Abstract
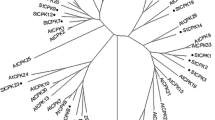
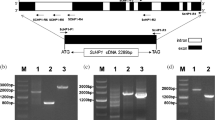
Using polyclonal antibodies raised against a previously cloned potato Mg2+-dependent soluble inorganic pyrophosphatase (ppa1 gene) [8], a second gene, called ppa2, could be isolated. A single locus homologous to ppa2 was mapped on potato chromosomes, unlinked to the two loci identified for ppa1. From a phylogenetic and structural point of view, the PPA1 and PPA2 polypeptides are more closely related to prokaryotic than to eukaryotic Mg2+-dependent soluble inorganic pyrophosphatases (soluble PPases). Subcellular localization by immunogold electron microscopy, using sections from leaf parenchyma cells, showed that PPA1 and PPA2 are localized to the cytosol. Based on these observations, the likely phylogenetic origin and the physiological significance of the cytosolic soluble pyrophosphatases are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantita-tion of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254(1976).
Cedegren R, Gray MW, Abel Y, Sankoff D: The evolutionary relationship among known life formas. J Mol Evol 28: 98–112 (1988).
Chen J, Brevet A, Fromant M, Leveque F, Schmitter JM, Blan-quet S, Plateau P:Pyrophosphatase is essential for growth of Escherichia coli. J Bact 172: 5686–5689(1990).
Commission of Plant Gene Nomenclature: Nomenclature of sequenced plant genes. Plant Mol Biol Rep 12: S1–S109 (1994).
Cooperman BS, Baykov AA, Lahti R: Evolutionary conserva-tion of the active site of soluble inorganic pyrophosphatase. Trends Biol Sci 17: 262–266(1992).
Dancer JE, ap Rees T:Effects of 2,4-dinitrophenol and anoxia on the inorganic pyrophosphate context of the spadix of Arum maculatum and the root apices of Pisum sativum. Planta 178: 421–424(1989).
Dancer JE, Veith R, Feil R, Komor E, Sttit M: Independent changes of inorganic pyrophosphatase and the ATP/ADP or UTP/UDP ratios in plant cell suspension cultures.Plant Sci 66: 59–63(1990).
du Jardin P, Rojas-Beltrán JA, Gebhardt C, Brasseur R: Mole-cular cloning and characterization of a soluble inorganic py-rophosphatase in potato. Plant Physiol 109: 853–860(1995).
Dubois F, Brugiè re N, Sangwan RS, Hirel B: Localization of tobacco cytosolic glutamine synthetase enzymes and the cor-responding transcripts shows organ-and cell-specific patterns of protein synthesis and gene expression. Plant Mol Biol 31: 803–817(1996).
Felsenstein J: PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) ver-sion 3.5c. Distributed by the author. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle (1993).
_Gebhardt C, Ritter E, Debener T, Schachtschabel U, Walke-meier B, Uhrig H, Salamini F: RFLP analysis and linkage mapping in Solanum tuberosum. Theor Appl Genet 78: 65–75 (1989).
Gebhardt C, Ritter E, Salamini F: RFLP map of the potato. In: Phillips RL, Vasil IK (eds), DNA-Based Markers in Plants, pp. 271–285. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands (1994).
Geigenberger P, Hajirezaei M, Geiger M, Deiting U, Son-newald U, Stitt M: Overexpression of pyrophosphatase leads to increase sucrose degradation and starch synthesis, increased activities of enzymes for sucrose-starch interconversions, and increased levels of nucleotides in growing potato tubers. Planta 205: 428–437(1998).
Gross P, ap Rees T: Alkaline inorganic pyrophosphatase and starch synthesis in amyloplasts. Planta 167: 140–145(1986).
Guynn RW, Veloso D, Lawson JWR, Veech RL: The concen-tration and control of cytoplasmic free inorganic pyrophos-phatase in rat liver in vivo. Biochem J 140: 369–375(1974).
Hajirezaei M, Sonnewald U, Viola R, Carlisle S, Dennis D, Stitt M: Transgenic potato plants with strongly decreased expression of pyrophosphate:fructose-6-phosphate phospho-transferase show no visible phenotype and only minor changes in metabolic fluxes in their tubers. Planta 192: 16–30(1994).
Harlow E, Lane D: Antibodies. A Laboratory Manual, 726 p. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1988).
Howe CJ: RNA polymerase and plastid evolution. Trends Plant Sci 1(10): 323–324(1996).
Huynh TV, Young RA, Davies RW: Construction and screen-ing cDNA libraries in _gt10 and _gt11. In: Glover DM(ed) DNA Cloning: A Practical Approach, pp. 49–78. IRL Press, Oxford (1985).
Jacob JL, Prevot JC, Clemet-Vidal A, d'Azuzac J: Inorganic pyrophosphate metabolism in Hevea brasiliensis latex. Char-acteristics of cytosolic alkaline inorganic pyrophosphatase. Plant Physiol Biochem 27: 355–364(1989).
Jelitto T, Sonnewald U, Willmitzer L, Hajirezaei MR, Stitt M: Inorganic pyrophosphate content and metabolites in leaves and tubers of potato and tobacco plants expressing E. coli pyrophosphatase in their cytosol. Planta 188: 238–244(1992).
