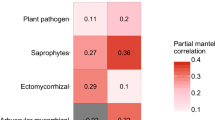
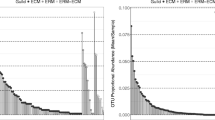
Abstract
The roots and rhizospheres of trees harbor diverse microbial communities that can modulate plant competition and facilitation, thereby influencing plant community dynamics. Understanding the factors structuring microbial communities is valuable for predicting how plant communities assemble. In temperate forests, host identity, biotic neighborhood, abiotic environment and geographic distance shape microbial communities, but the importance of these factors is less well studied in highly diverse tropical forests. In this study, we used high-throughput amplicon sequencing to characterize the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal (AMF) and rhizosphere bacterial (RB) communities of five tree species in an 8-year-old common garden planted into the understory of a selectively logged old-growth forest in Malaysian Borneo. We assessed the influence of host tree species, host traits and neighboring tree identity on the composition and diversity of both communities. The AMF and RB communities differed amongst host tree species; the tree species with the most distinct AMF communities associated with the lowest diversity of AMF. Alpha diversity of AMF correlated negatively with leaf phosphorus and potassium content. Density and abundance of AMF neighbor trees growing near focal trees influenced AMF community composition and was positively correlated with RB alpha diversity. Our results highlight the importance of considering both host tree identity and biotic neighborhood of trees in studies of microbial communities in tropical forests. Important next steps will be to elucidate the functional significance of shifts in AMF and RB community compositions and their implications for community and ecosystem dynamics in tropical forests.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Andrews S (2010) FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. GitHub. https://github.com/s-andrews/FastQC
Andrews LV (2018) akutils-v1.2: Facilitating analyses of microbial communities through QIIME. GitHub. https://github.com/alk224/akutils-v1.2/tree/v1.2.1a
Barberán A, McGuire KL, Wolf JA, Jones FA, Wright SJ, Turner BL, Essene A, Hubbell SP, Faircloth BC, Fierer N (2015) Relating belowground microbial composition to the taxonomic, phylogenetic, and functional trait distributions of trees in a tropical forest. Ecol Lett 18:1397–1405
Barto EK, Hilker M, Müller F, Mohney BK, Weidenhamer JD, Rillig MC (2011) The fungal fast lane: common mycorrhizal networks extend bioactive zones of allelochemicals in soils. PLoS One 6:e27195
Bennett JA, Maherali H, Reinhart KO, Lekberg Y, Hart MM, Klironomos J (2017) Plant-soil feedbacks and mycorrhizal type influence temperate forest population dynamics. Science 355:181–184
Berendsen RL, Pieterse CMJ, Bakker PA (2012) The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci 17:478–486
Berg G, Smalla K (2009) Plant species and soil type cooperatively shape the structure and function of microbial communities in the rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 68:1–13
Bever JD (2003) Soil community feedback and the coexistence of competitors: conceptual frameworks and empirical tests. New Phytol 157:465–473
Bokulich NA, Subramanian S, Faith JJ, Gevers D, Gordon JI, Knight R, Mills DD, Caporaso JG (2013) Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 10:57–59
Brearley FQ, Elliott DR, Iribar A, Sen R (2016) Arbuscular mycorrhizal community structure on co-existing tropical legume trees in French Guiana. Plant Soil 403:253–265
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chen X, Tang M, Zhang X, Hamel C, Liu S, Huo Y, Sheng M (2018) Effects of plant neighborhood on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal attributes in afforested zones. For Ecol Manag 422:253–262
Chen L, Swenson NG, Ji N, Mi X, Ren H, Guo L, Ma K (2019) Differential soil fungus accumulation and density dependence of trees in a subtropical forest. Science 366:124–128
