Abstract
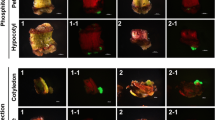
Resistance to bialaphos, a non-selective herbicide, was intro duced into cotton through genetic engineering. A gene encoding phosphinothric in acetyltransferase (bar) from Streptomyces hygroscopicus was inserted into elite varieties of cotton through particle bombardment. Based on the marker gene, β-glucuronidase (gus) expression, a total of 18 Pima (Gossypium barbadense), 45 DP50 (G. hirsutum L.), 20 Coker 312 (G. hirsutum) and 2 El Dorado (G. hirsutum) transgenic plants were recovered. Integration of the bar gene into cotton genomic DNA was confirmed by Southern blot analysis and gene expression was confirmed by northern blot and enzyme assays. Herbicide (Basta®) tolerance up to 15 000 ppm was demonstrated in greenhouse trials. The newly introduced herbicide tolerance trait is inherited in a Mendelian fashion in the progenies of germline transformants. This study demonstrates the potential for particle bombardment to introduce commerically important genes directly into elite varieties of cotton. This mode of gene transfer can expedite the introduction of transgenic cotton products into world markets
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayley, C., Trolinder, N., Ray, C., Morgan, M., Quisenberry, J.E. and Ow, D.W. (1992) Engineering 2,4-D resistance into cotton. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83, 645–9.
Christou, P., McCabe, D.E., Martinell, B.J. and Swain, W.F. (1990) Soybean genetic engineering-commercial production of transgenic plants. Trends Biotechnol. 8, 145–151.
Cooley, J., Ford, T. and Christou, P. (1995) Molecular and genetic characterization of elite transgenic rice plants produced by electric-discharge particle acceleration. Theor. Appl. Genet. 90, 97–104.
De Block, M., Botterman, J., Vandewiele, M., Dockx, J., Thoen, C., Gosseleâ, V., Rao Movva, N., Thompson, C., Van Montagu, M. and Leemans, J. (1987) Engineering herbicide resistance in plants by expression of a detoxifying enzyme. EMBO J. 6, 2513–18.
Devine, M.D., Hall, J.C., Romano, M.L., Marles, M.A.S., Thomson, L.W. and Shimabukuro, R.H. (1993) Diclofop and fenoxaprop resistance in wild oat is associated with an altered effect on the plasma membrane electrogenic potential. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 45, 167–77.
Droge, W., Broer, I. and Puhler, A. (1992) Transgenic plants containing the phosphinothricin-N-acetyltransferase gene metabolize the herbicide L-phosphinothricin (glufosinate) differently from untransformed plants. Planta 187, 142–51.
Jefferson, R.A. (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 5, 387–405.
Jenkins, J.N., McCarty, J.C. and Wofford, T. (1995) B.t. cotton: a new era in cotton production. Proceedings Beltwide Cotton Conference, National Cotton Council. Memphis, TN, USA. 1, 171–3.
John, M.E. (1992) An efficient method for isolation of RNA and DNA from plants containing polyphenolics. Nucl. Acids Res. 20, 2381.
John, M.E. (1995) Prospects for modification of fibers through genetic engineering of cotton In: Gebelein, C.G. and Carraher, C.E. eds. Industrial Biotechnological Polymers. Lancaster PA, USA: Technomic Publishing Co. Inc., pp. 69–79.
John, M.E. and Crow, L.J. (1992) Gene expression in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) fiber: cloning of the mRNAs. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5769–73.
John, M.E. and Keller, G. (1996) Metabolic pathway engineering in cotton: biosynthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate in fiber cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 12768–73.
Koziel, M.G., Beland, G.L., Bowman, C., Carozzi, N.B., Crenshaw, R., Crossland, L., Dawson, J., Desia, N., Hill, M., Kadwell, S., Lewiss, K., Launia, K., Maddox, D., McPherson, K., Meghji, M.R., Merlin, E., Rhodes, R., Warren, G.W., Wright, M. and Evola, S.V. (1993) Field performance of elite transgenic maize plants expressing an insecticidal protein derived from Bacillus thuringiensis. Bio/Technology 11, 194–200.
McCabe, D.E. and Martinell, B.J. (1993) Transformation of elite cotton cultivars via particle bombardment of meristems. Bio/Technol. 11, 596–8.
Rajasekaran, K., Grula, J.W., Hudspeth, R.L., Pofelis, S., Anderson, D.M. (1996) Herbicide-resistant Acala and Coker cottons transformed with the native gene encoding mutant forms of acetohydroxyacid synthase. Mol. Breeding. 2, 307–19.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F. and Maniatis, T. (1989) Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Shaw, W.V. (1975) Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase chloramphenicol-resistant bacteria. Methods Enzymol. 43, 737–55.
Stalker, D.M., Kiser, J.A., Baldwin, G., Coulombe, B. and Houck, C.M. (1996) Cotton weed control using the BXNTM system. In: Duke, S.O. Ed. Herbicide-Resistant Crops: Agricultural, Environmental, Economic, Regulatory and Technical Aspects. New York, USA: Lewis Publishers. pp. 93–105.
Strauch, E., Wohlleben, W. and Puhler, A. (1988) Cloning of the phosphinothricin N-acetyltransferase gene from Streptomyces viridochromogenes Tu94 and its expression in Streptomyces lividans and Escherichia coli. Gene 63, 65–74.
Trolinder, N.L. and Goodin, J.R. (1987) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Rep. 6, 231–4.
Umbeck, P., Johnson, G., Barton, K. and Swain, W. (1987) Genetically transformed cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) plants. Bio/Technol. 5, 263–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KELLER, G., SPATOLA, L., McCABE, D. et al. Transgenic cotton resistant to herbicide bialaphos. Transgenic Res 6, 385–392 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018483300902
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018483300902