Abstract
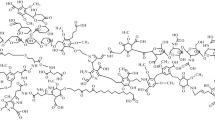
Hypotheses of humus formation on the basis of polymerization and oxidation reactions were considered. The most popular models of several authors and the general understanding of the structural features of natural polymers were analyzed. Multivariate statistical analysis was performed for zonal factors affecting the formation of humic substances. Evolutionary changes in the understanding of the biospheric functions of humus substances were evaluated. Statistical procedures were proposed for the prediction of the physicochemical behavior of humus substances in environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. N. Aleksandrova, Organic Matter of Soils and Processes of Its Transformation (Nauka, Moscow, 1980) [in Russsian].
R. V. Bagdoryanov, S. A. Ozernaya, A.-T. A. Pikhlak, and S. A. Timofeev “Radiogenic uranium-234 in humic acids of the graptolite mudstone,” Neftedobycha 1 (24), 73–89 (2007).
A. Baglieri, D. Vindrola, M. Gennari, and M. Negre, “Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of insoluble and soluble humic acid fractions at different pH values,” Chem. Biol. Tech. Agr. 9 (1), 1–11 (2014).
J. Barker and P. Fritz, “The occurrence and origin of methane in some groundwater flow systems,” Can. J. Earth Sci. 18, 1802–1816 (1981).
M. A. Barnes, W. C. Barnes, and R. M. Bustin, “Diagenesis chemistry and evolution of organic matter,” Geosci. Can. 11, 103–114 (1984).
L. L. Demina, Speciation of Heavy Metal Migration in the Ocean (Nauka, Moscow, 1982) [in Russian].
M. I. Dergacheva, Soil Organic Matter. Statistics and Dynamics (Evidence from West Siberia) (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1984) [in Russian].
M. I. Dinu, Influence of Functional Characteristics of Humic Substances on Metal Speciation in Natural Waters (TyumGU, Tyumen, 2012) [in Russian].
V. V. Dokuchaev, Theory of Natural Zones (Geografgiz, Moscow, 1948) [in Russian].
D. Dudare and M. Klavins, “The interaction between humic substances and metals, depending on structure and properties of humic substances,” 4th International Conference on Environmental, Energy and Biotechnology 85, 10–15 (2000).
J. H. Ephrai and B. Allard, Metal Ion Binding by Humic Substances in Modeling in Aquatic Chemistry (World, New York, 1997).
M. V. Fedorkova, E. P Pakhnenko, and N. I. Sanzharova, “Chemical forms of radioactive strontium interaction with organic matter of different soil types,” Mosc. Univ., Soil. Sci. Bull., 3, 133–136 (2012).
W. Flaig, “Organic compounds in soil,” Soil. Sci. 1 (111), 56–68 (1971).
A. Yu. Galaktionov and A. I. Karpukhin, “Content, profile distribution, and relation of heavy metals with groups and fractions of soil organic matter in the forest experimental area of GRAY–MSKhA,” Izv. Timiryazevsk. Sel’khoz. Akad., No. 3, 47–56 (2007).
L. Z. Granina and E. Callender, “Elements of the iron and manganese cycles in Lake Baikal,” Geochem. Int. 45 (9), 999–1007 (2007).
N. Yu. Grechishcheva, I. V. Perminova, V. A. Kholodov, and S. V. Meshcheryakova, “Stabilization of oil emulsions in water by highly dispersed particles: role in selfpurification and prospects of application,” Ross. Khim. Zh. 4 (59), 34–50 (2015).
E. A. Gurov, “Characteristics of IR spectra of complexes of humic-like acid of mummy samples with metals,” Sovremen. Probl. Nauki Obrazov., No. 6, 31–37 (2014).
M. V. Ivanov, A. Yu. Lein, and A. S. Savvichev, “Effect of phytoplankton and microorganisms on the isotopic composition of organic carbon in the Russian Arctic seas,” Microbiology 79 (5), 567–582 (2010).
V. A. Kholodov, E. Y. Milanovskiy, A. I. Konstantinov, Z. N. Tyugai, N. V. Yaroslavtseva, and I. V. Perminova, “Irreversible sorption of humic substances causes a decrease in wettability of clay surfaces as measured by a sessile drop contact angle method,” J. Soils Sediments 6, 16–24 (2016).
