Abstract
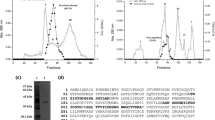
Benzamidine, an inhibitor of serine proteases, was used as an affinity ligand for the purification of aspartyl protease from culture filtrate of Rhizomucor miehei. The two step purification protocol (ion-exchange and affinity chromatography) resulted in a homogenous enzyme preparation with seven-fold purification and a final recovery of 22%. The purified enzyme was free of brown pigmentation, a factor inherently associated with the enzyme; it was stable and active at acidic pH (optimum pH 4.1 for proteolytic activity and 5.6 for milk clotting activity). The significant positive characteristic of the enzyme is its comparatively lower thermostability; the enzyme was comparable to calf rennet in its properties of thermostability, milk-clotting to proteolytic activity ratio and sensitivity to CaCl2. Limited protease digestion of the purified enzyme with proteinase K yielded a 20kDa fragment as shown by SDS–PAGE. Native gel electrophoresis of the digest showed an additional peak of activity corresponding to the 20kDa fragment on SDS–PAGE, this fragment retained both milk-clotting and proteolytic activities. It was also inhibited by pepstatin A and hence it is presumed that this fragment contained the active site of the enzyme.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, E.D., Wynne, M.G., Clarke, A.J. & Yada, R.Y. (1990) Puri fication of two fungal aspartyl proteases using fast protein liquid chromatography. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 54, 1563-1565.
Collin, J.C., DeRetta, G.M & Martin, P. (1982) Immunological identification of milk clotting enzymes. Journal of Dairy Research 49, 221-230.
Davis, B.J. (1964) Disc electrophoresis II. Method and application to human serum protein. Annals of the New York Academy of Science 120, 404-427.
Fruton, J.S. (1976) The mechanism of the catalytic action of pepsin and related acid proteinases. Advances in Enzymology 44, 1-36.
Garnot, P. (1985) Heat stability of milk clotting enzymes, technological consequences. International Dairy Federation Bulletin 194, 2-6.
Hyslop, D.B. & Swanson, A.M. (1979) Heat inactivation of milk clotting enzymes at different pH. Journal of Dairy Science 62, 1227-1232.
Kobayashi, H., Kusakbebe, I. & Murakami, K. (1982) Rapid isolation of microbial milk clotting enzymes by N-acetyl (or N-isobutyryl) pepstatin-aminohexylagarose. Analytical Biochemistry 122, 308-312.
Kobayashi, H. & Murakami, K. (1978) Rapid and large scale isolation of chymosin (Rennin) by pepstatin-aminohexylagarose. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 42, 2227-2231.
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680-685.
Langrange, A., Paquet, D. & Alais, C. (1980) Comparative study of two Mucor miehei acid proteases: Purification and some molecular properties. Journal of Biochemistry 11, 47-352.
Merril, C.R., Goldman, D. & Keuren, M.L.V. (1984) Gel protein stain: silver stain. Methods in Enzymology 104, 441-442.
Murakami, K. & Inagami, T. (1975) Isolation of pure and stable renin from hog kidney. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 62, 757-763.
Preetha, S. & Boopathy, R. (1994) Influence of culture conditions on the production of milk clotting enzyme from Rhizomucor. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 10, 527-530.
Rickert, W.S. & Elliot, J.R. (1973) Acid proteases from species of Mucor. Molecular weight of Mucor miehei protease from amino acid analysis data. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry 51, 1638-1646.
Rickert, W.S. & McBride-Warren, P.A. (1975) Acid proteases from species of Mucor II. Partial characterisation of acid proteases produced by a strain of Mucor miehei isolated in Cuba. Canadian Journal of Biochemistry 53, 269-274.
Smith, J.L. & Yada, R.Y. (1991) Characterization of two aspartyl proteinases from a commercial fungal (Mucor miehei) rennet. Canadian Institute of Food Science and Technology Journal 24, 48-53.
Sternberg, M.Z. (1971) Crystalline milk clotting protease from Mucor miehei and some of its properties. Journal of Dairy Science 54, 159-167.
Thunnel, R.K., Duersch, J.W. & Ernstrom, C.A. (1979) Thermal inactivation of residual milk clotting enzymes in whey. Journal of Dairy Science 62, 373-380.
Visser, S. (1981) Proteolytic enzymes and their action on milk proteins.Areview. Netherlands Milk and Dairy Journal 35, 65-88.
Voynick, I.M. & Fruton, J.S. (1971) The comparative specificity of acid proteinases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 68, 257-259.
Wynne, M.G. & Yada, R.Y. (1991) Isolation of Mucor miehei and Mucor pusillus aspartic proteinases from partially purified sources using preparative isoelectric focussing. Journal of Food Biochemistry 15, 347-366.
Yada, R.Y. & Nakai, S. (1986) Use of principal component analysis to study the relationship between physical/chemical properties and the milk clotting to proteolytic activity ratio of some aspartyl proteinases. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 34, 675-679.
Yamamoto, K., Katsuda, N. & Kato, K. (1978) Affinity purification and properties of cathepsin-E like acid protease from rat spleen. European Journal of Biochemistry 92, 499-508.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Preetha, S., Boopathy, R. Purification and characterization of a milk clotting protease from Rhizomucor miehei. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 13, 573–578 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018525711573
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018525711573