Abstract
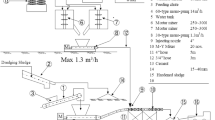
The 2n mixing theory was developed with the concept of Japanese noodle (UDON) making method. The mixing of dredging sludge was done with 20% (by volume) of expanded-poly-styrene beads in 15 units of M–Y Mixer using the cement paste. Samples were taken at starting, middle and end level of continuous mixing. Average unit weight was 1.07 gm/cm3, with its variation coefficient of 2.68%. Average 28 days compressive strength was 7.04 MPa, with a variation coefficient of 3.66%. The efficiency of the M–Y mixer was sufficient for continuous mixing of dredging sludge, giving required compressive strength for soil settlement.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Australian Urethane and Styrene. (2010). Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Technical Data, Australia
Chen, B., & Liu, J. (2005). Contribution of hybrid fibers on the properties of the high-strength lightweight concrete having good workability. Cement and Concrete Research, 35(5), 913–917.
EuDA, “Dredging", About Dredging, www.european-dredging.eu, Retrieved 3, 2018.
Gyawali, T.R. (1999). Development of less energy required and gravity effect continuous mixer based on new mixing theory, PhD Thesis, University of Tokyo.
Gyawali, T. R. (2014). Development of “pre-mix method” for mixing fiber reinforced concrete (FRC) in new energy saving continuous mixer. Journal of Science and Technology Khwopa Engineering College, 2, 5–14.
Gyawali, T.R., Joshi, B.R., & Matabee, K.M. (2010). Mixing performance of energy saving gravity (ESG) mixer for powder materials. ACI Materials Journal 116(2):2019
Gyawali, T. R., & Maeda, M. K. (2019). Mixing of dredging sludge with cement powder in new continuous M-Y Mixer. International Journal of Geosynthetics and Ground Engineering, 5(2), 10.
Gyawali, T. R., Maeda, M. K., Yamada, K., & Uchida, A. (1996). An Investigation on Properties of EPS Concrete Mixed Using New-Type Mixer (pp. 9–16). Maeda Corporation, Japan: Maeda Research Institute Technical Report.
Gyawali, T.R., & Matabee K.M., (2005) Practical aspects of new Japanese mixing technology in Nepal, 9th National Convention of Engineers, May 6–8, 2005, Nepal.
Gyawali, T.R., Yamada K., & Matabee K.M. (2000) High productivity continuous mixing system. In 17 th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Taiwan, September 2000
Higuchi, Y. (1980). Coated-sand technique produces high strength concrete. Concrete International, 2(4), 75–76.
Maeda, K. (1995). Development of a new type mixer, Edited by Maeda Corporation, Tokyo
Maeda, K., & Kishitani, K. (1993). Study on mixing performance test for new-type mixer. Peking: The Third Beijing International Symposium on Cement and Concrete.
Makoto, K., et al. (1998). Concept of super quality concrete and its property and structural performance: Development and diffusion association of super quality concrete structures. In international workshop on self compacting concrete, 23–26 August, 1998. Tosa-Yamada: Kochi University of Technology.
Matabee, K. M., Yamada, K., Uchida, A., & Gyawali, T. R. (1999). The use of new continuous mixer “M–Y MIXER” for mixing RCD and dam concrete. In International Symposium on Roller Compacted Concrete Dam (pp. 679–691). China: Chengdu.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. (2019). “What is dredging?”, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, (https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/dredging.html), Department of Commerce, US.
Ozawa, K., Maekawa, K., & Okamura, H. (2019). Development of high performance concrete. Journal of the Faculty of Engineering, The University of Tokyo, Vol. XLI, No.3
Okamura, H., Maekawa, K., & Ozawa, K. (1993). High Performance concrete. Tokyo: Gihodo. (In Japanese).
Tamimi, A.K. (1989). The effect of two stage mixing technique on the properties and the microstructure of the concrete structure, PhD Thesis, Paisley College.
Uchida A., Yamada K., Matabee, K.M., & Gyawali, T.R. (1997). Development of new concrete mixing system using the new type of vontinuous mixer “M–Y MIXER”, In 97 International Three Gorges Project Technical Seminar, Yicjang, pp. 1–10
Xu, Y., Jiang, L., Xu, J., & Li, Y. (2012). Mechanical properties of expanded polystyrene lightweight aggregate concrete and brick. Construction and Building Materials, 27(1), 32–38.
Acknowledgements
This research work was all carried out fully funded by Maeda Corporation, Tokyo, Japan. First Author was fully financed by the company for this research work. Second Author had a great research project under his own within Maeda Corporation on which first author was involved.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gyawali, T.R., Maeda, M.K. Mixing of dredging sludge with EPS beads and cement paste in continuous M–Y mixer. Asian J Civ Eng 20, 1129–1136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-019-00169-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-019-00169-3