B. M. Klenov, “Humus and anthropogenic impact,” INTEREKSPO GEO-SIBIR 2 (4), 59–63 (2016).
S. I. Kolesnikov, K. Sh. Kazeeva, and V. F. Val’kov, Ecological Consequences of Soil Pollution by Heavy Metals (SKHTs VSh, Rostov-on-Don, 2000) [in Russian].
M. M. Kononova, Soil Organic Matter: Its Nature, Properties, and Methods of Study (Akad. Nauk SSSR, Moscow, 1963) [in Russian].
M. M. Kononova, “Some controversial problems of soil humus,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Biol. 3, 364–373 (1970).
D. V. Kovalevskii, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s Dissertation in Chemistry (Moscow, 1998).
J. D. Kubicki, “Molecular modeling of humic and fulvic acid,” Am. Chem. Soc. Div. Environ. Chem. 2, 617–623 (2000).
J. D. Kubicki and S. E. Apitz, “Models of natural organic matter and interactions with organic contaminants,” Org. Geochem. 30, 911–927 (1999).
N. A. Kulikova, I. V. Permonova, and A. V. Kudryavtsev, “A comparative study of molecular weight distribution of water-soluble humic substances, humic acids and fulvic acids extracted from sod-podzolic soils,” Moscow Univ. Soil Sci. Bull. 4 (65), 155–158 (2010).
A. Yu. Lein, Ye. A. Novichkov, A. E. Rybalko, and M. V. Ivanov, “Carbon isotope composition of organic matter in Holocene sediments of the White Sea as one of the indicators of sedimentation conditions,” Dokl. Earth Sci. 452 (2), 1056–1061 (2014).
P. N. Linnik and B. I. Nabivanets, Speciation of Metal Migration in Surface Fresh Waters (Gidrometizdat, Leningrad, 1986) [in Russian].
G. A. Makharadze, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s Dissertation in Chemistry (Moscow, 1984) [in Russian].
S. M. Manskaya and T. V. Drozdova, Geochemistry of Organic Matter (Nauka, Moscow, 1964) [in Russian].
S. P. Mathur and R. S. Farnham, “Geochemistry of humic substances in natural and cultivated peatlands,” Humic Substances in Soil, Sediment, and Water (Wiley, New York, 1985).
M. Meaney, Trace Metal Speciation in Environmental Systems (City University, Dublin, 1996).
Yu. E. Milanovsky, Soil Humic Matter as Natural Hydrophobic–Hydrophilic Compounds (GEOS, Moscow, 2009) [in Russian].
T. I. Moiseenko, N. A. Gashkina, L. P. Kudryavtseva, Yu. A. Bylinyak, and S. S. Sandimirov, “Zonal features of the formation of water chemistry in small lakes in European Russia,” Water Res. 33 (2), 144–162 (2006)
T. I. Moiseenko, N. A. Gashkina, and M. I. Dinu, Acidification of Waters: Vulnerability and Critical Loadings (URSS, Moscow, 2017) [in Russian].
D. S. Nenakhov, E. S. Gasanov, and K. E. Stekol’nikov, “Spectroscopic study of composition of fulvic acids of leached chernozem,” Sorbts. Khromatograph. Prots. 9 (5), 659–664 (2009).
D. S. Orlov, “Element composition and degree of oxidation of humic acids,” Nauchn. Dokl. Vyssh. Shk., Biol. Nauki 1, 5–20 (1970).
D. S. Orlov, Humic Acids (Mosk. Gos. Univ., Moscow, 1974) [in Russian].
D. S. Orlov, “Kinetic theory of humification and a scheme of the possible structure of humic acids,” Nauchn. Dokl. Vyssh. Shk., Biol. Nauki 9, 5–16 (1977).
D. S. Orlov, Soil Chemistry (Mosk. Gos. Univ., Moscow, 1992) [in Russian].
D. S. Orlov, O. N. Biryukova, and N. I Sukhanova, Organic Matter of Soils of the Russian Federation (Nauka, Moscow, 1996) [in Russian].
D. S. Orlov, L. K. Sodovnikov, and I. N. Lazanovskaya, Ecology and Protection of the Biosphere during Chemical Pollution (Vysshaya Shkola, Moscow, 2002) [in Russian].
