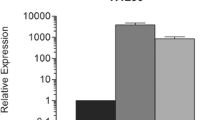
Survivin (BIRC5) belongs to the family of inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs). BIRC5 is expressed in embryonic tissues and in most malignant tumors but not in fully differentiated adult tissues. BIRC5, acting as an apoptosis inhibitor, presumably plays an important part in carcinogenesis, thus providing an attractive target for antitumor therapy. The mechanisms regulating the survivin level are insufficiently understood, but a significant role is ascribed to natural survivin inhibitors, SMAC and PML. The transcription levels of BIRC5, SMAC, and PML and the levels of their protein products were assessed by RT-PCR and immunoblotting in normal and tumor human tissues in non-small cell lung cancer and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BIRC5 transcription was observed only in tumor tissues, whereas SMAC and PML were expressed in tumor and normal tissues at similar levels. The protein levels corresponded to the mRNA levels. Thus, increased levels of survivin in tumor tissues are not a consequence of downregulation of its inhibitors SMAC and PML, whose levels do not differ between tumor and normal cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Philchenkov A., Zavelevich M., Kroczak T.J., Los M. 2004. Caspases and cancer: Mechanisms of inactivation and new treatment modalities. Exp. Oncol. 26, 82–97.
Singhal S., Vachani A., Antin-Ozerkis D., Kaiser L.R., Albelda S.M. 2005. Prognostic implications of cell cycle, apoptosis, and angiogenesis biomarkers in nonsmall cell lung cancer: A review. Clin. Cancer Res. 11, 3974–3986.
Ambrosini G., Adida C., Altieri D.C. 1997. A novel antiapoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nature Med. 3, 917–921.
Colnaghi R., Connell C.M., Barrett R.M., Wheatley S.P. 2006. Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 33450–33456.
Wheatley S.P., McNeish I.A. 2005. Survivin: a protein with dual roles in mitosis and apoptosis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 247, 35–88.
Adida C., Crotty P.L., McGrath J., Berrebi D., Diebold J., Altieri D.C. 1998. Developmentally regulated expression of the novel cancer anti-apoptosis gene survivin in human and mouse differentiation. Am. J. Pathol. 152, 43–49.
Fukuda S., Pelus L.M. 2006. Survivin, a cancer target with an emerging role in normal adult tissues. Mol. Cancer Ther. 5, 1087–1098.
Mahotka C., Wenzel M., Springer E., Gabbert H.E., Gerharz C.D. 1999. Survivin-deltaEx3 and survivin-2B: Two novel splice variants of the apoptosis inhibitor survivin with different antiapoptotic properties. Cancer Res. 59, 6097–6102.
Ling X., Yang J., Tan D., Ramnath N., Younis T., Bundy B.N., Slocum H.K., Yang L., Zhou M., Li F. 2005. Differential expression of survivin-2B and survivin-DeltaEx3 is inversely associated with disease relapse and patient survival in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer. 49, 353–361.
Sampath J., Pelus L.M. 2007. Alternative splice variants of survivin as potential targets in cancer. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 4, 174–191.
Duffy M.J., O’Donovan N., Brennan D.J., Gallagher W.M., Ryan B.M. 2007. Survivin: A promising tumor biomarker. Cancer Lett. 249, 49–60.
Fan J., Wang L., Jiang G.N., He W.X., Ding J.A. 2008. The role of survivin on overall survival of non-small cell lung cancer, a meta-analysis of published literatures. Lung Cancer, doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.11.011.
Altieri D.C. 2008. Survivin, cancer networks, and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 8, 61–70.
Li F. 2005. Role of survivin and its splice variants in tumorigenesis. Br. J. Cancer. 92, 212–216.
Verhagen A.M., Ekert P.G., Pakusch M., Silke J., Connolly L.M., Reid G.E., Moritz R.L., Simpson R.J., Vaux D.L. 2000. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell. 102, 43–53.
Shiozaki E.N., Shi Y. 2004. Caspases, IAPs and Smac/DIABLO: Mechanisms from structural biology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 29, 486–494.
Xu Z.X., Zhao R.X., Ding T., Tran T.T., Zhang W., Pandolfi P.P., Chang K.S. 2004. Promyelocytic leukemia protein 4 induces apoptosis by inhibition of survivin expression. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 1838–1844.
Rajalingam K., Oswald M., Gottschalk K., Rudel T. 2007. Smac/DIABLO is required for effector caspase activation during apoptosis in human cells. Apoptosis. 12, 1503–1510.
Sekimura A., Konishi A., Mizuno K., Kobayashi Y., Sasaki H., Yano M., Fukai I., Fujii Y. 2004. Expression of Smac/DIABLO is a novel prognostic marker in lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 11, 797–802.