Cipollini D, Rigsby CM, Barto EK (2012) Microbes as targets and mediators of allelopathy in plants. J Chem Ecol 38:714–727
Clarke KR (1993) Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral Ecol 18:117–143
Clarke K, Gorley R (2006) PRIMER v6: user manual/tutorial. Primer-E, Plymouth
Clarke KR, Chapman MG, Somerfield PJ, Needham HR (2006) Dispersion-based weighting of species counts in assemblage analyses. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 320:11–27
Courty PE, Walder F, Boller T, Ineichen K, Wiemken A, Rousteau A, Selosse MA (2011) Carbon and nitrogen metabolism in mycorrhizal networks and mycoheterotrophic plants of tropical forests: a stable isotope analysis. Plant Physiol 156:952–961
Das I (2011) fqgrep-Github repository. https://github.com/indraniel/fqgrep
Davison J, Öpik M, Daniell TJ, Moora M, Zobel M (2011) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in plant roots are not random assemblages. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 78:103–115
Davison J, Moora M, Öpik M, Adholeya A, Ainsaar L, Bâ A, Burla S, Diedhiou AG, Hiiesalu I, Jairus T, Johnson NC, Kane A, Koorem K, Kochar M, Ndiaye C, Pärtel M, Reier Ü, Saks Ü, Singh R, Vasar M, Zobel M (2015) Global assessment of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus diversity reveals very low endemism. Science 349:970–973
Davison J, Moora M, Jairus T, Vasar M, Öpik M, Zobel M (2016) Hierarchical assembly rules in arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungal communities. Soil Biol Biochem 97:63–70
Davison J, García de León D, Zobel M, Moora M, Bueno CG, Barceló M, Gerz M, León D, Meng Y, Pillar VD, Sepp SK, Soudzilovaskaia NA, Tedersoo L, Vaessen S, Vahter T, Winck B, Öpik M (2020) Plant functional groups associate with distinct arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities. New Phytol 226:1117–1128
de Boer W, Folman LB, Summerbell RC, Boddy L (2005) Living in a fungal world: impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:795–811
De Cáceres M, Legendre P, Moretti M (2010) Improving indicator species analysis by combining groups of sites. Oikos 119:1674–1684
de Vries FT, Manning P, Tallowin JR, Mortimer SR, Pilgrim ES, Harrison KA, Hobbs PJ, Quirk H, Shipley B, Cornelissen JH, Kattge J, Bardgett RD (2012) Abiotic drivers and plant traits explain landscape-scale patterns in soil microbial communities. Ecol Lett 15:1230–1239
Dean SL, Farrer EC, Porras-Alfaro A, Suding KN, Sinsabaugh RL (2015) Assembly of root-associated bacteria communities: interactions between abiotic and biotic factors. Environ Microbiol Rep 7:102–110
Ehrenfeld JG, Ravit B, Elgersma K (2005) Feedback in the plant-soil system. Annu Rev Environ Resour 30:75–115
Fitter AH, Moyersoen B (1996) Evolutionary trends in root-microbe symbioses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 351:1367–1375
Garbeva P, van Elsas JD, van Veen JA (2008) Rhizosphere microbial community and its response to plant species and soil history. Plant Soil 302:19–32
Gorzelak MA, Asay AK, Pickles BJ, Simard SW (2015) Inter-plant communication through mycorrhizal networks mediates complex adaptive behaviour in plant communities. AoB Plants 7:plv050
Gustafsson M, Gustafsson L, Alloysius D, Falck J, Yap S, Karlsson A, Ilstedt U (2016) Life history traits predict the response to increased light among 33 tropical rainforest tree species. For Ecol Manag 362:20–28
Hausmann NT, Hawkes CV (2009) Plant neighborhood control of arbuscular mycorrhizal community composition. New Phytol 183:1188–1200
Helgason T, Daniell TJ, Husband R, Fitter AH, Young JPW (1998) Ploughing up the wood-wide web? Nature 394:431–431
Hoeksema JD, Bever JD, Chakraborty S, Chaudhary VB, Gardes M, Gehring CA, Hart MM, Housworth EA, Kaonongbua W, Klironomos JN, Lajeunesse MJ, Meadow J, Milligan BG, Piculell BJ, Pringle A, Rúa MA, Umbanhowar J, Viechtbauer W, Wang YW, Wilson GWT, Zee PC (2018) Evolutionary history of plant hosts and fungal symbionts predicts the strength of mycorrhizal mutualism. Commun Biol 1:116
