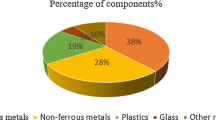
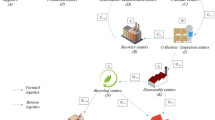
Abstract
The electronics industry, where the most important technological advancements have been made in the last decade, has a critical position within the framework of sustainability. Planning is made about a product’s life cycle, starting from the design, manufacturing, usage, and end-of-life stages. At the end of the life cycle, reuse, remanufacture/repair, and recycle decisions must be made. Reverse logistics and recycling are a substantial part of this process. Therefore, countries have regulations that draw boundaries for reverse logistics operations, for raw materials recovery. For sustainable planning of the precious and rare-earth elements that have supply risk, economic, environmental, and social dimensions have to be considered, simultaneously. So, in this study, a multi-objective mathematical model is proposed to optimize the reverse logistics and recycling processes of the waste electronic products, to extract precious and rare-earth elements, for the first time in literature, for a future horizon, in compliance with the governmental regulations. A sustainable planning approach is used based on economic, environmental, and social aspects. An application for a real recycling facility was made that revealed the huge recovery potential from electronic waste, such that hundreds of kilograms of gold, silver, palladium, and platinum can be recovered by a single facility, in 4-year future horizon. Besides, some reasonable profit can be obtained, vast amount of hazardous materials can be prevented to be disposed of the nature, and employment can be provided. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study aiming at sustainable and multi-objective planning of precious and rare elements’ recovery, from electronic products.
Graphical abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the Mendeley Data Repository, https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/jrnnst4wnc/1.
References
Agrawal S, Singh RK, Murtaza Q (2015) A literature review and perspectives in reverse logistics. Resour Conserv Recycl 97:76–92
Ahirwar R, Tripathi AK (2021) E-waste management: a review of recycling process, environmental and occupational health hazards, and potential solutions. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 15:100409
Arampantzi C, Minis I (2017) A new model for designing sustainable supply chain networks and its application to a global manufacturer. J Clean Prod 156:276–292
Zhang S, Ding Y, Liu B, Chang CC (2017) Supply and demand of some critical metals and present status of their recycling in WEEE. Waste Manage 65:113–127
Bakas I, Fischer C, Harding A, Haselsteiner S, McKinnon D, Kosmol J, Milios L, Plepys A, Tojo N, Wilts H, Wittmer D (2014). Present and potential future recycling of critical metals in WEEE. Copenhagen Resource Institute. https://www.cri.dk/sites/cri.dk/files/dokumenter/artikler/weee_recycling_paper_oct14.pdf
Bakas I, Herczeg M, Vea EB, Fråne A, Youhanan L, Baxter J (2016) Critical metals indiscarded electronics mapping recycling potentials from selected waste electronics in the Nordic Region. Norden, Denmark
Bal A, Satoglu SI (2018) A goal programming model for sustainable reverse logistics operations planning and an application. J Clean Prod 201:1081–1091
Bal A, Satoglu SI (2019) The use of data envelopment analysis in evaluating Pareto optimal solutions of the sustainable supply chain models. Proc Manuf 33:485–492
Baldé CP, Forti V, Gray V, Kuehr R, Stegmann P (2017) The global e-waste monitor 2017: Quantities, flows and resources. United Nations University, International Telecommunication Union, and International Solid Waste Association
Bressanelli G, Pigosso DC, Saccani N, Perona M (2021) Enablers, levers and benefits of circular economy in the electrical and electronic equipment supply chain: a literature review. J Clean Prod 298:126819
Buechler DT, Zyaykina NN, Spencer CA, Lawson E, Ploss NM, Hua I (2020) Comprehensive elemental analysis of consumer electronic devices: rare earth, precious, and critical elements. Waste Manage 103:67–75
European Commission (2020) Waste statistics - Electrical and Electronic Equipment. Retrieved from: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Waste_statistics_-_electrical_and_electronic_equipment. Accessed Feb 2021
Forti V, Balde CP, Kuehr R, Bel G (2020). The Global E-waste Monitor 2020: Quantities, flows, and the circular economy potential. Bonn, Geneva, and Rotterdam: United Nations University/United Nations Institute for Training and Research, International Telecommunication Union, and International Solid Waste Association
Geyer R, Blass VD (2010) The economics of cell phone reuse and recycling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 47(5–8):515–525
Government of Canada (2022) Platinum facts. Retrieved from https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/our-natural-resources/minerals-mining/minerals-metals-facts/platinum-facts/20520. Accessed Mar 2021
