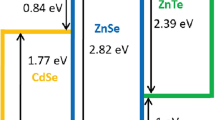
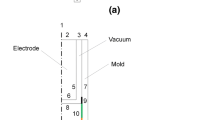
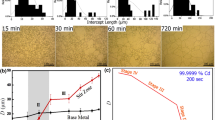
Abstract
The chemical composition and tribological properties of the thin-film diselenide molybdenum coatings deposited by pulsed laser deposition in vacuum and a rarefied inert gas (argon) atmosphere are studied. Upon deposition in a gas at a pressure of ∼2 Pa, stoichiometric coatings with improved antifriction properties as compared vacuum-deposited coatings form. However, a too strong increase in the argon pressure (to ∼10 Pa) degrades the tribological properties of the coating. Structure formation in the MoSe x coatings grown by pulsed laser deposition on an unheated substrate is investigated. Deposition in vacuum or argon at a pressure of 2 Pa leads to formation of rather smooth coatings with a dense amorphous structure containing molybdenum nanoinclusions. Deposition at a high argon pressure results in a developed surface relief and a loose coating structure. A mathematical model is developed using the kinetic Monte Carlo method in order to describe structure formation in the coatings that grow during physical deposition of an atomic flux. A comparative analysis demonstrates satisfactory agreement between the simulated and experimentally studied structures in the coatings created by pulsed laser deposition at various gas pressures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Savan, M. C. Simmonds, Y. Huang, et al., Thin Solid Films 489, 137 (2005).
V. Yu. Fominski, V. N. Nevolin, R. I. Romanov, et al., J. Appl. Phys. 89, 1449 (2001).
V. Yu. Fominski, V. N. Nevolin, R. I. Romanov, et al., Tribol. Lett. 17, 289 (2004).
V. N. Nevolin, V. Yu. Fominskii, A. G. Gnedovets, et al., Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 77(11), 88 (2007) [Tech. Phys. 52, 1475 (2007)].
V. Yu. Fominskii, A. M. Markeev, V. N. Nevolin, et al., Thin Solid Films 248, 240 (1994).
A. B. Bortz, M. H. Kalos, and J. L. Lebowitz, J. Comput. Phys. 17, 10 (1975).
J. T. Drotar, Y. P. Zhao, T. M. Lu, et al., Phys. Rev. B 62, 2118 (2000).
T. Karabacak, G. G. Wang, and T. M. Lu, J. Appl. Phys. 94, 7723 (2003).
D. Depla, Z. Y. Chen, A. Bogaerts, et al., J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 22, 1524 (2004).
Z. L. Liu, L. Yu, K. L. Yao, et al., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 38, 4202 (2005).
T. E. Itina, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 740 (2001).
A. A. Morozov, Z. Geretovszky, and T. Szorenyi, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 015303 (2008).
D. V. Shtansky, T. A. Lobova, V. Yu. Fominski, et al., Surf. Coat. Technol. 183, 328 (2004).
C. M. Lieber and Y. Kim, Thin Solid Films 206, 355 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.N. Nevolin, V.Yu. Fominski, A.G. Gnedovets, R.I. Romanov, 2009, published in Zhurnal Tekhnicheskoĭ Fiziki, 2009, Vol. 79, No. 1, pp. 118–124.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nevolin, V.N., Fominski, V.Y., Gnedovets, A.G. et al. Study and simulation of the growth of solid lubricant MoSe x coatings during pulsed laser deposition. Tech. Phys. 54, 117–123 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784209010174
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784209010174