Hubert NA, Gehring CA (2008) Neighboring trees affect ectomycorrhizal fungal community composition in a woodland-forest ecotone. Mycorrhiza 18:363–374
John R, Dalling JW, Harms KE, Yavitt JB, Stallard RF, Mirabello M, Hubbell SP, Valencia R, Navarrete H, Vallejo M, Foster RB (2007) Soil nutrients influence spatial distributions of tropical tree species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:864–869
Johnson NC, Wilson GWT, Bowker MA, Wilson JA, Miller RM (2010) Resource limitation is a driver of local adaptation in mycorrhizal symbioses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:2093–2098
Kadowaki K, Yamamoto S, Sato H, Tanabe AS, Hidaka A, Toju H (2018) Mycorrhizal fungi mediate the direction and strength of plant–soil feedbacks differently between arbuscular mycorrhizal and ectomycorrhizal communities. Commun Biol 1:196
Kiers ET, Lovelock CE, Krueger EL, Herre EA (2000) Differential effects of tropical arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inocula on root colonization and tree seedling growth: implications for tropical forest diversity. Ecol Lett 3:106–113
Kivlin SN, Hawkes CV (2016) Tree species, spatial heterogeneity, and seasonality drive soil fungal abundance, richness, and composition in Neotropical rainforests. Environ Microbiol 18:4662–4673
Kivlin SN, Bedoya R, Hawkes CV (2018) Heterogeneity in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities may contribute to inconsistent plant-soil feedback in a Neotropical forest. Plant Soil 432:29–44
Klironomos JN (2003) Variation in plant response to native and exotic arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Ecology 84:2292–2301
Knoblochová T, Kohout P, Püschel D, Doubková P, Frouz J, Cajthaml T, Kukla J, Vosátka M, Rydlová J (2017) Asymmetric response of root-associated fungal communities of an arbuscular mycorrhizal grass and an ectomycorrhizal tree to their coexistence in primary succession. Mycorrhiza 27:775–789
Koerselman W, Meuleman AFM (1996) The vegetation N:P ratio: a new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J Appl Ecol 33:1441
Koorem K, Tulva I, Davison J, Jairus T, Öpik M, Vasar M, Zobel M, Moora M (2017) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in forest plant roots are simultaneously shaped by host characteristics and canopy-mediated light availability. Plant Soil 410:259–271
Krüger C, Kohout P, Janoušková M, Püschel D, Frouz J, Rydlová J (2017) Plant communities rather than soil properties structure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities along primary succession on a mine spoil. Front Microbiol 8:719
Laliberté E, Lambers H, Burgess TI, Wright SJ (2015) Phosphorus limitation, soil-borne pathogens and the coexistence of plant species in hyperdiverse forests and shrublands. New Phytol 206:507–521
Lambais MR, Lucheta AR, Crowley DE (2014) Bacterial community assemblages associated with the phyllosphere, dermosphere, and rhizosphere of tree species of the Atlantic forest. Microb Ecol 68:567–574
Laughlin DC (2011) Nitrification is linked to dominant leaf traits rather than functional diversity. J Ecol 99:1091–1099
Lee J, Lee S, Young JPW (2008) Improved PCR primers for the detection and identification of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 65:339–349
Lovelock CE, Andersen K, Morton JB (2003) Arbuscular mycorrhizal communities in tropical forests are affected by host tree species and environment. Oecologia 135:268–279
Mahé F, Rognes T, Quince C, de Vargas C, Dunthorn M (2014) Swarm: robust and fast clustering method for amplicon-based studies. PeerJ 2:e593
Mandal S, Van Treuren W, White RA, Eggesbø M, Knight R, Peddada SD (2015) Analysis of composition of microbiomes: a novel method for studying microbial composition. Microb Ecol Health Dis 26:27663
Mangan SA, Schnitzer SA, Herre EA, Mack KML, Valencia MC, Sanchez EI, Bever JD (2010) Negative plant-soil feedback predicts tree-species relative abundance in a tropical forest. Nature 466:752–755