Kieber J, Signer E: Cloning and characterisation of an inor-ganic pyrophosphatase gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 16: 345–348(1991).
Kornberg A: On the significance of phosphorolytic and py-rophosphorolytic reactions. In: Kasha M, Pullman E (eds) Horizons in biochemistry, pp. 251–264. Academic Press, New York (1962).
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural proteins during the as-sembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685 (1970).
Lerchl J, Geigenberger P, Stitt M, Sonnewald U: Impaired pho-toassimilate partitioning caused by phloem-specific removal of pyrophosphate can be complemented by a phloem-specific cytosolic yeast-derived invertase in transgenic plants. Plant Cell 7: 259–270(1995).
Loiseaux-de Goë r S: Plastid lineages. Prog Phycol Res 10: 138–177(1994).
Lundin M, Deopujari SW, Lichko L, Pereira da Silva L, Baltscheffsky H: Characterization of a mitochondrial inor-ganic pyrophosphatase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta 1098: 217–223(1992).
Maeshima M: H C translocating inorganic pyrophosphatase of plant vacuoles: inhibition by Ca 2 C, stabilisation by Mg 2 C and immunological comparison with other inorganic pyrophos-phatase. Eur J Biochem 196: 11–17(1991).
Mortain-Bertrand A, El Amrani A, Stephane D, Rey P, Suire C, Lamant A: Purification and characterization of the plas-tidial inorganic pyrophosphatase from Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol Biochem 34: 343–352(1996).
Nakai K, Kanehisa M: A knowledge base for predicting protein localisation sites in eucaryotic cells. Genomics 14: 897–911(1992).
Pearson WR, Lipman DJ: Improved tools for biological se-quence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 2444–2448 (1988).
Quick P, Neuhaus E, Feil R, Stitt M: Fluoride leads to an increase of inorganic pyrophosphatase and an inhibition of photosynthetic sucrose synthesis in spinach leaves. Biochim Biophys Acta 973: 263–271(1989).
Rea PA, Kim Y, Sarafian V, Poole RJ, Davies JM, Sanders D: Vacuolar H C-translocating pyrophosphatases: a new category of ion translocase. Trends Biochem Sci 17: 348–353(1992).
Rea PA, Poole RJ: Vacuolar H C translocating pyrophos-phatase. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 44: 157–180 (1993).
Roderick D, Page M: Tree View. Distributed by the author. Di-vision of Environmental and Evolutionary Biology, University of Glasgow, Scotland, UK (1996).
Rojas-Beltrán JA: Etude moléculaire et physiologique de py-rophosphatases inorganiques solubles dépendantes de magné-sium chez Solanum tuberosum L. Ph.D. thesis, 189 pp. Fac-ulté Universitaire des Sciences Agronomiques de Gembloux, Belgium (1997).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2e ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463 (1977).
Sarafin V, Kim Y, Poole R. J, Rea PA: Molecular cloning and sequence of cDNA encoding the pyrophosphate-energized vacuolar membrane proton pump of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 1775–1779(1992).
Schimper AFW: Ñber die Entwickelung der Chlorophyl-lkörner und Farbkörper. Bot Z 41: 105–112(1883).
Sonnewald U: Expression of E. coli inorganic pyrophos-phatase in transgenic plants alters photoassimilate partitioning in leaves. Plant J 2: 571–581(1992).
Spychalla JP, Scheffler BE, Sowokinos JR, Bevan MW: Cloning, antisense RNA inhibition, and the coordinated expression of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase with starch biosynthetic genes in potato tubers. J Plant Physiol 144: 444–453(1994).
Vianello A, Zancani M, Casolo V, Macri F: Orientation of pea stem mitochondrial H+-pyrophosphatase and its differ-ent characteristics from the tonoplast counterpart. Plant Cell Physiol 38: 87–90(1997).
Volk SE, Baykov A: Isolation and subunit composition of membrane inorganic pyrophosphatase from rat-liver mito-chondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 791: 198–204(1984).
Weiner H, Stitt M, Heldt HW: Subcellular compartmentaliza-tion of pyrophosphate and alkaline pyrophosphatase in leaves. Biochim Biophys Acta 893: 13–21(1987).
Zancani M, Macri F, Peruffo A, Vianello A: Isolation of the catalytic subunit of a membrane-bound H C pyrophosphatase from pea stem mitochondria. Eur J Biochem 228: 138–143 (1995).
Zhen RG, Baykov AA, Bakuleva NP, Rea PA: Aminomethylenediphosphonate: a potent type-specific inhibitor of both plant and phototrophic bacterial H C-pyrophosphatases. Plant Physiol 104: 153–159(1994).
Zrenner R, Willmitzer L, Sonnewald U: Analysis of the expression of potato uridinediphosphate-glucose pyrophos-phorylase and its inhibition by antisense RNA. Planta 190: 247–252(1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rojas-beltrán, J.A., Dubois, F., Mortiaux, F. et al. Identification of cytosolic Mg2+-dependent soluble inorganic pyrophosphatases in potato and phylogenetic analysis. Plant Mol Biol 39, 449–461 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006136624210
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006136624210