Abstract
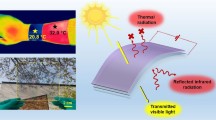
Intense heat waves pose a serious threat to public health and well-being, especially in outdoor spaces. Outdoor high-temperature environments without air conditioners are major challenges for humanity. However, an achievable approach that can provide outdoor cooling without consuming any energy is lacking. Hence, this work presents a novel hierarchical fabric emitter (HFET) used for sunshade sheds to provide radiative outdoor cooling for humanity, the HFET is composed of polyethylene/silicon dioxide/silicon nitride film, melt-blown polypropylene film, and polydimethylsiloxane film from top to bottom. In addition to reflecting 94% solar irradiance by its top surface, the HFET shows selective emission (0.82 in the atmospheric window and 0.38 outside the atmospheric window) on its top surface to outer space and broadband absorption (0.80 in the longwave infrared band) on its bottom surface from the inside. This bidirectional asymmetric emission enables the simulated skin to avoid overheating by 2–11 °C relative to the reverse HFET and bare cases under direct sunlight. Due to its excellent cooling capability, the HFET will be one of the most considerable solutions for outdoor cooling in hot summer environments.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials are available.
References
Fight heat waves to ensure food security. ChinaDaily. 2022. https://epaper.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202208/23/WS6303fe71a3109375516ee9c1.html. Accessed 23 Aug 2022.
Global climate alliance steps up joint action. ChinaDaily. 2022. https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202209/07/WS631801eea310fd2b29e766cb.html. Accessed 07 Sept 2022.
Cai L, Song AY, Li W, Hsu PC, Lin D, Catrysse PB, Liu Y, Peng Y, Chen J, Wang H, Xu J, Yang A, Fan S, Cui Y. Spectrally selective nanocomposite textile for outdoor personal cooling. Adv Mater. 2018;30: e1802152.
Hsu PC, Song AY, Catrysse PB, Liu C, Peng Y, Xie J, Fan S, Cui Y. Radiative human body cooling by nanoporous polyethylene textile. Science. 2016;353:1019.
Zeng S, Pian S, Su M, Wang Z, Wu M, Liu X, Chen M, Xiang Y, Wu J, Zhang M, Cen Q, Tang Y, Zhou X, Huang Z, Wang R, Tunuhe A, Sun X, Xia Z, Tian M, Chen M, Ma X, Yang L, Zhou J, Zhou H, Yang Q, Li X, Ma Y, Tao G. Hierarchical-morphology metafabric for scalable passive daytime radiative cooling. Science. 2021;373:692.
Liu Z, Lyu J, Fang D, Zhang X. Nanofibrous Kevlar aerogel threads for thermal insulation in harsh environments. ACS Nano. 2019;13:5703.
Wu J, Hu R, Zeng S, Xi W, Huang S, Deng J, Tao G. Flexible and robust biomaterial microstructured colored textiles for personal thermoregulation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12:19015.
Huang T, Zhu Y, Zhu J, Yu H, Zhang Q, Zhu M. Self-reinforcement of light, temperature-resistant silica nanofibrous aerogels with tunable mechanical properties. Adv Fiber Mater. 2020;26:338.
Wu J, Zhang M, Su M, Zhang Y, Liang J, Zeng S, Chen B, Cui L, Hou C, Tao G. Robust and flexible multimaterial aerogel fabric toward outdoor passive heating. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:1545.
Xue T, Zhu C, Feng X, Wali Q, Fan W, Liu T. Polyimide aerogel fibers with controllable porous microstructure for super-thermal insulation under extreme environments. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;2:338.
Mandal J, Fu Y, Overvig AC, Jia M, Sun K, Shi NN, Zhou H, Xiao X, Yu N, Yang Y. Hierarchically porous polymer coatings for highly efficient passive daytime radiative cooling. Science. 2018;362:315.
Munday JN. Tackling climate change through radiative cooling. Joule. 2019;3:1057–2060.
Raman AP, Anoma MA, Zhu L, Rephaeli E, Fan S. Passive radiative cooling below ambient air temperature under direct sunlight. Nature. 2014;515:13883.
