Abstract
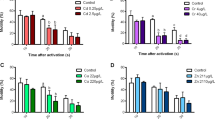
We determined the effect of environmental stressors on the physiological condition of Brachionus rotundiformis. For two morphologically distinct B. rotundiformis strains: Hawaii (average lorica length = 222 μm) and Langkawi strains (average lorica length 180 μm), neonates hatched from resting eggs were exposed to different levels of unionized ammonia (0.7–9.8 mg l−1), viscosity (relative viscosity against natural seawater = 1–1.17) and Euplotes sp. (protozoan) contamination (1–40 cells ml−1). Increasing stress decreased fecundity and lifespan of both rotifer strains. Glucosidase and phospholipase activities were correlated with reproductive responses of both the strains exposed to unionized ammonia. When culture water viscosity was changed, the activity of esterase and phospholipase was correlated with reproductive responses of the Hawaiian strain, and glucosidase activity was correlated with those of Langkawi strain.With the protozoan contamination, esterase and glucosidase activities were correlated only with reproductive responses of the Hawaiian strain, while activity of all three enzymes was correlated to those of the Langkawi strain. Glucosidase activity proved to be a reliable indicator of stress for cultured B. rotundiformis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo, A. B., A. Hagiwara & T.W. Snell, 2000. Effect of unionized ammonia, viscosity and protozoan contamination on the enzyme activity of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. Aquacult. Res. 31: 359–365.
Burbank, S. E. & T.W. Snell, 1994. Rapid toxicity assessment using esterase biomarkers in Brachionus calyciflorus (Rotifera). Envir. Toxicol. Wat. Qual. 9: l71–178.
Doi, M., J. D. Toledo, M. S. N. Golez, M. De Los Santos & A. Ohno, 1997. Preliminary investigation of feeding performance of larvae of early red-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides, reared with mixed zooplankton. Hydrobiologia 358: 259–263.
Ferrando, M. D., C. R. Janssen & G. Persoone, 1993. Ecotoxicological studies with the freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. III. The effects of chemicals on feeding behavior. Ecotoxicol. Envir. Safety 26: 1–9.
Fu, Y., K. Hirayama & Y. Natsukari, 1991. Morphological differences between two types of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis O. F. Muller. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 151: 29–41.
Hagiwara, A., T. Kotani, T. W. Snell, M. Assava-Aree & K. Hirayama, 1995. Morphology, reproduction, genetics and mating behavior of small, tropical marine Brachionus strains (Rotifera). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 194: 25–37.
Hagiwara, A., C.-S. Lee, G. Miyamoto & A. Hino, 1989. Resting egg formation and hatching of the S-type rotifer Brachionus plicatilis at varying salinities. Mar. Biol. 103: 327–332.
Hagiwara, A., N. Yamamiya & A. B. Araujo, 1998. Effect of water viscosity on the population growth of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis Müller. Hydrobiologia 386/387: 489–494.
Janssen, C. R., M. D. Ferrando & G. Persoone, 1993. Ecotoxicological studies with the freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyci-florus. IV. Conceptual framework and applications. Hydrobiologia 255/256 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 83): 21–32.
Janssen, C. R., M. D. Ferrando & G. Persoone, 1994. Ecotoxicological studies with the freshwater rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus. VI. Rotifer Behavior as a sensitive and rapid sublethal test criterion. Ecotoxicol. Envir. Safety 28: 244–255.
Janssen, C. R. & G. Persoone, 1993. Rapid toxicity screening tests for aquatic biota. 1. Methodology and experiments with Daphnia magna. Envir. Toxicol. Chem. 12: 711–717.
Juchelka, C. M. & T. W. Snell, 1994. Using rotifer ingestion rate rapid toxicity assessment. Arch. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 26: 549–554.
Jung, M.-M., A. Hagiwara & K. Hirayama, 1997. Interspecific interactions in the marine rotifer microcosm. Hydrobiologia 358: 121–126.
Kotani, T., A. Hagiwara & T. W. Snell, 1997. Genetic variation among marine Brachionus strains and function of mate recognition pheromone (MRP). Hydrobiologia 358: 105–112.
Kotani, T., M. Ozaki, K. Matsuoka, T. W. Snell & A. Hagiwara, 2001. Reproductive isolation among geographically and temporally isolated marine Brachionus strains. Hydrobiologia 446/447 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 153): 283–290.
Maeda, M. & A. Hino, 1991. Environmental management for mass culture of the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. In: Rotifer and microalgae culture systems, Proceedings of the U.S.-Asia Workshop, Oceanic Institute, Honolulu: 125–133. The Oceanic Institute Honolulu, Hawaii, U.S.A.
Moffat, B. D. & T. W. Snell, 1995. Rapid toxicity assessment using an in vivo enzyme test for Brachionus plicatilis (Rotifera). Ecotoxicol. Envir. Safety 30: 47–53.
Rumengan, I. F. M., V. Warouw & A. Hagiwara, 1998. Morphometry and resting egg production potential of the tropical ultraminute rotifer Brachionus rotundiformis (Manado strain) fed different algae. Bull. Fac. Fish. Nagasaki Univ. 79: 31–36
Snell, T. W. & G. Persoone, 1989a. Acute toxicity bioassays using rotifers. I. A test for brackish and marine environments with Brachionus plicatilis. Aquat. Toxicol. 14: 65–80.
Snell, T. W. & G. Persoone, 1989b. Acute toxicity bioassays using rotifers. II. A freshwater test with Brachionus rubens. Aquat. Toxicol. 14: 81–92.
Snell, T. W., R. Rico-Martinez, L. S. Kelly & T. E. Battle, 1995. Identification of a sex pheromone from a rotifer. Mar. Biol. 123: 347–353.
SPSS inc., 1997. SYSTAT 7.0: New Statistics. SPSS inc., U.S.A.
Yu, J.-P. & K. Hirayama, 1986. The effect of un-ionized ammonia on the population growth of the rotifer in mass culture. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 52: 1509–1513.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Araujo, A.B., Hagiwara, A. & Snell, T.W. Effect of unionized ammonia, viscosity and protozoan contamination on reproduction and enzyme activity of the rotifer Brachionus rotundiformis. Hydrobiologia 446, 363–368 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017567226012
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017567226012