Abstract
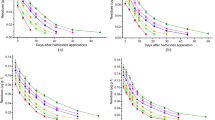
Soil pH and Eh play an important role in reducing heavy metal solubility in paddy soils. To assess the effects of flooding and organic matter application on changes in Eh, pH and solubility of Cd, Ni and Zn in contaminated soils, a growth chamber experiment with rice plants(Oryza sativa L.) was conducted. Eh values decreased with flooding time in all three soils. The changes of Eh values were more negative in the tannery and alum shale contaminated soils and stabilized after 30 days of submergence. The Eh changes were not so large in the city sewage contaminated soil as in the other two soils. Soil pH increased with flooding time. During the 65 days of submergence, pH increase was about 2, 1 and 0.6units in the tannery, city sewage and alum shale soils, respectively. In all three soils, organic matter treated soil showed lower Eh and higher pH values compared to untreated soil. Concentration of Cd, Ni and Zn in soil solution decreased with flooding time. The solution concentration of Cd and Zn in the city sewage soil and of Ni in the tannery soil was higher than in the alum shale soil. The soluble metal concentration in all three soils was lower inorganic matter treated soils. Reduced solubility of metals in the organic matter treated soils was related to larger changes of Eh and pH values in these soils. Correlation coefficient calculations also showed that metal solubility decreased with decreased Eh and increased pH in the soil solution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown P.H., Dunemann L., Schulz R. and Marschner H. 1989. Influence of redox potential and plant species on the uptake praveen of nickel and cadmium from soils. Pflanzenernahr. Bodenk 152: 85–91.
Charlatchka R. and Cambier P. 2000. Influence of reducing conditions on solubility of trace metals in contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 118: 143–167.
Delaune R.D. and Smith C.J. 1985. Release of nutrients and metals following oxidation of freshwater and saline sediments. J. Environ. Qual. 14: 164–168.
Elenon P. 1971. Particle size analysis of soil. Acta Agric. Fenn. 122: 1–122.
Elliott H.A., Liberati M.R. and Huang C.P. 1986. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals by soil. J. Environ. Qual. 15: 214–219.
Gambrell R.P. 1994. Trace and toxic metals in wetlands. J. Environ. Qual. 23: 883–891.
Gambrell R.P., Collard V. and Patrick J.W.H. 1980. Cadmium uptake by marsh plants as affected by sediment physicochemical conditions. In: Baker R.A. (ed.), Contaminants and Sediments. Ann Arbor Science, Ann Arbor, MI, pp. 425–445.
Gambrell R.P. and Patrick J.W.H. 1988. The influence of redox potential on the environmental chemistry of contaminants in soils and sediments. In: Hook D. (ed.), The Ecology and Management of Wetlands. Timber Press, pp. 319–333.
Gotoh S. and Patrick W.H. 1974. Transformation of iron in a waterlogged soil as influenced by redox potential and pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 38: 66–71.
Halder A. and Mandal L.N. 1979. Influence of soil moisture regimes and organic matter application on the extractable Zn and Cu content in rice soils. Plant Soil 53: 203–213.
Iu K.L., Pulford I.D. and Duncan H.J. 1981. Influence of waterlogging and lime or organic matter additions on the distribution of trace metals in an acid soil: I. Manganese and iron. Plant Soil 59: 317–326.
Jeng A.S. 1991. Weathering of some Norwegian Alum Shales. 1. laboratory simulations to study acid generation and the release of sulphate and metal cations (Ca, Mg & K). Acta Agric. Scand. 41: 13–35.
Jeng A.S. and Bergseth H. 1992. Chemical and mineralogical properties of Norwegian alum shale soils, with special emphasis on heavy metal content and availability. Acta Agric. Scand., Sect. B. Soil Plant Sci. 42: 88–93.
Kashem M.A. 2000, Mobility, chemical fractionation and plant uptake of Cd, Ni and Zn in contaminated soils, Ph.D. Dissertation, Agricultural University of Norway, Norway.
Kashem M.A. and Singh B.R. 2001a. Metal availability in contaminated soils: II. Uptake of Cd, Ni and Zn in rice plants as affected by moisture level and organic matter. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. (in this issue)
Kashem M.A. and Singh B.R. 2001b. Solid phase specification of Cd, Ni, and Zn in some contaminated and non-contaminated tropical soils. In: Ikander A., Kirkham M.B. and Beniu A. (eds), Trace Elements in Biochemistry Fluxes and Transfer in Soils and Soil Components. CRC press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 212–226.
Lindsay W.L. 1972. Inorganic phase equilibria of micronutrients in soils. In: Mortvedt J.J., Giodnano P.M. and Lindsay W.L. (eds), Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. Inc. Micronutrients in Agriculture., pp. 41–57.
Lindsay W.L. 1979. Chemical Equilibria in Soils. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY.
McBride M.B. 1994. Environmental chemistry of soils. Oxford University Press, New York, NY.
Minitab institute 1996. Statistical analysis software release 12.22. Narteh L.T. and Sahrawat K.L. 1999. Influence of flooding on electrochemical and chemical properties of West African soils. Geoderma 87: 179-207.
Narwal R.P. and Singh B.R. 1998. Effect of organic materials on partioning, exchangeability and plant uptake of metal in alum shale soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 103: 405–421.
Page A.L., Miller R. and Keeney D.R. 1982. Method of soils Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological properties. 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Madison, WI.
Patra B.N. and Mohanty S.K. 1994. Effects of nutrients and liming on changes in pH, redox potential, and uptake of iron and manganese by wetland rice in iron-toxic soil. Boil Fertil. Soils 17: 285–288.
Ponnamperuma F.N. 1972. The chemistry of submerged soils. Adv. Agron. 24: 29–96.
Reddy K.R. and Graetz D.A. 1988. The influence of redox potential on the environmental chemistry of contaminants in soils and sediments. In: Hook D. (ed.), The Ecology and Management of Wetlands. Timber Press, pp. 307–318.
Reddy C.N. and Patrick W.H. 1977. Effect of redox potential and pH on the uptake of cadmium and lead by rice plants. J. Environ. Qual. 6: 259–262.
Sajwan K.S. and Lindsay W.L. 1986. Effects of redox on zinc deficiency in paddy rice. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50: 1264–1269.
SigmaPlot I. 1997. SigmaPlot for version 4.00. IPSS.
Stahl R.S. and James B.R. 1991. Zinc sorption by manganese-oxide-coated sand as a function of pH. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 55: 1291–1294.
Soil Survey Staff 1998. Keys to Soil Taxonomy. 8th edn. U.S. Dept. of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington, DC.
Van Den Berg G.A., Loch J.P.G. and Winkels H.J. 1998. Effect of fluctuating hydrological conditions on the mobility of heavy metals in soils of a freshwater estuary in the Netherlands. Water Air Soil Pollut. 102: 377–388.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashem, M., Singh, B. Metal availability in contaminated soils: I. Effects of floodingand organic matter on changes in Eh, pH and solubility of Cd, Ni andZn. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 61, 247–255 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013762204510
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013762204510