Abstract
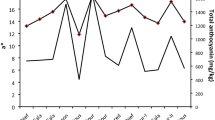
From sowing till emergence of the fourth trifoliolate leaf, beans were exposed for seven hr a day to four ozone concentrations in open-top chambers: filtered air (FA), non-filtered air (NF), non-filtered air plus 30 ppb ozone (NF+) and non-filtered air plus 60 ppb ozone (NF++). Controls in ambient air of open plots (AA) were also available. The free polyphenolic pool of the first trifoliolate leaf was systematically investigated using HPLC. The groups of phenolics to which the three main chromatographic signals belonged were identified as hydroxycinnamic acid derivative for peak No 1 and flavonoids for peaks Nos 4 and 6. The metabolic regulation of phenolic accumulation could be recognized as different clusters based on specific phenolic patterns that reflected some of the tested atmospheric conditions. The comparison of AA and NF conditions revealed a ‘chamber effect’. FA and NF atmospheres gave rise to almost the same phenolic equilibriums dominated by a hydroxycinnamic acid derivative (about 53% of the total phenolics). Ozone addition was associated with a regular reduction of the percentage of peak No 1: about 40% for NF+ and 19% for NF++. Therefore, the significant decrease of the vacuolar storage of this phenolic compound (from 23 mg g-1 dry weight for NF to about 3 mg g-1 dry weight for NF++) can be regarded as a useful tool for monitoring long-term exposure to elevated ozone concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biolley, J. P., Jay, M. and Barbe, J. P.: 1992, Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 20(7), 697.
Biolley, J. P., Bonte, J. and Maunas, L.: 1995, in European Stress Physiology and Climate Experiment — Project 1: Wheat (Environment Programme, Commission of the European Union, Contract No EV5VCT930301), Progress Report: January 1995 — December 1995., Hertstein, U. and Jäger, H. J. (eds.), Justus-Liebig-University Giessen, Deutchland, pp. 97–110.
Buckingham, J., Macdonald, F. M. and Bradley, H. M. (eds.): 1994, Dictionary of Natural Products, Chapman and Hall, London.
Eckey-Kaltenbach, H., Ernst, D., Heller, W. and Sandermann Jr, H.: 1994, Plant Physiology 104, 67.
Fangmeier, A., Stein, W. and Jäger, H. J.: 1992, Angewandte Botanik 66, 97.
Galaup, S.: 1992, Etude des effets combinés de l'ozone et de la contrainte hydrique sur la productivité et le fonctionnement stomatique du haricot (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivé en chambres à ciel ouvert, thesis, Université Paris Val de Marne, 251 pp.
Galliano, H., Heller, W. and Sandermann Jr., H.: 1993, Phytochemistry 32(3), 557.
Harborne, J. B.: 1984, Phytochemical Methods, Chapman and Hall, London.
Heagle, A. S., Body, D. E. and Heck, W. W.: 1973, J. Environ. Qual. 2, 365.
Heagle, A. S., Philbeck, R. B., Rogers, H. H. and Letchworth, M. B.: 1979, Phytopathology 69, 15.
Heagle, A. S.: 1989, Annual Review of Phytopathology 27, 397.
Heggestad, H. E.: 1991, Environmental Pollution 74, 264.
Hertstein, U., Grünhage, L. and Jäger, H. J.: 1995, Atmospheric Environment 29(16), 2031.
Kangasjärvi, J., Talvinen, J., Utriainen, M. and Karjalainen, R.: 1994, Plant, Cell and Environment 17, 783.
Mabry, T. J., Markham, K. R. and Thomas, M. B. (eds.): 1970, The Systematic Identification of Flavonoids, Springer, Berlin.
Markham, K. R.: 1982, Techniques of Flavonoid Identification, Academic Press, London.
Pihl Karlsson, G., Selldén, G., Skärby, L. and Pleijel, H.: 1995, New Phytologist 129, 355.
Rosemann, D., Heller, W. and Sandermann Jr., H.: 1991, Plant Physiology 97, 1280.
Rubin, B., Penner, D. and Saettler, A. W.: 1983, Environ Toxicol Chem 2, 295.
Salam, M. A. and Soja, G.: 1995, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 85(3), 1533.
Sanders, G. E., Colls, J. J., Clark, A. G., Galaup, S., Bonte, J. and Cantuel, J.: 1992, Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 38, 31.
Wold, S., Esbensen, K. and Geladi, P.: 1987, Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems 2, 37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biolley, J., Lauga, B., Cagnon, C. et al. Phenolic Pattern of Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as an Indicator of Chronic Ozone Stress. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 106, 355–368 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005050805136
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005050805136