Abstract
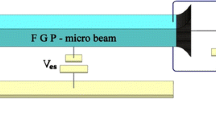
Based on the Modified Couple Stress Theory, a functionally graded micro-beam under electrostatic forces is studied. The FGM micro-beam is made of two materials and material properties vary continuously along the beam thickness according to a power-law. Dynamic and static pull-in voltages are obtained and it is shown that the static and dynamic pull-in voltages for some materials cannot be obtained using classic theories and components of couple stress must be taken into account. In addition, it is shown that the values of pull-in voltages depend on the variation through the thickness of the volume fractions of the two constituents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohammadi, M., Saidi, A. and Jomehzadeh, E., Levy solution for buckling analysis of functionally graded rectangular plates. Applied Composite Materials, 2010, 17(2): 81–93.
Kang, Y.-A. and Li, X.-F., Bending of functionally graded cantilever beam with power-law non-linearity subjected to an end force. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics , 2009, 44(6): 696–703.
Simsek, M., Fundamental frequency analysis of functionally graded beams by using different higher-order beam theories. Journal of Nuclear Engineering Design, 2010, 240(4): 697–705.
Craciunescu, C.M. and Wuttig, M., New ferromagnetic and functionally grade shape memory alloys. J Optoelectron Advance Material, 2003, 5(1): 139–146.
Fu, Y.Q., Du, H. J. and Zhang, S., Functionally graded TiN/TiNi shape memory alloy films. Material Letters, 2003, 57(20): 2995–2999.
Fu, Y.Q., Du, H.J., Huang, W.M., Zhang, S. and Hu, M., TiNi-based thin films in MEMS applications: a review. Sensors and Actuators A, 2004, 112(2–3): 395–408.
Witvrouw, A. and Mehta, A., The use of functionally graded poly-SiGe layers for MEMS applications. Material Science Forum, 2005, 492–493: 255–260.
Lee, Z., Ophus, C. and Fischer, L.M., et al., Metallic NEMS components fabricated from a nanocomposite Al-Mo films. Nanotechnology, 2006, 17(12): 3063–3070.
Rahaeifard, M., Kahrobaiyan, M.H. and Ahmadian, M.T., Sensitivity analysis of atomic force microscope cantilever made of functionally graded materials. In: DETC2009-86254, 3rd International Conference on Micro- and Nanosystems (MNS3), August 30-September 2, 2009, San Diego, CA, USA.
Kong, S., Zhou, S., Nie, Z. and Wang, K., The size-dependent natural frequency of Bernoulli-Euler micro-beams. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2008, 46(5): 427–437.
Nix, W.D., Mechanical properties of thin fillms. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 1989, 20A(11): 2217–2245.
Fleck, N.A., Muller G.M., Ashby, M.F. and Hutchinson, J.W., Strain gradient plasticity: theory and experiment. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1994, 42(2): 475–487.
Poole, W.J., Ashby, M.F. and Fleck, N.A., Micro-hardness of annealed and work-hardened copper polycrystals. Scripta Materialia, 1996, 34(4): 559–564.
Lam, D.C.C. and Chong, A.C.M., Indentation model and strain gradient plasticity law for glassy polymers. Journal of Materials Research, 1999, 14(9): 3784–3788.
Lam, D.C.C., Yang, F. and Chong, A.C.M., et al., Experiments and theory in strain gradient elasticity. Journal of Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2003, 51(8): 1477–1508.
McFarland, A.W. and Colton, J.S., Role of material microstructure in plate stiffness with relevance to micro cantilever sensors. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2005, 15(5): 1060–1067.
Chasiotis, I. and Knauss, W.G., The mechanical strength of polysilicon films: Part 2. Size effects associated with elliptical and circular perforations. Journal of Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2003, 51(8): 1551–1572.
Mindlin, R.D. and Tiersten, H.F., Effects of couple-stresses in linear elasticity. Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 1962, 11(1): 415–448.
Toupin, R.A., Elastic materials with couple-stresses. Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 1962, 11(1): 385–414.
Mindlin, R.D., Micro-structure in linear elasticity. Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 1964, 16(1): 51–78.
Koiter, W.T., Couple-stresses in the theory of elasticity: I and II. Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. B, 1964, 67(1): 17–44.
Mindlin, R.D., Stress functions for a Cosserat continuum. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1965, 1(3): 265–271.
Cosserat, E. and Cosserat, F., Theorie des corps deformables. Hermann et Fils, Paris, 1909.
Yang, F., Chong, A.C.M., Lam, D.C.C. and Tong, P., Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2002, 39(10): 2731–2743.
Park, S.K., Gao, X.L., Bernoulli-Euler beam model based on a modified couple stress theory. J Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2006, 16(11): 2355–2359.
Tsiatas, G.C., A new Kirchhoff plate model based on a modified couple stress theory. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2009, 46(13): 2757–2764.
