Abstract
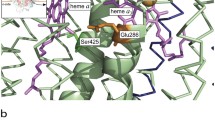
The effect of Zn2+ on the P-side of proteoliposomes containing membrane-incorporated Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome c oxidase was investigated by the time-resolved electrometrics following a single electron injection into the enzyme prepared in the F state. The wild-type enzyme was examined along with the two mutants, N139D and D132N. All obtained data indicate that the primary effect of Zn2+ added from the P-side of the membrane is slowing of the pumped proton release from the proton loading site (PLS) to the bulk aqueous phase on the P-side of the membrane. The results strongly suggest the presence of two pathways by which the pumped proton can exit the protein from the PLS and of two separate binding sites for Zn2+. A model is presented to explain the influence of Zn2+ on the kinetics of membrane-potential generation by the wild-type COX, as well as by the N139D and D132N mutants.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COX:
-
cytochrome c oxidase
- F, O, and P:
-
states of cytochrome c oxidase, respectively
- P- and N-phases:
-
positively and negatively charged aqueous phases, respectively separated by the coupling membrane
- Rubpy:
-
tris-bipyridyl complex of ruthenium(II)
References
Ferguson-Miller, S., and Babcock, G. T. (1996) Heme/copper terminal oxidases, Chem. Rev., 7, 2889-2907.
Siletsky, S. A. (2013) Steps of the coupled charge translocation in the catalytic cycle of cytochrome c oxidase, Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed), 18, 36-57.
Borisov, V. B., and Siletsky, S. A. (2019) Features of organization and mechanism of catalysis of two families of terminal oxidases: heme-copper and bd-type, Biochemistry (Moscow), 84, 1390-1402, doi: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297919110130.
Wikstrom, M. (1977) Proton pump coupled to cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria, Nature, 266, 271-273.
Iwata, S., Ostermeier, C., Ludwig, B., and Michel, H. (1995) Structure at 2.8 Å resolution of cytochrome c oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans, Nature, 376, 660-669.
Tsukihara, T., Aoyama, H., Yamashita, E., Takashi, T., Yamaguichi, H., et al. (1996) The whole structure of the 13-subunit oxidized cytochrome c oxidase at 2.8 Å, Science, 272, 1136-1144.
Svensson-Ek, M., Abramson, J., Larsson, G., Tornroth, S., Brzezinski, P., and Iwata, S. (2002) The X-ray crystal structures of wild-type and EQ(I-286) mutant cytochrome c oxidases from Rhodobacter sphaeroides., J. Mol. Biol., 321, 329-339.
Konstantinov, A. A., Siletsky, S., Mitchell, D., Kaulen, A., and Gennis, R. B. (1997) The roles of the two proton input channels in cytochrome c oxidase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides probed by the effects of site-directed mutations on time resolved electrogenic intraprotein proton transfer, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 9085-9090.
Siletsky, S. A., Pawate, A. S., Weiss, K., Gennis, R. B., and Konstantinov, A. A. (2004) Transmembrane charge separation during the ferryl-oxo → oxidized transition in a non-pumping mutant of cytochrome c oxidase., J. Biol. Chem., 279, 52558-52565.
Han, D., Namslauer, A., Pawate, A. S., Morgan, J. E., Nagy, S., et al. (2006) Replacing Asn207 by aspartate at the neck of the D channel in the aa3-type cytochrome c oxidase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides results in decoupling the proton pump, Biochemistry, 45, 14064-14074.
Siletsky, S. A., Zhu, J., Gennis, R. B., and Konstantinov, A. A. (2010) Partial steps of charge translocation in the nonpumping N139L mutant of Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome c oxidase with a blocked D-channel, Biochemistry, 49, 3060-3073, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi901719e.
Proshlyakov, D. A., Pressler, M. A., DeMaso, C., Leykam, J. F., DeWitt, D. L., and Babcock, G. T. (2000) Oxygen activation and reduction in respiration: involvement of redox-active tyrosine 244, Science, 290, 1588-1591.
Siletsky, S. A., and Konstantinov, A. A. (2012) Cytochrome c oxidase: charge translocation coupled to single-electron partial steps of the catalytic cycle, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1817, 476-488, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.08.003.