Martínez-García LB, Richardson SJ, Tylianakis JM, Peltzer DA, Dickie IA (2015) Host identity is a dominant driver of mycorrhizal fungal community composition during ecosystem development. New Phytol 205:1565–1576
McGee KM, Eaton WD, Porter TM, Shokralla S, Hajibabaei M (2019) Soil microbiomes associated with two dominant Costa Rican tree species, and implications for remediation: a case study from a Costa Rican conservation area. Appl Soil Ecol 137:139–153
Morris EK, Buscot F, Herbst C, Meiners T, Obermaier E, Wäschke NW, Wubet T, Rillig MC (2013) Land use and host neighbor identity effects on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community composition in focal plant rhizosphere. Biodivers Conserv 22:2193–2205
Mummey DL, Rillig MC, Holben WE (2005) Neighboring plant influences on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community composition as assessed by T-RFLP analysis. Plant Soil 271:83–90
Newsham KK, Fitter AH, Watkinson AR (1995) Arbuscular mycorrhiza protect an annual grass from root pathogenic fungi in the field. J Ecol 83:991
Nguyen NH, Song Z, Bates ST, Branco S, Tedersoo L, Menke J, Schilling JS, Kennedy PG (2016) FUNGuild: an open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol 20:241–248
Öpik M, Metsis M, Daniell TJ, Zobel M, Moora M (2009) Large-scale parallel 454 sequencing reveals host ecological group specificity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a boreonemoral forest. New Phytol 184:424–437
Öpik M, Vanatoa A, Vanatoa E, Moora M, Davison J, Kalwij JM, Reier Ü, Zobel M (2010) The online database MaarjAM reveals global and ecosystemic distribution patterns in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomeromycota). New Phytol 188:223–241
Paoli GD, Curran LM, Zak DR (2006) Soil nutrients and beta diversity in the Bornean Dipterocarpaceae: evidence for niche partitioning by tropical rain forest trees. J Ecol 94:157–170
Parada AE, Needham DM, Fuhrman JA (2016) Every base matters: assessing small subunit rRNA primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples. Environ Microbiol 18:1403–1414
Peay KG, Garbelotto M, Bruns TD (2010) Evidence of dispersal limitation in soil microorganisms: Isolation reduces species richness on mycorrhizal tree islands. Ecology 91:3631–3640
Peay KG, Russo SE, McGuire KL, Lim Z, Chan JP, Tan S, Davies SJ (2015) Lack of host specificity leads to independent assortment of dipterocarps and ectomycorrhizal fungi across a soil fertility gradient. Ecol Lett 18:807–816
Prescott CE, Grayston SJ (2013) Tree species influence on microbial communities in litter and soil: current knowledge and research needs. For Ecol Manag 309:19–27
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D590
Quince C, Lanzen A, Davenport RJ, Turnbaugh PJ (2011) Removing noise from pyrosequenced amplicons. BMC Bioinform 12:38
Reinhart KO, Wilson GWT, Rinella MJ (2012) Predicting plant responses to mycorrhizae: integrating evolutionary history and plant traits. Ecol Lett 15:689–695
Rodríguez-Echeverría S, Teixeira H, Correia M, Timóteo S, Heleno R, Öpik M, Moora M (2017) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi communities from tropical Africa reveal strong ecological structure. New Phytol 213:380–390
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, Quince C, Mahé F (2016) VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 4:e2584
Scheublin TR, Ridgway KP, Young JPW, van der Heijden MGA (2004) Nonlegumes, legumes, and root nodules harbor different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6240–6246
Schlatter DC, Bakker MG, Bradeen JM, Kinkel LL (2015) Plant community richness and microbial interactions structure bacterial communities in soil. Ecology 96:134–142
Sikes BA, Cottenie K, Klironomos JN (2009) Plant and fungal identity determines pathogen protection of plant roots by arbuscular mycorrhizas. J Ecol 97:1274–1280
Simard SW, Beiler KJ, Bingham MA, Deslippe JR, Philip LJ, Teste FP (2012) Mycorrhizal networks: mechanisms, ecology and modelling. Fungal Biol Rev 26:39–60