Grunow M, Gobbi C (2009) Designing the reverse network for WEEE in Denmark. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 58(1):391–394
Guide Jr VDR, Van Wassenhove LN (2009) OR FORUM—the evolution of closed-loop supply chain research. Oper Res 57(1):10–18
Yuksekdag A, Kose-Mutlu B, Kaya B, Kumral M, Wiesner MR, Koyuncu I (2021) Comprehensive characterization of secondary sources originating from Turkey in terms of rare earth elements and scandium. Sci Total Environ 777:146033
Islam MT, Huda N (2018) Reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chain of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)/E-waste: a comprehensive literature review. Resour Conserv Recycl 137:48–75
Jeurissen R (2000) John Elkington, Cannibals with forks: the triple bottom line of 21st century business. J Bus Ethics 23(2):229–231
Kapukaya EN, Bal A, Satoglu SI (2019) A bi-objective model for sustainable logistics and operations planning of WEEE recovery. Int J Optimiz Cont Theor Appl 9(2):89–99
Korhonen J, Honkasalo A, Seppälä J (2018) Circular economy: the concept and its limitations. Ecol Econ 143:37–46
Lee DH, Dong M (2009) Dynamic network design for reverse logistics operations under uncertainty. Transp Res E Logist Transp Rev 45(1):61–71
Mavrotas G (2009) Effective implementation of the ε-constraint method in multi-objective mathematical programming problems. Appl Math Comput 213(2):455–465
Mavrotas G, Florios K (2013) An improved version of the augmented ε- constraint method (AUGMECON2) for finding the exact Pareto set in multi-objective integer programming problems. Appl Math Comput 219(18):9652–9669
Meskers CEM, Hagelüken C, Salhofer S, Spitzbart M (2009) Impact of pre-processing routes on precious metal recovery from PCs. Proceedings of EMC, vol 7
Mineral Research and Exploration General Directorate (2021) Silver in the World and Turkey. Retrieved from https://www.mta.gov.tr/v3.0/sayfalar/bilgi-merkezi/maden-serisi/dunyada-ve-turkiyede-gumus.pdf. Accessed Mar 2021
Ministry of Environment and Urbanisation (2012) Regulation for control of waste electric and electronic equipment. Official J. Turkish Republic 28300. Retrieved from: https://www.resmigazete.gov.tr/eskiler/2012/05/20120522-5.htm. Accessed Feb 2021
Ministry of Environment and Urbanisation (2019) Regulation draft for control of waste electric and electronic equipment. Official J Turkish Republic 28300. Retrieved from: https://cygm.csb.gov.tr/atik-elektrikli-ve-elektronik-esyalarin-kontrolu-yonetmeligi-nde-degisiklik-yapilmasina-dair-yonetmelik-taslagi-goruse-acilmistir-duyuru-121939
Oguchi M, Sakanakura H, Terazono A (2013) Toxic metals in WEEE: characterization and substance flow analysis in waste treatment processes. Sci Total Environ 463–464:1124–1132
Polat O, Capraz O, Gungor A (2018) Modelling of WEEE recycling operation planning under uncertainty. J Clean Prod 180:769–779
Presidency of Strategy and Budget (2018) Retrieved from https://www.sbb.gov.tr/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/MadencilikPolitikalariOzelIhtisasKomisyonuRaporu.pdf. Accessed Feb 2021
Reddy KN, Kumar A, Sarkis J, Tiwari MK (2020) Effect of carbon tax on reverse logistics network design. Comput Ind Eng 139:106–184
Satoglu SI, Simsek E, Özdemir Z (2022) Sustainable planning of precious and rare elements’ recycling from waste electronic products. Mendeley Data. https://doi.org/10.17632/jrnnst4wnc.1
Stock JR (1992) Reverse logistics: White paper. Council of Logistics Management
Temur GT, Bolat B (2017) Evaluating efforts to build sustainable WEEE reverse logistics network design: comparison of regulatory and non-regulatory approaches. Int J Sustain Eng 10(6):358–383
TUBİSAD (2019) Evimizdeki Değer E-Atıklar. Retrieved from: http://www.tyk.org.tr/tr/Yetkilendirilmis-Kurulus/detay/DOKUMANLAR/53/161/0. Accessed Mar 2021
United Nations (2018) The 17 Goals. Goal 12 | Department of Economic and Social Affairs. https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/files/report/2018/TheSustainableDevelopmentGoalsReport2018-EN.pdf. Accessed Dec 2021
Valero A, Valero A, Calvo G, Ortego A (2018) Material bottlenecks in the future development of green technologies. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 93:178–200
Vodafone (2020) Dünyada ve Türkiye’de Elektronik Atık Mevcut Durumu Araştırma Raporu (in Turkish). Retrieved from: https://rec.org.tr/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/AtiginOtesinde2020.pdf. Accessed Feb 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simsek, E., Ozdemir, Z. & Satoglu, S. Sustainable Planning of Precious and Rare Elements’ Recycling from Waste Electronic Products: a Multi-objective Model and Application. Process Integr Optim Sustain 6, 723–735 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-022-00245-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-022-00245-3