M. F. Ovchinnikova, Extended Abstracts of Doctoral Dissertation in Biology (Moscow, 2007) [in Russian].
I. V. Perminova, Doctoral Dissertation in Chemistry (Moscow, 2000) [in Russian].
I. V. Perminova and N. N. Danchenko, “Detoxication of heavy metals, polyaromatic hydrocarbons, and pesticides by humic matters in waters and soils,” Proceedings of International Congress “Water: Ecology and Technology,” 1136–1143 (1994).
L. R. Pivovarov, “On the nature of physiological activity in relation with their structure,” Humic Fertilizers. Theory and Practice of Their Application, 2, 433–443 (1962).
V. V. Ponomareva and T. A. Plotnikova, Humus and Soil Formation: Methods and Results of Study (Nauka, Leningrad, 1980) [in Russian].
A. I. Popov, Humic Substances: Properties, Structure, and Formation (St. Petersburg Gos. Univ., St. Petersburg, 2004) [in Russian].
I. A. Potapova, E. V. Burova, and P. P. Purygin, “Extraction and study of toxic and therapeutic properties of salts of humic acids and possibility of their application as a food additive,” Bashkir. Khim. Zh. 5 (19), 54–65 (2012).
N. S. Prilutskaya, T. A. Korel’skaya, L. F. Popova, and V. A. Leont’eva, “IR spectroscopic study of structural–functional composition of humic acids from the soils of the Euroarctic region,” Vestn. SAFU, Ser. Estestv. Nauki Biologiya 4, 26–35 (2016).
R. A. A. Puebla, C. Valenzuela-Calahorro, and J. J. Garrido, “Theoretical study of fulvic acid structure, conformation and aggregation molecular modelling approach,” Sci. Tot. Environ. 358, 243–254 (2006).
P. P. Purygin, I. A. Potapova, and D. V. Vorob’ev, “Humic acids: their extraction, structure, and application in biology, chemistry, and medicine,” Sekts. Aktual. Probl. Biol. Khim. Medits. 16, 25–50 (2008).
N. G. Rachkova, I. I. Shuktomova, and A. I. Taskaev, “The state of natural radionuclides of uranium, radium, and thorium in soils,” Euras. Soil Sci. 43 (6), 651–658 (2010).
G. N. Shigbaeva, “Element composition and content of functional groups of humic substances of soils and peats of different genesis,” Vestn. Tyumen Univ. 12, 45–53 (2014).
G. V. Slavinskaya and V. F. Selemnev, Fulvic Acids of Natural Waters (Voronezhskii Gos. Univ., Voronezh, 2001) [in Russian].
B. S. Smolyakov and V. I. Belevantsev, “Chemical species of copper, cadmium, and lead in freshwater basins,” Khim. Int. Ust. Razvitiya 7, 575–583 (1999).
D. A. Sokolov, “Determination of organic matters of pedogenic nature in soils of technogenic landscapes,” Vestn. Tomsk. Gos. Univ. Biologiya 2 (18), 17–25 (2012).
R. L. Tate, Soil Organic Matter (Wileys, New York, 1987).
I. V. Tyurin, Soil Organic Matter and Its Role (Mir, Moscow, 1965) [in Russian].
G. M. Varshal, T. K. Velyukhanova, and I. Ya Koshcheeva, “Geochemical role of humic acids in element migration,” Humic Substances in the Biosphere (Nauka, Moscow, 1993), pp. 97–117 [in Russian].
A. A. Vetrov, I. P. Semiletov, O. V. Dudarev, V. I. Peresypkin, and A. N. Charkin, “Composition and genesis of the organic matter in the bottom sediments of the East Siberian Sea,” Geochem. Int. 46 (2), 156–167 (2008).
G. S. Wang, S. T. Hsieh, and C. S. Hong, “Destruction of humic acid in water by UV light-catalyzed oxidation with hydrogen peroxide,” Water Res. 34 (15), 3882–3887 (2000).
L. I. Wassenaar, R. Aravena, P. Ertis, and J. Barker, “Isotopic composition (13C, 14C, 2H) and geochemistry of aquatic humic substances from groundwater,” Org. Geochem. 4 (15), 383–396 (1990).
W. Ziechmann, “Humic substances and their medical effectiveness,” 10th International Peat Congress (2), 546–554 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.I. Dinu, 2017, published in Geokhimiya, 2017, No. 10, pp. 917–933.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinu, M.I. Formation of organic substances of humus nature and their biospheric properties. Geochem. Int. 55, 911–926 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702917100032
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702917100032