Slik JF, Paoli G, McGuire K, Amaral I, Barroso J, Bastian M, Blanc L, Bongers F, Boundja P, Clark C, Collins M et al (2013) Large trees drive forest aboveground biomass variation in moist lowland forests across the tropics. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 22:1261–1271
Smith SE, Read DJ (2010) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic Press, Cambridge
Soudzilovskaia NA, Vaessen S, Barcelo M, He J, Rahimlou S, Abarenkov K et al (2019) FungalRoot: global online database of plant mycorrhizal associations. New Phytol 227:955–966
Streitwolf-Engel R, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (1997) Clonal growth traits of two Prunella species are determined by co-occurring arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi from a calcareous grassland. J Ecol 85:181–191
Talbot JM, Bruns TD, Taylor JW, Smith DP, Branco S, Glassman SI et al (2014) Endemism and functional convergence across the North American soil mycobiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:6341–6346
Tedersoo L, Bahram M, Cajthaml T, Põlme S, Hiiesalu I et al (2016) Tree diversity and species identity effects on soil fungi, protists and animals are context dependent. ISME J 10:346–362
Urbanová M, Šnajdr J, Baldrian P (2015) Composition of fungal and bacterial communities in forest litter and soil is largely determined by dominant trees. Soil Biol Biochem 84:53–64
Ushio M, Wagai R, Balser TC, Kitayama K (2008) Variations in the soil microbial community composition of a tropical montane forest ecosystem: does tree species matter? Soil Biol Biochem 40:2699–2702
van der Heijden MGA, Bardgett RD, van Straalen NM (2008) The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 11:296–310
Vestergård M, Henry FH, Rangel-Castro JI, Michelsen A, Prosser JI, Christensen SC (2008) Rhizosphere bacterial community composition responds to arbuscular mycorrhiza, but not to reductions in microbial activity induced by foliar cutting. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64:78–89
Vogelsang KM, Reynolds HL, Bever JD (2006) Mycorrhizal fungal identity and richness determine the diversity and productivity of a tallgrass prairie system. New Phytol 172:554–562
Wang Z, Jiang Y, Deane DC, He F, Shu W, Liu Y (2019) Effects of host phylogeny, habitat and spatial proximity on host specificity and diversity of pathogenic and mycorrhizal fungi in a subtropical forest. New Phytol 223:462–474
Weremijewicz J, O’Reilly LD, Janos DP (2018) Arbuscular common mycorrhizal networks mediate intra- and interspecific interactions of two prairie grasses. Mycorrhiza 28:71–83
Zemunik G, Turner BL, Lambers H, Laliberté E (2016) Increasing plant species diversity and extreme species turnover accompany declining soil fertility along a long-term chronosequence in a biodiversity hotspot. J Ecol 104:792–805
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the staff at INIKEA and Yayasan Sabah with special thanks to David Alloysius, Vita Juin, Albert Lojingi and Dizolkeply Sundolon for making the challenging field work possible. Thanks to Dr. Vijay Kumar and Rolando Robert for turning soil and roots into valuable amplicon data. Thanks to Dr. Lela V. Andrews for her patience in guiding me through all aspects of the bioinformatics process and for creating the excellent akutils package. Michaela Hayer helped show me the ropes for Primer when I got lazy with command line. Thanks to the Kamprad Foundation for funding this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure statement
The corresponding author confirms on behalf of all authors that there have been no involvements that might raise the question of bias in the work reported or in the conclusions, implications, or opinions stated.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cowan, J.A., Gehring, C.A., Ilstedt, U. et al. Host identity and neighborhood trees affect belowground microbial communities in a tropical rainforest. Trop Ecol 63, 216–228 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42965-021-00203-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42965-021-00203-z