Abstract
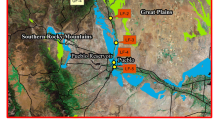
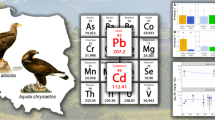
Previous research reported that concentrations of selenium in the livers of 88–95% of lesser scaup from locations in Lake Erie, Lake St. Clair, and Lake Michigan, USA were either elevated (10–33 µg/g dry weight [dw]) or in the potentially harmful range (>33 µg/g dw). In order to determine the geographic extent of these high selenium concentrations, we collected lesser scaup in Louisiana, Arkansas, Illinois, Minnesota, Wisconsin, and Manitoba and analyzed the livers for 19 trace elements. We found that all trace element concentrations, except for selenium, generally were low. Arsenic, which usually is not detected in liver samples, was detected in Louisiana and may be related to past agricultural usages. Chromium, which also is not usually detected, was only present in lesser scaup from Arkansas and may be related to fertilizer applications. Cadmium and mercury concentrations did not differ among locations and concentrations were low. Selenium concentrations in Arkansas (geometric mean=4.2 µg/g dw) were significantly lower than those in Louisiana (10.7 µg/g dw), Illinois (10.5 µg/g dw), and Minnesota (8.0 µg/g dw); concentrations in Wisconsin and Manitoba were intermediate (6.6 and 6.5 µg/g dw). About 25% of lesser scaup livers contained elevated selenium concentrations; however, none were in the harmful range. We concluded that selenium concentrations in lesser scaup in the Mississippi Flyway are elevated in some individuals, but not to the extent that has been documented in the industrial portions of the Great Lakes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, G.T., Caithamer, D.F. and Otto, M. (1999). A review of the status of greater and lesser scaup in North America. Report of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Washington, DC, July 1999, 45pp.
Afton, A.D. and Anderson, M.G. (2001). Declining scaup populations: a retrospective analysis of long-term population and harvest survey data. J. Wildl. Manag. 65, 781-96.
Austin, J.E. Custer, C.M. and Afton, A.D. (1998). Lesser scaup (Aythya affinis). In E. Poole and F. Gill (eds) The Birds of North America, No. 338, 32 pp. Philadelphia PA: The Birds of North America.
Austin, J.E., Afton, A.D., Anderson, M.G., Clark, R.G. Custer, C.M., Lawrence, J.S., Pollard, J.B. and Ringelman, J.A. (1999). Declines of Greater and Lesser Scaup Populations: Issues, Hypotheses, and Research Directions. USGS, Northern Prairie Wildlife Research Center, Jamestown ND, Unpubl. Report, February 1999, 28 pp.
Austin, J.E., Afton, A.D., Anderson, M.G., Clark, R.G., Custer, C.M., Lawrence, J.S., Pollard, J.B. and Ringelman, J.A. (2000). Declining scaup populations: issues, hypotheses, and research needs. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 28, 254-63.
Bellrose, F.C. (1976). Ducks, Geese & Swans of North America. Pennsylvania: Stackpole Books.
Custer, C.M. and Custer, T.W. (2000). Organochlorine and trace element contamination in wintering and migrating diving ducks in the southern Great Lakes, USA, since the zebra mussel invasion. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19, 2821-9.
Custer, T.W., Custer, C.M., Hines, R.K. and Sparks, D.W. (2000). Trace elements, organochlorines, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, dioxins, and furans in lesser scaup wintering on the Indiana Harbor Canal. Environ. Pollut. 110, 469-82.
Custer, T.W., Franson, J.C., Moore, J.F. and Myers, J.E. (1986). Reproductive success and heavy metal contamination in Rhode Island common terns. Environ. Pollut. 41A, 33-52.
Custer, T.W. and Hohman, W. (1994). Trace elements in canvasbacks from Louisiana, USA: 1987–1988. Environ. Pollut. 84, 252-9.
Di Giulio, R.T. and Scanlon, P.F. (1984). Heavy metals in tissues of waterfowl from the Chesapeake Bay, USA. Environ. Pollut. 35, 29-48.
Dubovsky, J.A., Moore, C.T., Bladen, J.P., Smith, G.W. and Keywood, P.D. (1997). Trends in duck breeding populations, 1955–97. US Fish and Wildlife Service: Administrative Report, Laurel Maryland, USA.
Eisler, R. (1986). Chromium hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. US Fish and Wildlife Service, Biol. Rep. 85(1.6), Washington DC, USA.
Eisler, R. (1988). Arsenic hazards to fish, wildlife, and invertebrates: a synoptic review. US Fish and Wildlife Service, Biol. Rep. 85(1.12), Washington DC, USA.
Eisler, R. (2000). Handbook of Chemical Risk Assessment Health Hazards to Human, Plants, and Animals. Vols 1–3. Florida: Lewis Publishers.
Esselink, H., Van der Geld, F.M., Jager, L.P., Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A., Zoun, P.E.F. and Baars, A.J. (1995). Biomonitoring heavy metals using the barn owl (Tyto alba guttata): Sources of variation especially relating to body condition. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 28, 471-86.