Li J, Wang X, Liang D, Xu N, Zhu B, Li W, Yao P, Jiang Y, Min X, Huang Z, Zhu S, Fan S, Zhu J. A tandem radiative/evaporative cooler for weather-insensitive and high-performance daytime passive cooling. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabq0411.
Feng S, Zhou Y, Liu C, Zhang T, Bu X, Huang Y, He M. Skeleton-inspired optical-selective cellulose-based bio-film as passive radiative cooler and the energy-saving performance evaluation. Chem Eng J. 2023;452: 139377.
Si Y, Shi S, Dong Z, Wu H, Sun F, Yang J, Hu J. Bioinspired stable single-layer Janus fabric with directional water/moisture transport property for integrated personal cooling management. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00200-4.
Shi NN, Tsai CC, Camino F, Bernard GD, Yu N, Wehner R. Keeping cool: enhanced optical reflection and radiative heat dissipation in Saharan silver ants. Science. 2015;349:298.
Wehner R, Marsh AC, Wehner S. Desert ants on a thermal tightrope. Nature. 1992;357:586.
Tao S, Xu X, Chen M, Xu W, Li L, Fang Z, Zhu C, Lu C, Xu Z. Construction of efficient passive radiative cooling emitter with selective emission in the whole atmospheric window and durable anti-contamination performance. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2021;224: 110998.
Zhai Y, Ma Y, David SN, Zhao D, Lou R, Tan G, Yang R, Yin X. Scalable-manufactured randomized glass-polymer hybrid metamaterial for daytime radiative cooling. Science. 2017;355:1062.
Lin C, Li Y, Chi C, Kwon YS, Huang J, Wu Z, Zheng J, Liu G, Tso CY, Chao CYH. A solution-processed inorganic emitter with high spectral selectivity for efficient subambient radiative cooling in hot humid climates. Adv Mater. 2022;34:2109350.
Xiang B, Zhang R, Luo Y, Zhang S, Meng X. 3D porous polymer film with designed pore architecture and auto-deposited SiO2 for highly efficient passive radiative cooling. Nano Energy. 2021;81: 105600.
Yang M, Zou W, Guo J, Qian Z, Wiersma DS. A Bioinspired, “skin” with cooperative thermo-optical effect for daytime radiative cooling. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2020;12:25286.
Yang ZB, Zhang J. Bioinspired radiative cooling structure with randomly stacked fibers for efficient all-day passive cooling. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2021;13:43387.
Wang T, Wu Y, Shi L, Hu X, Chen M, Wu L. A structural polymer for highly efficient all-day passive radiative cooling. Nat Commun. 2021;12:365.
Li T, Zhai Y, He S, Gan W, Wei Z, Heidarinejad M, Dalgo D, Mi R, Zhao X, Song J, Dai J, Chen C, Aili A, Vellore A, Martini A, Yang R, Srebric J, Yin X, Hu L. A radiative cooling structural material. Science. 2019;364:760.
Zhao H, Sun Q, Zhou J, Deng X, Cui J. Switchable cavitation in silicone coatings for energy saving cooling and heating. Adv Mater. 2020;23:2000870.
Zhong S, Zhang J, Yuan S, Xu T, Zhang X, Xu L, Zuo T, Cai Y, Yi L. Self-assembling hierarchical flexible cellulose films assisted by electrostatic field for passive daytime radiative cooling. Chem Eng J. 2023;451: 138558.
Xiang B, Zhang R, Zeng X, Luo Y, Luo Z. An easy-to-prepare flexible dual-mode fiber membrane for daytime outdoor thermal management. Adv Fiber Mater. 2022;4:1058.
Liu X, Zhang M, Hou Y, Pan Y, Liu C, Shen C. Hierarchically superhydrophobic stereo-complex poly (lactic acid) aerogel for daytime radiative cooling. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32:2207414.
Liang J, Wu J, Guo J, Li H, Zhou X, Liang S, Qiu C, Tao G. Radiative cooling for passive thermal management towards sustainable carbon neutrality. Natl Sci Rev. 2022;10:nwac208.
Zhu H, Wang Y, Qu M, Pan Y, Zheng G, Dai K, Huang M, Alhadhrami A, Ibrahim M, El-Bahy Z, Liu C, Shen C, Liu X. Electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/silica film for radiative cooling. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater. 1966;2022:5.