Siletsky, S. A., Borisov, V. B., and Mamedov, M. D. (2017) Photosystem II and terminal respiratory oxidases: molecular machines operating in opposite directions, Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed), 22, 1379-1426.
Shirey, K., Stover, K. R., Cleary, J., Hoang, N., and Hosler, J. (2016) Membrane-anchored cyclic peptides as effectors of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, Biochemistry, 55, 2100-2111, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01368.
Frederickson, C. J., and Bush, A. I. (2001) Synaptically released zinc: physiological functions and pathological effects, Biometals, 14, 353-366, doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1012934207456.
Fudge, D. H., Black, R., Son, L., LeJeune, K., and Qin, Y. (2018) Optical recording of Zn(2+) dynamics in the mitochondrial matrix and intermembrane space with the GZnP2 sensor, ACS Chem. Biol., 13, 1897-1905, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.8b00319.
Sheline, C. T., Behrens, M. M., and Choi, D. W. (2000) Zinc-induced cortical neuronal death: contribution of energy failure attributable to loss of NAD(+) and inhibition of glycolysis, J. Neurosci., 20, 3139-3146.
Gazaryan, I. G., Krasnikov, B. F., Ashby, G. A., Thorneley, R. N., Kristal, B. S., and Brown, A. M. (2002) Zinc is a potent inhibitor of thiol oxidoreductase activity and stimulates reactive oxygen species production by lipoamide dehydrogenase, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 10064-10072, doi: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M108264200.
Sharpley, M. S., and Hirst, J. (2006) The inhibition of mitochondrial complex I (NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase) by Zn2+, J. Biol. Chem., 281, 34803-34809, doi: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M607389200.
Link, T. A., and von Jagow, G. (1995) Zinc ions inhibit the QP center of bovine heart mitochondrial bc1 complex by blocking a protonatable group, J. Biol. Chem., 270, 25001-25006, doi: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.42.25001.
Schulte, M., Mattay, D., Kriegel, S., Hellwig, P., and Friedrich, T. (2014) Inhibition of Escherichia coli respiratory complex I by Zn(2+), Biochemistry, 53, 6332-6339, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi5009276.
Mills, D. A., Schmidt, B., Hiser, C., Westley, E., and Ferguson-Miller, S. (2002) Membrane potential-controlled inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase by zinc, J. Biol. Chem., 277, 14894-14901.
Kuznetsova, S. S., Azarkina, N. V., Vygodina, T. V., Siletsky, S. A., and Konstantinov, A. A. (2005) Zink ions as cytochrome c oxidase inhibitors: two sites of action, Biochemistry (Moscow), 70, 128-136.
Lee, H. J., and Adelroth, P. (2013) The heme-copper oxidase superfamily shares a Zn2+-binding motif at the entrance to a proton pathway, FEBS Lett., 587, 770-774, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.069.
Aagaard, A., and Brzezinski, P. (2001) Zinc ions inhibit oxidation of cytochrome c oxidase by oxygen, FEBS Lett., 494, 157-160.
Francia, F., Giachini, L., Boscherini, F., Venturoli, G., Capitanio, G., et al. (2007) The inhibitory binding site(s) of Zn2+ in cytochrome c oxidase, FEBS Lett., 581, 611-616.
Kannt, A., Ostermann, T., Muller, H., and Ruitenberg, M. (2001) Zn2+ binding to the cytoplasmic side of Paracoccus denitrificans cytochrome c oxidase selectively uncouples electron transfer and proton translocation, FEBS Lett., 503, 142-146.
Nicholls, P., and Singh, A. P. (1988) Effect of zinc on proteoliposomal cytochrome oxidase, Life Sci. Adv. (Biochemistry, Delhi), 7, 321-326.
Vygodina, T. V., Zakirzyanova, W., and Konstantinov, A. A. (2008) Inhibition of membrane-bound cytochrome c oxidase by zinc ions: High-affinity Zn(2+)-binding site at the P-side of the membrane, FEBS Lett., 582, 4158-4162.
Faxen, K., Salomonsson, L., Adelroth, P., and Brzezinski, P. (2006) Inhibition of proton pumping by zinc ions during specific reaction steps in cytochrome c oxidase, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1757, 388-394.