Krepela E., Prochazka J., Fiala P., Zatloukal P., Selinger P. 2006. Expression of apoptosome pathway-related transcripts in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 132, 57–68.
Ceballos-Cancino G., Espinosa M., Maldonado V., Melendez-Zajgla J. 2007. Regulation of mitochondrial Smac/DIABLO-selective release by survivin. Oncogene. 26, 7569–7575.
Vogler M., Giagkousiklidis S., Genze F., Gschwend J.E., Debatin K.M., Fulda S. 2005. Inhibition of clonogenic tumor growth: A novel function of Smac contributing to its antitumor activity. Oncogene. 24, 7190–7202.
Salomoni P., Pandolfi P.P. 2002. The role of PML in tumor suppression. Cell. 108, 165–170.
Bernardi R., Pandolfi P.P. 2003. Role of PML and the PML-nuclear body in the control of programmed cell death. Oncogene. 22, 9048–9057.
Li L., He D., He H., Wang X., Zhang L., Luo Y., Nan X. 2006. Overexpression of PML induced apoptosis in bladder cancer cell by caspase dependent pathway. Cancer Lett. 236, 259–268.
Chan J.Y., Li L., Fan Y.H., Mu Z.M., Zhang W.W., Chang K.S. 1997. Cell-cycle regulation of DNA damage-induced expression of the suppressor gene PML. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 240, 640–646.
Salomoni P., Bellodi C. 2007. New insights into the cytoplasmic function of PML. Histol. Histopathol. 22, 937–946.
Fagioli M., Alcalay M., Pandolfi P.P., Venturini L., Mencarelli A., Simeone A., Acampora D., Grignani F., Pelicci P.G. 1992. Alternative splicing of PML transcripts predicts coexpression of several carboxy-terminally different protein isoforms. Oncogene. 7, 1083–1091.
Jensen K., Shiels C., Freemont P.S. 2001. PML protein isoforms and the RBCC/TRIM motif. Oncogene. 20, 7223–7233.
Condemine W., Takahashi Y., Zhu J., Puvion-Dutilleul F., Guegan S., Janin A., de The H. 2006. Characterization of endogenous human promyelocytic leukemia isoforms. Cancer Res. 66, 6192–6198.
Condemine W., Takahashi Y., Le Bras M., de The H. 2007. A nucleolar targeting signal in PML-I addresses PML to nucleolar caps in stressed or senescent cells. J. Cell Sci. 120, 3219–3227.
Slizhikova D.K., Zinov’eva M.V., Kuz’min D.V., Snezhkov E.V., Shakhparonov M.I., Dmitrirev R.I., Antipova N.V., Zavalova L.L., Sverdlov E.D. 2007. Decrease in expression of human J-chain in lung squamous cell cancer and adenocarcinoma. Mol. Biol. 41, 659–665.
Harlow E., Lane D. 1988. Antibodies. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: CSG Press.
Ikeguchi M., Kaibara N. 2002. survivin messenger RNA expression is a good prognostic biomarker for oesophageal carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer. 87, 883–887.
Kato J., Kuwabara Y., Mitani M., Shinoda N., Sato A., Toyama T., Mitsui A., Nishiwaki T., Moriyama S., Kudo J., Fujii Y. 2001. Expression of survivin in esophageal cancer: Correlation with the prognosis and response to chemotherapy. Int. J. Cancer. 95, 92–95.
Gambacorta M., Flenghi L., Fagioli M., Pileri S., Leoncini L., Bigerna B., Pacini R., Tanci L.N., Pasqualucci L., Ascani S., Mencarelli A., Liso A., Pelicci P.G., Falini B. 1996. Heterogeneous nuclear expression of the promyelocytic leukemia (PML) protein in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Am. J. Pathol. 149, 2023–2035.
Zhang P., Chin W., Chow L.T., Chan A.S., Yim A.P., Leung S.F., Mok T.S., Chang K.S., Johnson P.J., Chan J.Y. 2000. Lack of expression for the suppressor PML in human small cell lung carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer. 85, 599–605.
Vousden K.H., Lu X. 2002. Live or let die: The cell’s response to p53. Nature Rev. Cancer. 2, 594–604.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.A. Vayshlya, M.V. Zinovyeva, A.V. Sass, E.P. Kopantzev, T.V. Vinogradova, E.D. Sverdlov, 2008, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2008, Vol. 42, No. 4, pp. 652–661.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vayshlya, N.A., Zinovyeva, M.V., Sass, A.V. et al. Increased expression of BIRC5 in non-small cell lung cancer and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma does not correlate with the expression of its inhibitors SMAC/DIABLO and PML . Mol Biol 42, 579–587 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893308040146
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893308040146