Abstract
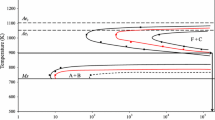
The austenite grain refinement through control of the grain growth during reheating process after thermo-mechanical controlled process (TMCP) in a vanadium microalloyed steel was achieved. The formation of ultra-fine grained austenite was attributed to the high density of austenite nucleation at the ferrite/martensite structure and to the inhibition of austenite growth by (Ti, V)C particles at the relatively low reheating temperature. Corresponding with the precipitation behavior of (Ti,V)C with temperature, the growth behavior of austenite in the vanadium microalloyed steel could be divided into two regions. At lower reheating temperature, austenite grains grew slowly, and ultra-fine grained austenite smaller than 5 μm was successfully obtained. By contrast, the austenite grains grew rapidly at high temperature due to the dissolution of (Ti,V)C particles. According to the measured and predicted results of austenite growth kinetics, two models were developed to describe the growth behavior of austenite grains in two different temperature regions, and the apparent activation energy Qapp for grain growth was estimated to be about 115 and 195 kJ/mol, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Yu, Y. J. Qian, H. B. Wu, Y. H. Yang, J. Iron Steel Res Int. 18 (2011) No. 2, 64–69.
J. Y. Yoo, W. Y. Choo, T. W. Park, Y. W. Kim, ISIJ Int. 35 (1995) 1034–1040.
C. Ouchi, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 542–553.
S. K. Dhua, S. K. Sen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528 (2011) 6356–6365.
M. Zhou, L. X. Du, X. H. Liu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18 (2011) No. 3, 59–64.
A. K. Giumelli, M. Militzer, E. B. Hawbolt, ISIJ Int. 39 (1999) 271–280.
S. Jiao, J. Penning, F. Leysen, Y. Houbaert, E. Aernoudt, ISIJ Int. 4. (2000) 1035–1040.
J. Lee, Y. K. Lee, Mater. Des. 29 (2008) 1840–1844.
S. S. Zhang, M. Q. Li, Y. G. Liu, J. Luo, T. G. Liu, Mater Sci. Eng. A 528 (2011) 4967–4972.
S. J. Yao, L. X. Du, X. H. Liu, G. D. Wang, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 25 (2009) 615–618.
SISC IAS V8.0, Scientific Instrument Software Co., Ltd., Beijing, China, 2003.
J. W. Cahn, Acta Metal. 4 (1956) 449–459.
N. Nakada, T. Tsuchiyama, S. Takaki, N. Milano, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 299–304.
B. Hutchinson, J. Hagström, O. Karlsson, D. Lindela, M. Tornberga, F. Lindberga, M. Thuvander, Acta Mater. 59 (2011) 5845–5858.
T. Hara, N. Maruyama, Y. Shinohara, H. Asahi, G. Shigesato, M. Sugiyama, T. Koseki, ISIJ Int. 49 (2009) 1792–1800.
M. Suehiro, Z. K. Liu, J. Ågren, Acta Mater. 44 (1996) 4241–4251.
H. Hu, B. B. Rath, Metal. Trans. 1 (1970) 3181–3184.
P. A. Beck, L. C. Kremer, L. J. Demer, Trans. AIME 175 (1948) 372–400.
S. Uhm, J. Moon, C. H. Lee, J. Yoon, B. Lee, ISIJ Int. 44 (2004) 1230–1237.
P. D. Hodgson, R. K. Gibbs, ISIJ Int. 32 (1992) 1329–1338.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation Item: Item Sponsored by National Basic Research Program of China (2010CB630805); National Natural Science Foundation of China (51201036); China Iron and Steel Research Institute Group (120G0840A)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Gw., Sun, Xj., Yong, Ql. et al. Austenite Grain Refinement and Isothermal Growth Behavior in a Low Carbon Vanadium Microalloyed Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21, 757–764 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60138-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60138-2