Abstract
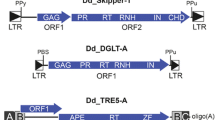
We identified a novel human-specific family of transposable elements that consists of fused copies of the CpG-island containing the first exon of gene MAST2 and retrotransposon SVA. We propose a mechanism for the formation of this family termed CpG-SVA, comprising 5′-transduction by an SVA insert. After the divergence of human and chimpanzee ancestor lineages, retrotransposon SVA has inserted into the first intron of gene MAST2 in the sense orientation. Due to splicing of an aberrant RNA driven by MAST2 promoter, but terminally processed using SVA polyadenylation signal, the first exon of MAST2 has fused to a spliced 3′-terminal fragment of SVA retrotransposon. The above ancestor CpG-SVA element due to retrotranspositions of its own copies has formed a novel family represented in the human genome by 76 members. Recruitment of a MAST2 CpG island was most likely beneficial to the hybrid retrotransposons because it could significantly increase retrotransposition frequency. Also, we show that human L1 reverse transcriptase adds an extra cytosine residue to the 3′ terminus of the nascent first strand of cDNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- REs:
-
retroelements
References
Baltimore, D. (1970) Nature, 226, 1209–1211.
Temin, H. M., and Mizutani, S. (1970) Nature, 226, 1211–1213.
Eickbush, T. H. (1997) Science, 277, 911–912.
Buzdin, A. A. (2004) Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 61, 2046–2059.
Mills, R. E., Bennett, E. A., Iskow, R. C., Luttig, C. T., Tsui, C., Pittard, W. S., and Devine, S. E. (2006) Am. J. Hum. Genet., 78, 671–679.
Buzdin, A. (2007) Sci. World J., 7, 1848–1868.
Jurka, J. (1997) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 1872–1877.
Kazazian, H. H., Jr., and Goodier, J. L. (2002) Cell, 110, 277–280.
Furano, A. V. (2000) Progr. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol., 64, 255–294.
Ullu, E., and Tschudi, C. (1984) Nature, 312, 171–172.
Kramerov, D. A., and Vassetzky, N. S. (2005) Int. Rev. Cytol., 247, 165–221.
Wang, H., Xing, J., Grover, D., Hedges, D. J., Han, K., Walker, J. A., and Batzer, M. A. (2005) J. Mol. Biol., 354, 994–1007.
Goodier, J. L., and Kazazian, H. H. (2008) Cell, 135, 23–35.
Xing, J., Wang, H., Belancio, V. P., Cordaux, R., Deininger, P. L., and Batzer, M. A. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 103, 17608–17613.
Babushok, D. V., Ostertag, E. M., and Kazazian, H. H. (2007) Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 64, 542–554.
Buzdin, A., Gogvadze, E., Kovalskaya, E., Volchkov, P., Ustyugova, S., Illarionova, A., Fushan, A., Vinogradova, T., and Sverdlov, E. (2003) Nucleic Acids Res., 31, 4385–4390.
Gogvadze, E., Barbisan, C., Lebrun, M. H., and Buzdin, A. (2007) BMC Genom., 8, 360.
Brosius, J. (1999) Genetica, 107, 209–238.
Jurka, J., Kapitonov, V. V., Pavlicek, A., Klonowski, P., Kohany, O., and Walichiewicz, J. (2005) Cytogenet. Genome Res., 110, 462–467.
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W., and Lipman, D. J. (1990) J. Mol. Biol., 215, 403–410.
Thompson, J. D., Higgins, D. G., and Gibson, T. J. (1994) Nucleic Acids Res., 22, 4673–4680.
Felsenstein, J. (1993) Distributed by the author, Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle.
Hancks, D., Ewing, A., Chen, J. E., Tokunaga, K., and Kazazian, H. (2009) Genome Res., August 3 (E-pub ahead of print).
Damert, A., Raiz, J., Horn, A., Lower, J., Wang, H., Xing, J., Batzer, M., Lower, R., and Schumann, G. (2009) Genome Res., July 27 (E-pub ahead of print).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2009, Vol. 74, No. 12, pp. 1709–1717.
Originally published in Biochemistry (Moscow) On-Line Papers in Press, as Manuscript BM09-214, November 15, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bantysh, O.B., Buzdin, A.A. Novel family of human transposable elements formed due to fusion of the first exon of gene MAST2 with retrotransposon SVA. Biochemistry Moscow 74, 1393–1399 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297909120153
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297909120153