Li X, Peoples J, Yao P, Ruan X. Ultrawhite BaSO4 paints and films for remarkable daytime subambient radiative cooling. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13:21733.
Li D, Liu X, Li W, Lin Z, Zhu B, Li Z, Li J, Li B, Fan S, Xie J. Scalable and hierarchically designed polymer film as a selective thermal emitter for high-performance all-day radiative cooling. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021;16:13729.
Chen Z, Zhu L, Raman A, Fan S. Radiative cooling to deep sub-freezing temperatures through a 24-h day–night cycle. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13729.
Heo SY, Lee GJ, Kim DH, Kim YJ, Song YM. A Janus emitter for passive heat release from enclosures. Sci Adv. 2020;6:eabb1906.
Yang Z, Zhou Z, Sun H, Chen T, Zhang J. Construction of a ternary channel efficient passive cooling composites with solar-reflective, thermoemissive, and thermoconductive properties. Compos Sci Technol. 2021;207: 108743.
Yue X, Zhang T, Yang D, Qiu F, Wei G, Zhou H. Multifunctional Janus fibrous hybrid membranes with sandwich structure for on-demand personal thermal management. Nano Energy. 2019;63: 103808.
Chen M, Pang D, Yan H. Highly solar reflectance and infrared transparent porous coating for non-contact heat dissipations. iScience. 2022;25:104726.
Yang Z, Jia Y, Zhang J. Hierarchical-morphology metal/polymer heterostructure for scalable multimodal thermal management. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14:24755.
Yang Z, Sun H, Xi Y, Qi Y, Mao Z, Wang P, Zhang J. Bio-inspired structure using random, three-dimensional pores in the polymeric matrix for daytime radiative cooling. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2021;227: 111101.
Fan X, Zheng W, Singh DJ. Light scattering and surface plasmons on small spherical particles. Light Sci Appl. 2014;3: e179.
Yang Z, Mao Z, Xiang B, Zhang J. Construction of a binary channel efficient cooling composites with reflective and phase-change properties. Compos Part B: Eng. 2019;178: 107517.
Sun H, Wang L, Yi J, Wang F, Gao Y, Sha X, Feng J. The influence of melt temperature on the crystal orientation of polypropylene containing talc. Polymer. 2022;256: 125179.
Zhou L, Song H, Liang J, Singer M, Gan Q. A polydimethylsiloxane-coated metal structure for all-day radiative cooling. Nat Sustain. 2019;2:1.
Zhao D, Aili A, Zhai Y, Xu S, Tan G, Yin X, Yang R. Radiative sky cooling: fundamental principles, materials, and applications. Appl Phys Rev. 2019;6: 021306.
Liu Y, Zhan L, Wen L, Cheng L, Liu S. Effects of particle size and color on photocuring performance of Si3N4 ceramic slurry by stereolithography. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2020;41:2386.
Li P, Wang A, Fan J, Kang Q, Jiang P, Bao H, Huang X. Thermo-optically designed scalable photonic films with high thermal conductivity for subambient and above-ambient radiative cooling. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;32:2109542.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Prof. Jiayue Yang of the Optics-Thermal Radiation Research Center of Shandong University for technical support of the complex refractive index measurement. This work was supported by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institution (PAPD), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52204222), and National Students’ Platform for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (202210291001Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
42765_2023_271_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary data related to this article can be found at Section 1. Heat Transfer Model Analysis; Section 2. FDTD Simulations; Section 3. MB–PP Structure Before and After Hot Pressing; Section 4. LWIR Absorption of Common Functional Groups; Section 5. FTIR Spectrum of SiO2 and Si3N4; Section 6. Scattering Efficiency of PP Fibers with Different Diameters; Section 7. The Effect of Si3N4 Content on Optical Properties; Section 8. Solar Transmittance of the PE/SiO2/Si3N4 film; Section 9. Comparison with Commercial Sunshade Shed Samples; Section 10. UV Aging Resistance Test of the HFET; Section 11. Mechanical Property Test of the HFET. (DOCX 6503 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Chen, T., Tang, X. et al. Hierarchical Fabric Emitter for Highly Efficient Passive Radiative Heat Release. Adv. Fiber Mater. 5, 1367–1377 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00271-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-023-00271-x