Abstract
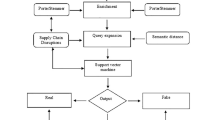
In recent years, with the implementation of the policy of “Replacing Business Tax with Value-Added Tax” and “Streamlining Administration, Delegating Powers and Improving Regulation and Services” in China, criminals have been issuing false invoices, and such cases have shown a trend of high frequency in the category of economic crimes. Tax departments and public security departments are facing increasingly a serious crime situation that has created a new challenge. By studying the current trend of false invoice crime, the difficulties of investigation in such cases are analyzed. Using the tax information of enterprises that have conducted false invoice as the breakthrough point, the machine learning method is introduced to build a risk pre-warning assessment model based on the Support Vector Machine (SVM) method to detect enterprises issuing false invoices. Three steps were designed in this paper. First, a risk pre-warning assessment model was established to detect enterprises issuing false invoices. Second, enterprises were classified into three groups according to the risk levels: A, B, and C. Third, collected data were used to make an empirical analysis, and the results show that the accuracy rate of the model is 97%. In China, due to the high crime rate of tax fraud cases, it is important to obtain data from tax and public security departments to establish a model that can detect such crimes as early as possible. The police and tax authorities can use this model to jointly combat such crimes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chai, Ruijuan. 2017. Extraterritorial experience of supervision sandbox and its enlightenment. Law Science 08: 27–40 ((in Chinese)).
Chen, Changwen, and Guangwei Tian. 2017. Model design of public security information automatic classification system based on SVM. Network Security Technology and Application 2017 (07): 46–48.
Chen, Ying. 2004. Research on technical methods for tax audit selection. Tianjin (in Chinese): Tianjin University.
Dai, Peng. 2008. New trends of virtual invoicing crimes and investigation countermeasures. Journal of Political Science and Law 1: 10–13 ((in Chinese)).
Dan, Liu. 2018. Early warning of economic crimes. Beijing: China People’s Public Security University Press ((in Chinese)).
Ding, N., M. Ma, and Y. Zhai. 2021. Serial theft case linkage based on a two-step cumulative probability model. Journal of Investigative Psychology and Offender Profiling 18: 3–17.
Ding, N., and Y. Zhai. 2019. Crime prevention of bus pickpocketing in Beijing, China: Does air quality affect crime? Security Journal. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41284-019-00226-1.
Goerke, L. 2014. Tax evasion by individuals. IAAEU Discussion Papers, 1–8.
Goumagias, N.D., and D. Hristu-Varsakelis. 2013. A Markov-based decision model of tax evasion for risk-averse firms in Greece. In Optimization theory, decision making, and operations research applications. New York: Springer.
Harris, Terry. 2015. Credit scoring using the clustered support vector machine. Expert Systems with Applications 42 (2): 741–750.
Hirk, R., K. Hornik, and L. Vana. 2019. Multivariate ordinal regression models: an analysis of corporate credit ratings. Statistical Methods and Applications 28 (422): 1–33.
Jian, Lin, Li. Song, Yu. Xianfeng, and Wang Xiangzhen. 2017. Research and application of real-time risk prevention and control system in public security police Big Data—taking Guizhou Province “Real-Time Risk Prevention and Control System in Qianxinan Prefecture” as an example. Journal of the Chinese People’s Public Security University 23 (2): 38–42 ((in Chinese)).
Korndörfer, M., I. Krumpal, and S.C. Schmukle. 2014. Measuring and explaining tax evasion: Improving self-reports using the crosswise model. Journal of Economic Psychology 45: 18–32.
Li, C., N. Ding, Y. Zhai, et al. 2021. Comparative study on credit card fraud detection based on different support vector machines. Intelligent Data Analysis 25 (01): 105–119.
Li, Chonggang, and Xu. Huiquan. 2018. Smoke index: Big data monitoring internet financial risks. Big Data 4 (04): 76–84 ((in Chinese)).
Li, M., Z. Zhang, and R. Bai. 2014. The study on risk rating model of commercial bank credit based on SVM. In Practical applications of intelligent systems. Berlin: Springer.
Li, Xuanju. 1998. Research on tax audit selection model. Financial Research 08: 11–15 ((in Chinese)).
Liu, Wei. 2016. Research on tax inspection based on game model. Inner Mongolia Statistics 2016 (04): 14–15 ((in Chinese)).
Ma, Qingguo, Weihong Wang, Jian Chen, Guanyun Huang, and Hezhong Dai. 2002. Application of neural network in tax auditing selection. Quantum Economics and Technology Economics Research 2002 (08): 98–101 ((in Chinese)).
Paternoster, Raymond, and Sally Simpson. 1996. Sanction threats and appeals to morality: Testing a rational choice model of corporate crime. Law & Society Review 30 (3): 549–584.
Rad, M.S., and A. Shahbahrami. 2016. Detecting high risk taxpayers using data mining techniques. In 2016 2nd International Conference of Signal Processing and Intelligent Systems (ICSPIS). IEEE.
Vapnik, V. 1995. The nature of statistical learning theory. New York: Springer.
Wang, Na., and Xingchen Li. 2018. Comparison of penalty regulations on tax evasion in China and the United States. Journal of Liaoning Public Security Judicial Administration Cadre College 04: 93–96 ((in Chinese)).
Yuan, Ye. 2019. Research on H-city tax audit selection model based on Logistic regression to identify companiess’ tax evasion. Tongliao (in Chinese): Inner Mongolia University.
Zhang, Juan. 2014. Characteristics of tax-related crimes in the new era and countermeasures for detection and prevention. Journal of Liaoning Police Academy 16 (02): 51–57 ((in Chinese)).
Zhao, Lingfeng. 2016. Study on automatic identification method of tax inspection and selection based on SVM. Journal of Jiangsu Institute of Technology 22 (02): 22–25 ((in Chinese)).
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Soft Science Research Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2021C35060). This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71904194) and National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2020YFC1522600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, N., Zhang, X., Zhai, Y. et al. Risk assessment of VAT invoice crime levels of companies based on DFPSVM: a case study in China. Risk Manag 23, 75–96 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41283-021-00068-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/s41283-021-00068-5