Abstract
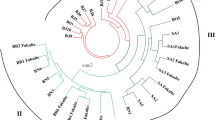
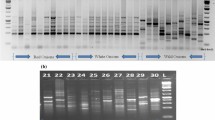
Data on AFLP (eight primer pairs) and 14 phenotypic traits, collected on 55 elite and exotic bread wheat genotypes, were utilized for estimations of genetic diversity. We earlier used these 55 genotypes for a similar study using SSRs and SAMPL. As many as 615 scorable AFLP bands visualized included 287 (46.6%) polymorphic bands. The phenotypic traits included yield and its component traits, as well as physiomorphological traits like flag leaf area. Dendrograms were prepared using cluster analysis based on Jaccard's similarity coefficients in case of AFLP and on squared Euclidean distances in case of phenotypic traits. PCA was conducted using AFLP data and a PCA plot was prepared, which was compared with clustering patterns in two dendrograms, one each for AFLP and phenotypic traits. The results were also compared with published results that included studies conducted elsewhere using entirely different wheat germplasm and our own SSR and SAMPL studies based on the same 55 genotypes used in the present study. It was shown that molecular markers are superior to phenotypic traits and that AFLP and SAMPL are superior to other molecular markers for estimation of genetic diversity. On the basis of AFLP analysis and keeping in view the yield performance and stability, a pair of genotypes (E3876 and E677) was recommended for hybridization in order to develop superior cultivars.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ayele, M., Tefera, H., Assefa, K., and Nguyen, T. (1999). Genetic characterization of two Eragrostisspecies using AFLP and morphological traits. Hereditas 130:33–40.
Bar-Hen, A., Charcosset, A., Bourgoin, M., and Guiard, J. (1995). Relationship between genetic markers and morphological traits in a maize inbred lines collection. Euphytica 84:145–154.
Barrett, B. A., and Kidwell, K. K. (1998). AFLP-based genetic diversity assessment among wheat cultivars from the pacific northwest. Crop Sci. 38:1261–1271.
Bohn, M., Utz, H. F., and Melchinger, A. E. (1999). Genetic similarities among winter wheat cultivars determined on the basis of RFLPs, AFLPs and SSRs and their use for predicting progeny variance. Crop Sci. 39:228–237.
Chen, H. B., Martin, J. M., Lavin, M., and Talbert, L. E. (1994). Genetic diversity in hard red spring wheat based on sequence-tagged-site PCR markers. Crop Sci. 34:1628–1632.
Corbellini, M., Perenzin, M., Accerbi, M., Vaccino, P., and Borghi, B. (2002). Genetic diversity in bread wheat, as revealed by coefficient of perentage and molecular markers, and its relationship to hybrid performance. Euphytica 123:273–285.
Davila, J. A., Loarce, Y., Ramsay, L., Waugh, R., and Ferrer, E. (1999). Comparison of RAMPL and SSR markers for the study of wild barley genetic diversity. Hereditas 131:5–13.
Dillmann, C., Bar-Hen, A., Guerin, D., Charcosset, A., and Murigneux, A. (1997). Comparison of RFLP and morphological distaces between maize Zea maysL. inbred lines. Consequences for germplasm protection purposes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95:92–102.
dos Santos, J. B., Nienhuis, J., Skroch, P., Tivang, J., and Slocum, M. K. (1994). Comparison of RAPD and RFLP genetic markers in determining genetic similarity among Brassica oleraceaL. genotypes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 87:909–915.
Doshi, S. P., and Gupta, K. C. (1991). SPAR I: Users Manual Statistical Package for Agricultural Research Data Analysis. Indian Agricultural Statistical Research Institute, New Delhi.
Elias, M., Panaud, O., and Robert, T. (2000). Assessment of genetic variability in a traditional cassava (Manihot esculentaCrantz) farming system, using AFLP markers. Heredity 85:219–230.
Hartl, L., Mohler, V., Zeller, F. J., Hsam, S. L. K., and Schweizer, G. (1999). Identification of AFLP markers closely linked to the powdery mildew resistance genes Pmlcand Pm4ain commomn wheat (Triticum aestivumL.). Genome 42:322–329.
Hazen, P. S., Leroy, P., and Ward, R. (2002). AFLP in Triticum aestivumL.: Patterns of diversity and genome distributrion. Euphytica 125:89–102.