Kahrobaiyan, M.H., Asghari, M., Rahaeifard, M. and Ahmadian, M.T., Investigation of the size-dependent dynamic characteristics of atomic force microscope microcantilevers based on the modified couple stress theory. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2010, 48(12): 1985–1994.
Wang, L., Size-dependent vibration characteristics of fluid-conveying Microtubes. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2010, 26(4): 675–684.
Xia, W., Wang, L. and Yin, L., Nonlinear non-classical microscale beams: Static bending, postbuckling and free vibration. International Journal of Engineering Science, 2010, 48(12): 2044–2053.
Asghari, M., Ahmadian, M.T., Kahrobaiyan, M.H. and Rahaeifard, M., On the size-dependent behavior of functionally graded micro-beams. Materials and Design, 2010, 31(5): 2324–2329.
Ke, L.L. and Wang, Y.S., Size effect on dynamic stability of functionally graded microbeams based on a modified couple stress theory. Composite Structures, 2011, 93(2): 342–350.
Senturia, S., Microsystem Design. Norwell, MA: Kluwer, 2001.
Sadeghian, H., Rezazadeh, G. and Osterberg, P.M., Application of the generalized differential quadrature method to the study of pull-in phenomena of MEMS switches. J. Microelectromechanical System, 2007, 16(6): 1334–1340.
Rezazadeh, G., Khatami, F. and Tahmasebi, A., Investigation of the torsion and bending effects on static stability of electrostatic torsional micromirrors. Microsystem Technologies, 2007, 13(7): 715–722.
Sazonova, V., A Tunable Carbon Nanotube Resonator, Ph.D. Thesis, Cornell University, 2006.
Rezazadeh, G., Tahmasebi, A. and Zubtsov, M., Application of piezoelectric layers in electrostatic MEM actuators: Controlling of pull-in voltage. Microsystem Technologies, 2006, 12(12): 1163–1170.
Bao, M. and Wang, W., Future of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 1996, 56(1–2): 135–141.
Mehdaoui, Pisani, M.B., Tsamados, D., Casset, F., Ancey, P. and Ionescu, A.M., MEMS tunable capacitors with fragmented electrodes and rotational electro-thermal drive. Microsystem Technologies, 2007, 13(11): 1589–1594.
Zhang, Y. and Zhao, Y., Numerical and analytical study on the pull-in instability of micro-structure under electrostatic loading. Sensors and Actuators A, 2006, 127(2): 366–367.
Nguyen, C.T.C., Katehi, L.P.B. and Rebeiz, G.M., Micromachined devices for wireless communications. Proc. IEEE, 1998, 86(8): 1756–1768.
Hasanyan, D.J., Batra, R.C. and Harutyunyan, S., Pull-in Instabilities in functionally graded microthermo-electromechanical systems. Journal of Thermal Stresses, 2008, 31(10): 1006–1021.
Jia, X.L., Yang, J. and Kitipornchai, S., Characterization of FGM micro-switches under electrostatic and Casimir forces. IOP Conference Series, Materials Science and Engineering, 2010, 10, 012178.
Ballestra, A., Brusa, E., De Pasquale, G., Munteanu, M.G. and Soma, A., FEM modelling and experimental characterization of microbeams in presence of residual stress. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 2010, 63(3): 477–488.
Sadeghian, H., Goosen, H., Bossche, A., Thijsse, B. and van Keulen, F., On the size-dependent elasticity of silicon nanocantilevers: impact of defects. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2011, 44(7): 072001.
Rezazadeh, G., Fathalilou, M., Shabani, R., Tarverdilou, S. and Talebian, S., Dynamic characteristics and forced response of an electrostatically-actuated micro-beam subjected to fluid loading. Microsystem Technologies, 2009, 15(9): 1355–1363.
Pacheco, S.P., Katehi, L.P.B. and Nguyen, C.T.C., Design of low actuation voltage RF MEMS switch. Microwave Symposium Digest., 2000 IEEE MTT-S International, 2000, 1(11–16): 165–168.
Son, D., Kim, J.J., Kim, J.Y. and Kwon, D., Tensile properties and fatigue crack growth in LIGA nickel MEMS structures. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 406(1–2): 274–278.
Lin, W.H. and Zhao, Y.P., Stability and bifurcation behavior of electrostatic torsional NEMS varactor influenced by dispersion forces. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2007, 40(6): 1649–1654.
Seydel, R., Practical Bifurcation and Stability Analysis, Third Edition, Springer, aDOI 10.1007/978-1-4419-1740-9.
Azizi, S., Design of micro accelerometer to use as airbag activator, MSc thesis, Mechanical Engineering Department, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran, 2008: 53–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasnejad, B., Rezazadeh, G. & Shabani, R. Stability analysis of a capacitive FGM micro-beam using modified couple stress theory. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 26, 427–440 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-9166(13)60038-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-9166(13)60038-5