Mitchell, D. M., and Gennis, R. B. (1995) Rapid purification of wildtype and mutant cytochrome c oxidase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides by Ni2+-NTA affinity chromatography, FEBS Lett., 368, 148-150.
Siletsky, S., Kaulen, A. D., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1999) Resolution of electrogenic steps coupled to conversion of cytochrome c oxidase from the peroxy to the ferryl-oxo state, Biochemistry, 38, 4853-4861.
Siletskiy, S., Soulimane, T., Azarkina, N., Vygodina, T. V., Buse, G., et al. (1999) Time-resolved generation of membrane potential by ba3 cytochrome c oxidase from Thermus thermophilus. Evidence for reduction-induced opening of the binuclear centre, FEBS Lett., 457, 98-102.
Azarkina, N., Siletsky, S., Borisov, V., von Wachenfeldt, C., Hederstedt, L., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1999) A cytochrome bb'-type quinol oxidase in Bacillus subtilis strain 168, J. Biol. Chem., 274, 32810-32817.
Siletsky, S. A., Belevich, I., Wikstrom, M., Soulimane, T., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2009) Time-resolved OH→EH transition of the aberrant ba3 oxidase from Thermus thermophilus, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1787, 201-205.
Siletsky, S. A., Belevich, I., Belevich, N. P., Soulimane, T., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2011) Time-resolved single-turnover of caa3 oxidase from Thermus thermophilus. Fifth electron of the fully reduced enzyme converts OH into EH state, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1807, 1162-1169, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.05.006.
Siletsky, S. A., Zaspa, A. A., Poole, R. K., and Borisov, V. B. (2014) Microsecond time-resolved absorption spectroscopy used to study CO compounds of cytochrome bd from Escherichia coli, PLoS One, 9, e95617, doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095617.
Siletsky, S. A., Rappaport, F., Poole, R. K., and Borisov, V. B. (2016) Evidence for fast electron transfer between the high-spin haems in cytochrome bd-I from Escherichia coli, PLoS One, 11, e0155186, doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155186.
Drachev, L. A., Jasaitis, A. A., Kaulen, A. D., Kondrashin, A. A., Liberman, E. A., et al. (1974) Direct measurement of electric current generation by cytochrome oxidase, H+-ATPase and bacteriorhodopsin, Nature, 249, 321-324.
Zaslavsky, D., Kaulen, A., Smirnova, I. A., Vygodina, T. V., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1993) Flash-induced membrane potential generation by cytochrome c oxidase, FEBS Lett., 336, 389-393.
Zaslavsky, D. L., Smirnova, I. A., Siletsky, S. A., Kaulen, A. D., Millett, F., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1995) Rapid kinetics of membrane potential generation by cytochrome c oxidase with the photoactive Ru(II)-tris-bipyridyl derivative of cytochrome c as electron donor, FEBS Lett., 359, 27-30.
Siletsky, S. A., Belevich, I., Jasaitis, A., Konstantinov, A. A., Wikstrom, M., Soulimane, T., and Verkhovsky, M. I. (2007) Time-resolved single-turnover of ba3 oxidase from Thermus thermophilus, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1767, 1383-1392, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2007.09.010.
Siletsky, S. A., Belevich, I., Soulimane, T., Verkhovsky, M. I., and Wikstrom, M. (2013) The fifth electron in the fully reduced caa(3) from Thermus thermophilus is competent in proton pumping, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1827, 1-9, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2012.09.013.
Kalaidzidis, Y. L., Gavrilov, A. V., Zaitsev, P. V., Korolev, E. V., and Kalaidzidis, A. L. (1997) PLUK- an environment for software development, Progr. Comp. Soft., 23, 206-211.
Mamedov, M. D., Tyunyatkina, A. A., Siletsky, S. A., and Semenov, A. Y. (2006) Voltage changes involving photosystem II quinone-iron complex turnover, Eur. Biophys. J., 35, 647-654.
Siletsky, S. A., Mamedov, M. D., Lukashev, E. P., Balashov, S. P., Dolgikh, D. A., et al. (2016) Electrogenic steps of light-driven proton transport in ESR, a retinal protein from Exiguobacterium sibiricum, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1857, 1741-1750, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2016.08.004.
