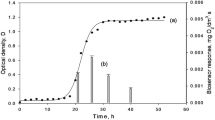
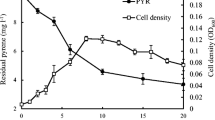
Abstract
The effects of stress factors (drying, low temperature, and long-term storage) on the survival of the actinobacteria Gordonia polyisoprenivorans 135, which is used as a biosensor receptor to detect sodium benzoate in water solutions, were studied, as well as the effects of these factors on the biodegradation of aromatic compounds. The cells remained viable after starvation and subsequent long-term storage in suspension. Immobilization of G. polyisoprenivorans 135 cells prevented the loss of the viability when they were dried prior to storage. The immobilized cells, which were used as a biosensor receptor element, were active in relation to benzoate for more than 9 months. Storage of the receptor at 4°C for four months led to a sensor response to 10–4 and 10–3 M benzoate at a level of 69 and 79% of the maximum, respectively, while the response was 58 and 51% (70 pA/s and 140 pAs), respectively, after 9 months of storage. These results suggest that actinobacterial cells can survive an adverse environment and can be used to create highly stable and sensitive bioreceptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russell, A.D. and Furr, J.R., Science Progress, 1996, vol. 79, no. 1, pp. 27–48.
Warth, A.D., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1988, vol. 54, no. 8, pp. 2091–2095.
Piper, P.W., Free Radic. Biol. Med., 1999, vol. 27, nos. 11–12, pp. 1219–1227.
World Health Organization, Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 26: Benzoic Acid and Sodium Benzoate, Geneva: World Health Organization, 2000.
AlGadir, M.I., Ihaimer, M.M., Sabah, Elkhier M.K., and Idri., O.F., Asia J. Clin. Nutr., 2009, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 83–87.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration, FDA, USFDA: Data on Benzene in Soft Drinks and Other Beverages, 2006.
Solyanikova, I.P., Emelyanova, E.V., Shumkova, E.S., Egorova, D.O., Korsakova, E.S., Plotnikova, E.G., and Golovleva, L.A., Int. Biodeter. Biodegr., 2015, vol. 100, pp. 155–164.
RF Patent no. 151960, 2015.
Abdallah, F.B., Kallel, H., and Bakhrouf, A., Arch. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 191, no. 6, pp. 493–500.
Trevors, J.T., J. Microbiol. Methods, 2011, vol. 86, pp. 266–273.
Carvalhais, V., Franca, A., Cerca, F., Vitorino, R., Pier, G.B., Vilanova, M., and Cerca, N., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 98, no. 6, pp. 2585–2596.
Soina, V.S., Mulyukin, A.L., Demkina, E.V., Vorobyova, E.A., and El-Registan, G.I., Astrobiology, 2004, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. P. 345–358.
Mulyukin, A.L., Demkina, E.V., Kryazhevskikh, N.A., Suzina, N.E., Vorob’eva, L.I., Duda, V.I., Gal’chenko, V.F., and El’-Registan, G.I., Microbiology (Moscow), 2009, vol. 78, no. 4, pp. 407–418.
Loiko, N.G., Kryazhevskikh, N.A., Suzina, N.E., Demkina, E.V., Muratova, A.Yu., Turkovskaya, O.V., Kozlova, A.N., Gal’chenko, V.F., and El’-Registan, G.I., Microbiology (Moscow), 2011, vol. 80, no. 4, pp. 472–482.
Anuchin, A.M., Mulyukin, A.L., Suzina, N.E., Duda, V.I., El-Registan, G.I., and Kaprelyants, A.S., Microbiology, 2009, vol. 155, no. 4, pp. 1071–1079.
Kaprelyants, A.S., Gottschal, J.C., and Kell, D.B., FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 1993, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 271–285.
Dworkin, J. and Shah, I.M., Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 8, no. 12, pp. 890–896.
Casabianca, A., Orlandi, C., Barbieri, F., Sabatini, L., Cesare, A.D., Sisti, D., Pasquaroli, S., Magnani, M., and Citterio, B., Arch. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 197, no. 3, p. 1007.
Shapiro, J.A., Nguyen, V.L., and Chamberlain, N.R., J. Med. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 60, no. 7, pp. 950–960.
Williamson, K.S., Richards, L.A., Perez-Osorio, A.C., Pitts, B., McInnerney, K., Stewart, P.S., and Franklin, M.J., J. Bacteriol., 2012, vol. 194, no. 8, pp. 2062–2073.
Kim, J., Hahn, J.S., Franklin, M.J., Stewart, P.S., and Yoon, J., J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 2009, vol. 63, pp. 129–135.
Cerca, F., Andrade, F., Franca, A., Andrade, E.B., Ribeiro, A., Almeida, A.A., Cerca, N., Pier, G., Azeredo, J., and Vilanova, M., J. Med. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 1717–1724.
Bishop, A.H. and Rachwal, P.A., Curr. Microbiol., 2014, vol. 68, p. 1007.
Solyanikova, I.P., Mulyukin, A.L., Suzina, N.E., El-Registan, G.I., and Golovleva, L.A., J. Environm. Sci. Health, vol. 46, no. 7, pp. 638–647.
Ivshina, I.B., Mukhutdinova, A.N., Tyumina, H.A., Vikhareva, H.V., Suzina, N.E., El’-Registan, G.I., and Mulyukin, A.L., Curr. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 70, no. 3, pp. 307–314.
Solyanikova, I.P., Golovlev, E.L., Lisnyak, O.V., and Golovleva, L.A., Biokhimiya, 1999, vol. 64, no. 7, pp. 982–989.
Solyanikova, I.P., Suzina, N.E., Mulyukin, A.L., El’-Registan, G.I., and Golovleva, L.A., Microbiology (Moscow), 2013, vol. 82, no. 5, pp. 562–571.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.V. Emelyanova, N.E. Souzina, V.N. Polivtseva, A.N. Reshetilov, I.P. Solyanikova, 2017, published in Prikladnaya Biokhimiya i Mikrobiologiya, 2017, Vol. 53, No. 5, pp. 510–518.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emelyanova, E.V., Souzina, N.E., Polivtseva, V.N. et al. Survival and biodegradation activity of Gordonia polyisoprenivorans 135: Basics of a biosensor receptor. Appl Biochem Microbiol 53, 580–586 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683817050039
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683817050039