Fimreite, N. (1974). Mercury contamination of aquatic birds in northwestern Ontario. J. Wildl. Manag. 38, 120-31.
Franson, J.C., Koehl, P.S., Derksen, D.V., Rothe, T.C., Bunck, C.M. and Moore, J.F. (1995). Heavy metals in seaducks and mussels from Misty Fjords National Monument in southeast Alaska. Environ. Monitor. Assess. 36, 149-67.
Furness, R.W. (1996). Cadmium in birds. In W.N. Beyer, G.H. Heinz and A.W. Redmon-Norwood (eds) Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife, Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, pp. 43-50. Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry Special Publication Series, New York: Lewis Publishers.
Gasaway, W.S. and Buss, I.O. (1972). Zinc toxicity in the mallard duck. J. Wildl. Manag. 26, 1107-17.
Goede, A.A. (1985). Mercury, selenium, arsenic and zinc in waders from the Dutch Wadden Sea. Environ. Pollut. 37A, 287-308.
Heinz, G.H. (1996). Selenium in birds. In W.N. Beyer, G.H. Heinz, and A.W. Redmon-Norwood (eds) Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife, Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, pp. 447-58. New York: Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry Special Publication Series, Lewis Publishers.
Heinz, G.H. and Fitzgerald, M.A. (1993). Reproduction of mallards following overwinter exposure to selenium. Environ. Pollut. 81, 117-22.
Heinz, G.H., Hoffman, D.J. and Gold, L.G. (1989). Impaired reproduction of mallards fed an organic form of selenium. J. Wildl. Manag. 53, 418-28.
Heinz, G.H., Pendleton, G.W., Krynitsky, A.J. and Gold, L.G. (1990). Selenium accumulation and elimination in mallards. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 19, 374-9.
Henny, C.J., Rudis, D.D., Roffe, T.J. and Robinson-Wilson, E. (1995). Contaminants and sea ducks in Alaska and the circumpolar region. Environ. Health Persp. 103, 41-9.
Hodson, P.V., Whittle, D.M., Hallett, D.J. (1984). Selenium contamination of the Great Lakes and its potential effects on aquatic biota. In J.O. Nriagu and M.S. Simmons (eds) Toxic Contaminants in the Great Lakes, pp. 371-91. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Hothem, R.L., Lonzarich, D.G., Takekawa, J.E. and Ohlendorf, H.M. (1998). Contaminants in wintering canvasbacks and scaups from San Francisco Bay, California. Environ. Monit. Assess. 50, 67-84.
Nystrom, J., Dunca, E., Mutvel, H. and Lindh, U. (1996). Environmental history as reflected by freshwater pearl mussels in the River Vramsan, southern Sweden. Ambio 25, 350-5.
Ohlendorf, H.M. (1989). Bioaccumulation and effects of selenium in wildlife. In L.W. Jacobs (ed.) Selenium in Agriculture and the Environment, pp. 133-77. Soil Science Society of America: Madison WI, Spec. Publ. 23.
Outridge, P.M. and Scheuhammer, A.M. (1993). Bioaccumulation and toxicology of chromium: implications for wildlife. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 130, 31-77.
Puls, R. (1994). Mineral Levels in Animal Health: Diagnostic data 2nd edn. British Columbia: Sherpa International.
Scheuhammer, A.M. (1987). The chronic toxicity of aluminium, cadmium, mercury, and lead in birds: a review. Environ. Pollut. 46, 263-95.
Scheuhammer, A.M., Wong, A.H.K. and Bond, D. (1998). Mercury and selenium accumulation in common loons (Gavia immer) and common mergansers (Mergus merganser) from eastern Canada. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 197-201.
Stout, J.H., Trust, K.A., Cochrane, J.F., Suydam, R.S. and Quakenbush, L.T. (2002). Environmental contaminants in four eider species from Alaska and arctic Russia. Environ. Pollut. 119, 215-26.
Takekawa, J.Y., Wainwright-De La Cruz, S.E., Hothem, R.L. and Yee, J. (2002). Relating body condition to inorganic contaminant concentrations of diving ducks wintering in coastal California. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 42, 60-70.
Thompson, D.R. (1996). Mercury in birds and terrestrial mammals. In W.N. Beyer, G.H. Heinz and A.W. Redmon-Norwood (eds) Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife, Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, pp. 341-56. New York: Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry Special Publication Series, Lewis Publishers.
Trust, K.A., Rummel, K.T., Scheuhammer, A.M., Brisbin, I.L. Jr and Hooper, M.J. (2000). Contaminant exposure and biomarker responses in spectacled eiders (Somateria fischeri) from St Lawrence Island, Alaska. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 38, 107-13.
US Fish and Wildlife Service and Environment Canada (1986). North American Waterfowl Management Plan: a Strategy for Cooperation. Report of the US Fish and Wildlife Service and Environment Canada. May 1986. 19pp.
White, D.H. and Dieter, M.P. (1978). Effects of dietary vanadium in mallard ducks. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 4, 43-50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Custer, C.M., Custer, T.W., Anteau, M.J. et al. Trace Elements in Lesser Scaup (Aythya affinis) from the Mississippi Flyway. Ecotoxicology 12, 47–54 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022584712262
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022584712262