Siletsky, S. A., Mamedov, M. D., Lukashev, E. P., Balashov, S. P., Dolgikh, D. A., et al. (2019) Elimination of proton donor strongly affects directionality and efficiency of proton transport in ESR, a light-driven proton pump from Exiguobacterium sibiricum, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg., 1860, 1-11, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2018.09.365.
Siletsky, S. A., Belevich, I., Belevich, N. P., Soulimane, T., and Wikstrom, M. (2017) Time-resolved generation of membrane potential by ba3 cytochrome c oxidase from Thermus thermophilus coupled to single electron injection into the O and OH states, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1858, 915-926, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2017.08.007.
Medvedev, D. M., Medvedev, E. S., Kotelnikov, A. I., and Stuchebrukhov, A. A. (2005) Analysis of the kinetics of the membrane potential generated by cytochrome c oxidase upon single electron injection., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1710, 47-56.
Siletsky, S. A., Han, D., Brand, S., Morgan, J. E., Fabian, M., et al. (2006) Single-electron photoreduction of the PM intermediate of cytochrome c oxidase, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1757, 1122-1132, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.07.003.
Vygodina, T. V., and Konstantinov, A. A. (1988) H2O2-induced conversion of cytochrome c oxidase peroxy complex to oxoferryl state, Ann. NY Acad. Sci., 550, 124-138.
Sugitani, R., and Stuchebrukhov, A. A. (2009) Molecular dynamics simulation of water in cytochrome c oxidase reveals two water exit pathways and the mechanism of transport, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1787, 1140-1150.
Yoshikawa, S., Shinzawa-Itoh, K., Nakashima, R., Yaono, R., Inoue, N., et al. (1998) Redox-coupled crystal structural changes in bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase, Science, 280, 1723-1729.
Mills, D. A., and Ferguson-Miller, S. (2002) Influence of structure, pH and membrane potential on proton movement in cytochrome oxidase, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1555, 96-100.
Popovic, D. M., and Stuchebrukhov, A. A. (2005) Proton exit channels in bovine cytochrome c oxidase, J. Phys. Chem. B, 109, 1999-2006, doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0464371.
Muramoto, K., Hirata, K., Shinzawa-Itoh, K., Yoko-o, S., Yamashita, E., et al. (2007) A histidine residue acting as a controlling site for dioxygen reduction and proton pumping by cytochrome c oxidase, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 104, 7881-7886.
Qin, L., Mills, D. A., Hiser, C., Murphree, A. R., Garavito, M., et al. (2007) Crystallographic location and mutational analysis of Zn and Cd inhibitory sites and role of lipidic carboxylates in rescuing proton path mutants in cytochrome c oxidase, Biochemistry, 46, 6239-6248.
Klishin, S. S., Junge, W., and Mulkidjanian, A. Y. (2002) Flash-induced turnover of the cytochrome bc1 complex in chromatophores of Rhodobacter capsulatus: binding of Zn2+ decelerates likewise the oxidation of cytochrome b, the reduction of cytochrome c1 and the voltage generation, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1553, 177-182, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0005-2728(01)00250-x.
Mulkidjanian, A. Y. (2005) Ubiquinol oxidation in the cytochrome bc1 complex: reaction mechanism and prevention of short-circuiting, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1709, 5-34, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2005.03.009.
Axelrod, H. L., Abresch, E. C., Paddock, M. L., Okamura, M. Y., and Feher, G. (2000) Determination of the binding sites of the proton transfer inhibitors Cd2+ and Zn2+ in bacterial reaction centers, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97, 1542-1547, doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.4.1542.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Ilya Oleynikov for technical assistance in the production of Fig. 10. The authors express their gratitude to anonymous Reviewers, especially to the Reviewer 2 and Reviewer 3.
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (research project no. 19-14-00063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interests in financial or any other field. This article does not contain descriptions of studies performed by authors with the participation of humans or using animals as objects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siletsky, S.A., Gennis, R.B. Time-Resolved Electrometric Study of the F→O Transition in Cytochrome c Oxidase. The Effect of Zn2+ Ions on the Positive Side of the Membrane. Biochemistry Moscow 86, 105–122 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297921010107
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297921010107