Lefebvre, V., Goffinet, B., Chauvet, J. C., Caromel, B., Signoret, P., Brand, R., and Palloix, A. (2001). Evaluation of genetic distances between pepper inbred lines for cultivar protection purposes: comparison of AFLP, RAPD and phenotypic data. Theor. Appl. Genet. 102:741–750.
Lubberstedt, T., Melchinger, A. E., Dule, C., Vuylsteke, M., and Kuiper, M. (2000). Relationships among early European maize inbreds: IV. Genetic diversity revealed with AFLP markers and comparison with RFLP, RAPD, and pedigree data. Crop. Sci. 40:783–791.
Ma, Z.-Q., and Lapitan, N. L. V. (1998). A comparison of amplified and restriction fragment length polymorphism in wheat. Cereal. Res. Commun. 26:1–7.
Maestri, E., Malcevschi, A., Massari, A., and Marmiroli, N. (2002). Genome analysis of cultivated barley (Hordeum vulgare) using sequence-tagged molecular markers. Estimates based on divergence based on RFLP and PCR markers derived from stress-responsive genes, and simple sequence repeats (SSRs). Mol. Genet. Genomics 267:186–201.
Manifesto, M. M., Schlatter, A. R., Hopp, H. E., Suarez, E. Y., and Dubcovsky, J. (2001). Quantitative evaluation of genetic diversity in wheat germplasm using molecular markers. Crop. Sci. 41:682-690.
Mantel, N. A. (1967). The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res. 27:209–220.
Maughan, P. J., Saghai Maroof, M. A., Buss, G. R., and Huestis. G. M. (1996). Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) in soybean: Species diversity, inheritance, and near-isogenic line analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 93:392–401.
Messmer, M. M., Melchinger, A. E., Hermann, R. G., and Boppenmaier, J. (1993). Relationships among early European maize inbreds: II. Comparison of pedigree and RFLP data. Crop. Sci. 33:1033–1040.
Morgante, M., and Olivieri, A. M. (1993). PCR-amplified microsatellites as markers in plant genetics. Plant J. 3:175–182.
Nagaoka, T., and Ogihara, Y. (1997). Applicability of inter-simple sequence repeat polymorphisms in wheat for use as DNA markers in comparison to RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 94:597–602.
Pakniyat, H., Powell,W., Baird, E., Handley, L. L., Robinson, D., Scrimgeour, C. M., Nevo, E., Hackett, C. A., Caligari, P. D. S., and Forster, B. P. (1997). AFLP variation in wild barley (Hordeum spontaneumC. Koch) with reference to salt tolerance and associated ecogeography. Genome 40:332–341.
Papa, R., Attene, G., Barcaccia, G., Ohgata, A., and Konishi, T. (1998). Genetic diversity in landrace populations of Hordeum vulgareL. from Sardinia, Italy, as revealed by RAPDs, isozymes and morphological traits. Plant Breed 117:523–530.
Paull, J. G., Chalmers, K. J., Karakousis, A., Kretschmer, J. M., Manning, S., and Langridge, P. (1998). Genetic diversity in Australian wheat varieties and breeding material based on RFLP data. Theor. Appl. Genet. 96:435–446.
Powell, W., Morgante, M., Andre, C., Hanafey, M., Vogel, J., Tingey, S., and Rafalski, A. (1996). The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol. Breed 2:225–238.
Prabhu, R. R., Webb, D., Jessen, H., Luk, S., Smith, S., and Gresshoff, P. (1997). Genetic relatedness among soybean genotypes using DNA amplification fingerprinting (DAF), RFLP, and pedigree. Crop. Sci. 37:1590–1595.
Prasad, M., Varshney, R. K., Kumar, A., Balyan, H. S., Sharma, P. C., Edwards, K. J., H.-Singh, Dhaliwal, H. S., Roy, J. K., and Gupta, P. K. (1999). A microsatellite marker associated with a QTL for grain protein content on chromosome arm 2DL of bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 99:341–345.
Prasad, M.,Varshney, R. K., Roy, J. K., Balyan, H. S., and Gupta, P. K. (2000). The use of microsatellites for detecting DNA polymorphism, genotype identification and genetic diversity in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 100:584–592.
Qi, X., Stam, P., and Lindhout, P. (1998). Use of locus specific AFLP markers to construct a high-density map in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 96:376–384.
Renganayaki, K., Read, J. C., and Fritz, A. K. (2001). Genetic diversity among Texas bluegrass genotypes (Poa arachniferaTorr.) revealed by AFLP and RAPD markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 102:1037–1045.
Roa, A. C., Maya, M. M., Dugue, M. C., Tohme, J., Allem, A. C., and Bonierbale, M. W. (1997). AFLP analysis of relationships among cassava and other Manihotspecies. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95:741–750.
Roder, M. S., Korzun, V., Wendehake, K., Plaschke, J., Tixier, M.-H., Leroy, P., and Ganal, M. W. (1998). A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023.
Roldan-Ruiz, I., Dendauw, J., Van Bockstaele, E., Depicker, A., and De Loose, M. (2000). AFLP markers reveal high polymorphic rates in ryegrasses (Loliumspp.). Mol. Breed 6:125–134.
Roy, J. K., Prasad, M., Varshney, R. K., Balyan, H. S., Blake, T. K., Dhaliwal, H. S., Edwards, K. J., and Gupta, P. K. (1999). Identification of a microsatellite on chromosome 6B and a STS on 7D of bread wheat showing an association with preharvest sprouting tolerance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 99:336–340.
Roy, J. K., Balyan, H. S., Prasad, M., and Gupta, P. K. (2002). Use of SAMPL for a study of DNA polymorphism, genetic diversity and possible gene tagging in bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 104:465–472.
Russell, J. R., Fuller, J. D., Macaulay, M., Hatz, B. G., Jahoor, A., Powell, W., and Waugh, R. (1997). Direct comparison of levels of genetic variation among barley accessions detected by RFLPs, AFLPs, SSRs and RAPDs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95:714–722.
Schondelmaier, J., Steinrucken, G., and Jung, C. (1996). Integration of AFLP markers into a linkage map of sugar beet (Beta VulgarisL). Plant Breeding 115:231–237.
Smith, J. S. C., Chin, E. C. L., Shu, H., Smith, O. S., Wall, S. J., Senior, M. L., Mitchell, S. E., Kresowich, S., and Ziegle, J. (1997). An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea maysL.): Comparisons with data from RFLPs and pedigree. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95:163–173.
Van Eck, H. J., Rouppe van der Voort, J., Draaistra, J., van Zand-voort, P., van Enckevort, E., Segers, B., Peleman, J., Jacobsen, E., Helder, J., and Bakker, J. (1995). The inheritance and chromosomal localisation of AFLP markers in a non-inbred potato offspring. Mol. Breeding 1:397–410.
Varshney, R. K., Sharma, P. C., Gupta, P. K., Balyan, H. S., Ramesh, B., Roy, J. K., Kumar, A., and Sen, A. (1998). Low level of polymorphism detected by SSR probes in bread wheat. Plant Breeding 117:182–184.
Varshney, R. K., Prasad, M., Roy, J. K., Kumar, N., Harjit-Singh, Dhaliwal, H. S., Balyan, H. S., Gupta, P. K. (2000). Identification of eight chromosomes and a microsatellite marker on 1AS associated with QTL for grain weight in bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 100:1290–1294.
Vos, P., Hogers, R., Bleeker, R., Reijans, M., van de Lee, T., Homes, M., Frijters, A., Pot, J., Peleman, J., Kupier, M., and Zabeau, M. (1995). AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl. Acids. Res. 23:4407–4414.
Vuylsteke, M., Mank, R., Antonise, R., Bastiaans, E., Senior, M. L., Stuber, C. W., Melchinger, A. E., Lubberstedt, T., Xia, X. C., Stam, P., Zabeau, M., and Kuiper,M. (1999). Two high-density AFLP linkage maps of Zea mays L.: Analysis of distribution of AFLP markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 99:921–935.
Weissenbach, J., Gyapay, G., Dib, C., Vignal, A., Morissette, J., Millasseau, P., Vaysseix, G., and Lathrop, M. (1992). A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature 359:794-801.
Young, W. P., Schupp, J. M., and Kiem, P. (1999). DNA methylation and AFLP marker distribution in the soybean genome. Theor. Appl. Genet. 99:785–790.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, J.K., Lakshmikumaran, M.S., Balyan, H.S. et al. AFLP-Based Genetic Diversity and Its Comparison with Diversity Based on SSR, SAMPL, and Phenotypic Traits in Bread Wheat. Biochem Genet 42, 43–59 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIGI.0000012143.48298.71
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIGI.0000012143.48298.71